SUM Subsystem Introduction
between the two signals is arbitrary.
l This command is applicable only with internal sum source (SUM:SOURce INTernal).
l You cannot use SUM when DC is the carrier.
l An arbitrary waveform may not simultaneously be a carrier and a sum waveform.
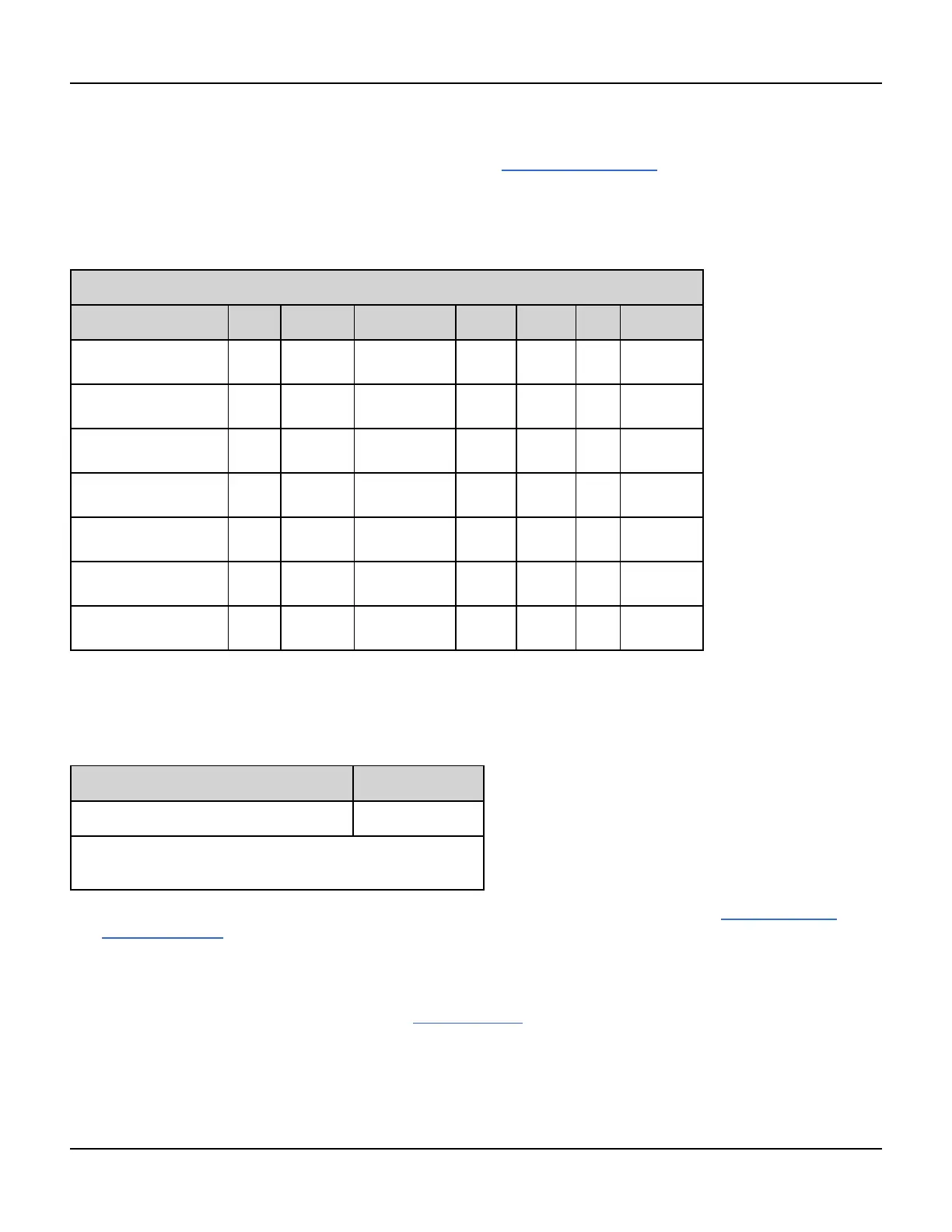
The following table shows which carriers can be associated with which internal functions.
Modulating Signal
Carrier Sine Square Tri / Ramp Noise PRBS Arb External
Sine
• • • • • • •
Square/Pulse
• • • • • • •
Triangle/Ramp
• • • • • • •
Gaussian Noise
• • • • • •
PRBS
• • • • • •
Arbitrary
• • • • • •
Sequenced Arbitrary
• • • • • •
[SOURce[1|2]:]SUM:SOURce {INTernal|EXTernal}
[SOURce[1|2]:]SUM:SOURce?
Selects source of summing signal.
Parameter Typical Return
{INTernal|EXTernal}, default INTernal INT or EXT
Set the sum source to EXTernal:
SUM:SOUR EXT
l You can synchronize the phase between the primary signal and the SUM signal by sending SOURce[1|2]:PH-
ASe:SYNChronize after setting the functions for the primary signal and the SUM signal. Otherwise, the phase
between the two signals is arbitrary.
l SUM:SOURce EXTernal: carrier waveform is summed with external waveform. The amplitude and polarity of
the sum signal is determined by the ±5 V signal level on rear-panel Modulation In connector. For example, if you
have set the SUM Amplitude to 2.0 Vpp using SUM:AMPLitude, then when EXT signal is at +5 V, the sum signal will
be at 2 Vpp. When the modulating signal is at -5 V, the sum signal will be at full amplitude and opposite polarity.
294 Agilent 33500 Series Operating and Service Guide

 Loading...
Loading...