6-8 Programmer’s Guide
Trace Data Transfers
Using Binary Data Encoding
Trace Data Transfer Sizes
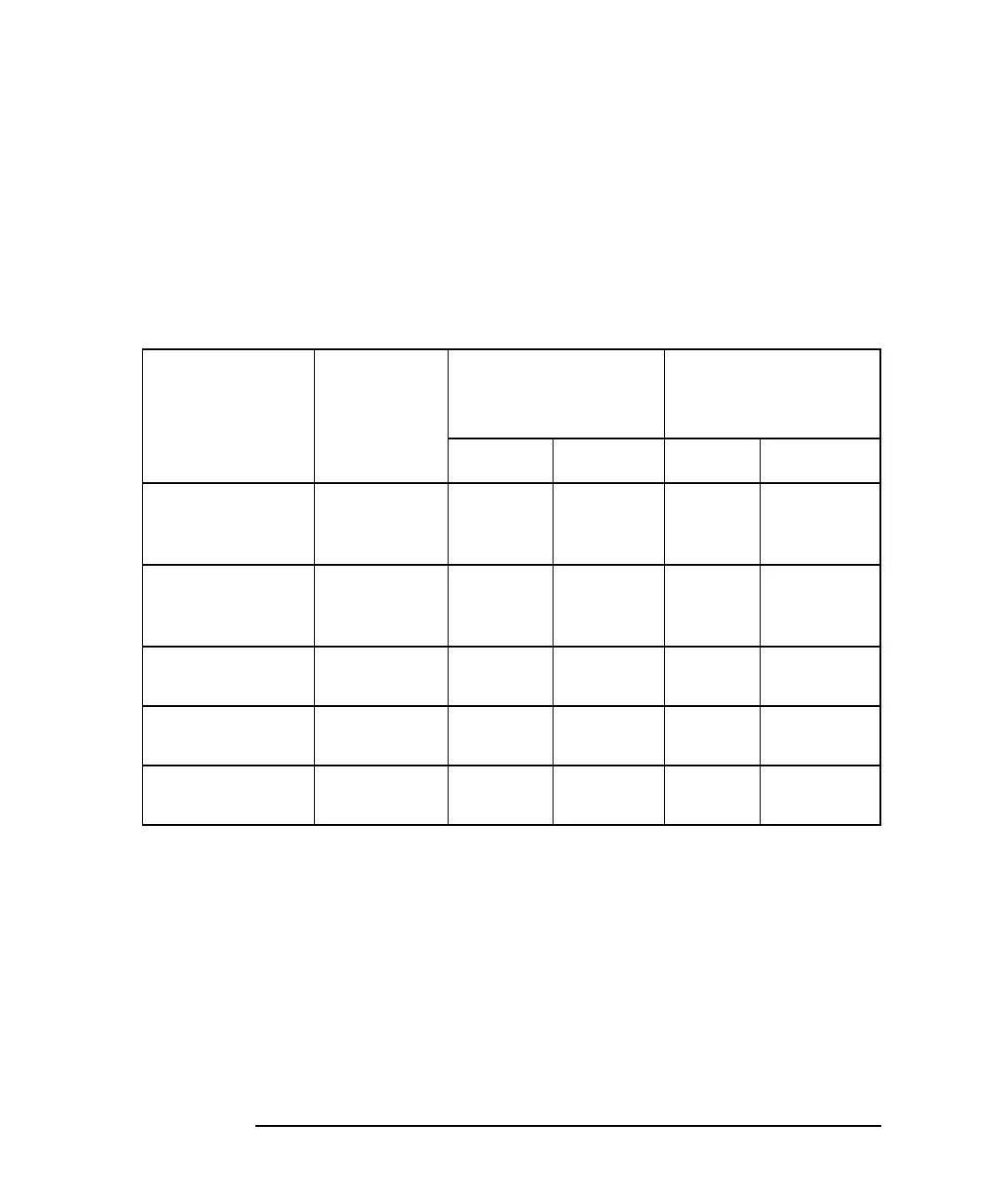
The following table shows how many bytes are transmitted during trace
data transfers. The left column shows the format of the data, which you
can specify using the SCPI command Format:DATA. As you can see, the
size of the measurement point data and trace data varies as you change
format.
Table 6-2 Trace Data Transfer Size Using TRACE:DATA Command
When transmitting data in "REAL" or "INT" format, a header is sent
before the data block. The header indicates the size of the data block. The
header size varies in length from 3 to 11 bytes. Refer to Chapter 4, “Data
Types and Encoding,” for details on the header.
Transmitting ASCII data requires no header. The ASCII values are
separated by commas, and a linefeed is sent after the last value. The
sizes shown in the table include the size of the comma(s) and terminating
linefeed. Typical data in ASCII,5 format:
-1.2254E+000,+5.0035E-001,+4.5226E-001,...
Format Type
(FORMat:DATA)
Type of
Data
Size of Single
Measurement Point
(bytes)
Size of 201 Point
Trace
(bytes)
Real Complex Real Complex
REAL,32 IEEE 32-bit
Floating
Point
4 8 809 1614
REAL,64 IEEE 64-bit
Floating
Point
8 16 1614 3222
ASCII,5 ASCII
numbers
13 26 2613 5226
ASCII,3 ASCII
numbers
11 22 2211 4422
INT,16 Internal
Binary
— 8 — 1614

 Loading...
Loading...











