10 Drive Start-Up Procedure
YASKAWA TOEPC71061737B GA800 Drive Installation & Primary Operation 63
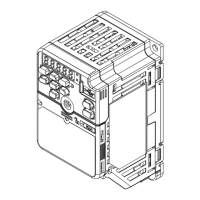
◆ Switches and Jumpers on the Terminal Board
The terminal board has switches to adapt the drive I/Os to the external control signals as shown in Figure 10.11.
Set the switches to select the functions for each terminal.
Figure 10.11 Locations of Switches
Table 10.8 I/O Terminals and Switches Functions
Position Switch Terminal Function Default
A DIP switch S2 -
Enables and disables the MEMOBUS/Modbus communications
termination resistor.
OFF
B Jumper switch S5 FM, AM Sets terminals FM and AM to voltage or current output.
FM: V (voltage output)
AM: V (voltage output)
C
DIP switch S1-1 A1 Sets the input signal type (voltage/current). V (voltage input)
DIP Switch S1-2 A2 Sets the input signal type (voltage/current). I (current input)
DIP switch S1-3 A3 Sets the input signal type (voltage/current). V (voltage input)
D Dip switch S4 A3 Sets MFAI or PTC input. AI (analog input)
◆ Control I/O Connections
This section gives information about the settings for the listed control circuit I/O signals.
• MFDI (terminals S1 to S8)
• Pulse train output (terminal MP)
• MFAI (terminals A1 to A3)
• PTC input (terminal A3)
• MFAO (terminals FM, AM)
• MEMOBUS/Modbus communications (terminals D+, D-, AC)
■ Pulse Train Output
You can use pulse train monitor output terminal MP for sourcing mode or for sinking mode.
• Use for sourcing mode
The load impedance changes the voltage level of the pulse train output signal.
Load Impedance
R
L
(kΩ)
Output Voltage
V
MP
(V)
1.5 kΩ or more 5 Vor more
4.0 kΩ or more 8 Vor more
10 kΩ or more 10 Vor more
Note:
Use the formula in Figure 10.12 to calculate the necessary load resistance (kΩ) to increase output voltage V
MP
(V).

 Loading...
Loading...