Basic offset
The basic offset describes the coordinate transformation between BCS and BZS. It can be
used, for example, to define the palette zero.
The basic offset comprises:
● External work offset
● DRF offset
● Overlaid movement
● Chained system frames
● Chained basic frames
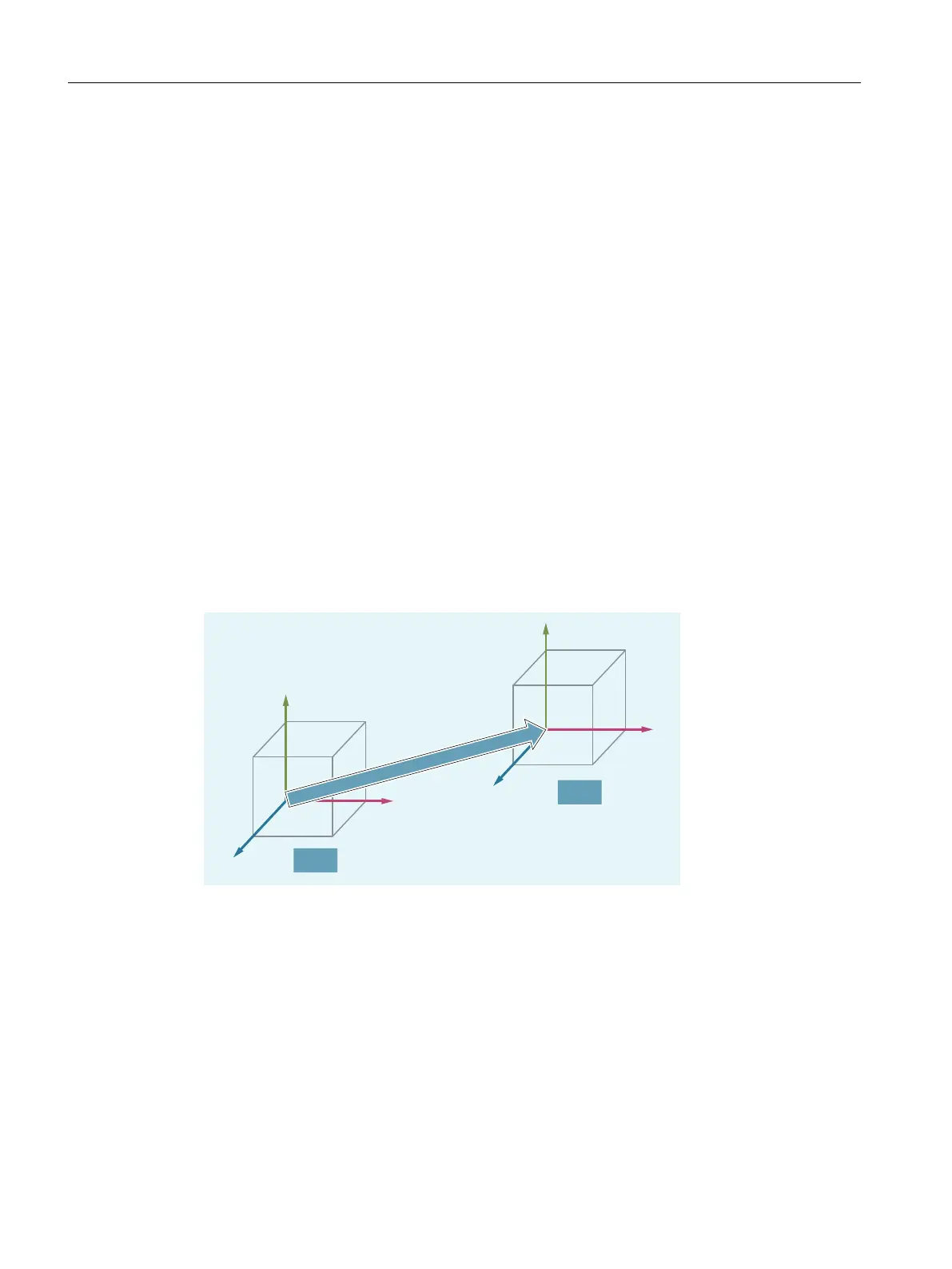
2.1.4.4 Settable zero system (SZS)
Settable work offset
The "settable zero system" (SZS) is obtained from the basic zero system (BZS) as a result of
the settable work offset.
Settable work offsets are activated in the NC program with the G commands G54 ... G57 and
G505 ... G599.
%=6
6=6
6HWWDEOHZRUNRIIVHW
<
;
=
<
;
=
If no programmable coordinate transformations (frames) are active, then the "settable zero
system" is the workpiece coordinate system (WCS).
Fundamentals
2.1 Fundamental Geometrical Principles
NC programming
40 Programming Manual, 12/2019, 6FC5398-2EP40-0BA0

 Loading...
Loading...























