Chapter 4 – Functions of the instrument
UM-23100B-U User manual ATEQ F CLASS Page 44/90
Associated parameters to be set: Start (Initial value of the transient), Transient (actual
and non modifiable value of the transient), Percentage drift (Drift tolerance on
acquisition of the transient, as a % of the FAIL level).
) Select the option and enter settings if necessary.
9 ATR 2:
The value of the
transient is not
known but the
possible leak of the
part is taken into
account when the
transient value is
computed during
the special cycle.
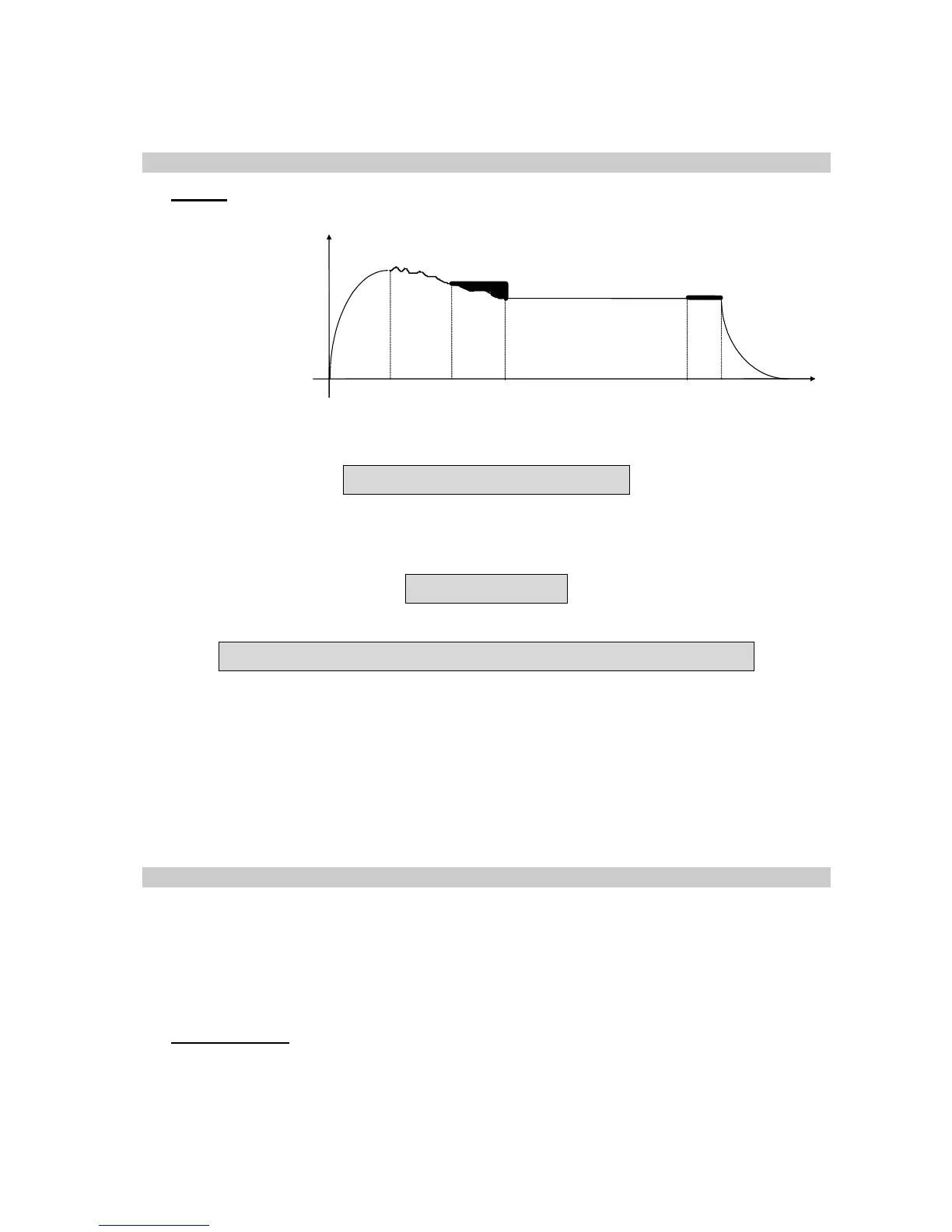
Fill Stab Test1 Wait time 5 x test time Test2 Dump
Time
Pressure
P 1
∆P 2
At the end of test time 1, the ATEQ saves the pressure variation ∆P1, function of the
transient and the leak is there is one.
∆P1 = Leak + Transient
Following the waiting time (equivalent to 5 times the normal test time), we consider that
transient phenomena have disappeared. During the second test time, the ATEQ
instrument reads a second pressure drop ∆P2 which corresponds to the leak.
∆P2 = Leak
By taking these two pressure variations, we can calculate the transient.
∆P1 - ∆P2 = (Leak + Transient) - Leak = Transient
It is this transient which will be taken away from the leak measurement of the following
cycles.
Through the use of the ATR, the ATEQ instrument is able to differentiate a Good
(PASS) part from a Bad (FAIL) part without being influenced by the transient effects
whilst keeping a short stabilisation time.
Associated parameters to be set: Start (Initial value of the transient), Transient (actual
and non modifiable value of the transient), Percentage drift (Drift tolerance on
acquisition of the transient, as a % of the reject level).
) Select the option and enter settings if necessary.
For ATR learning cycles, refer to paragraph 3.3.10 "ATR learning".
When a parameter is modified but no learning cycle has been carried out, an ATR error
occurs. The Alarm and End of Cycle outputs are activated.
Learning may be carried out on a value greater than the reject (FAIL) level and the
Pass and End of Cycle outputs are then activated.
9 Transient drift
Due to the evolution of the test conditions (temperature variations...), the value of the
transient can vary through time. It is therefore necessary to track its evolution.
 Loading...
Loading...