2. Use the no ip ssh command to disable the SSH server that disconnects all active
SSH sessions.
3. Use the show ip ssh command to display SSH configuration information and
information about any active SSH sessions.
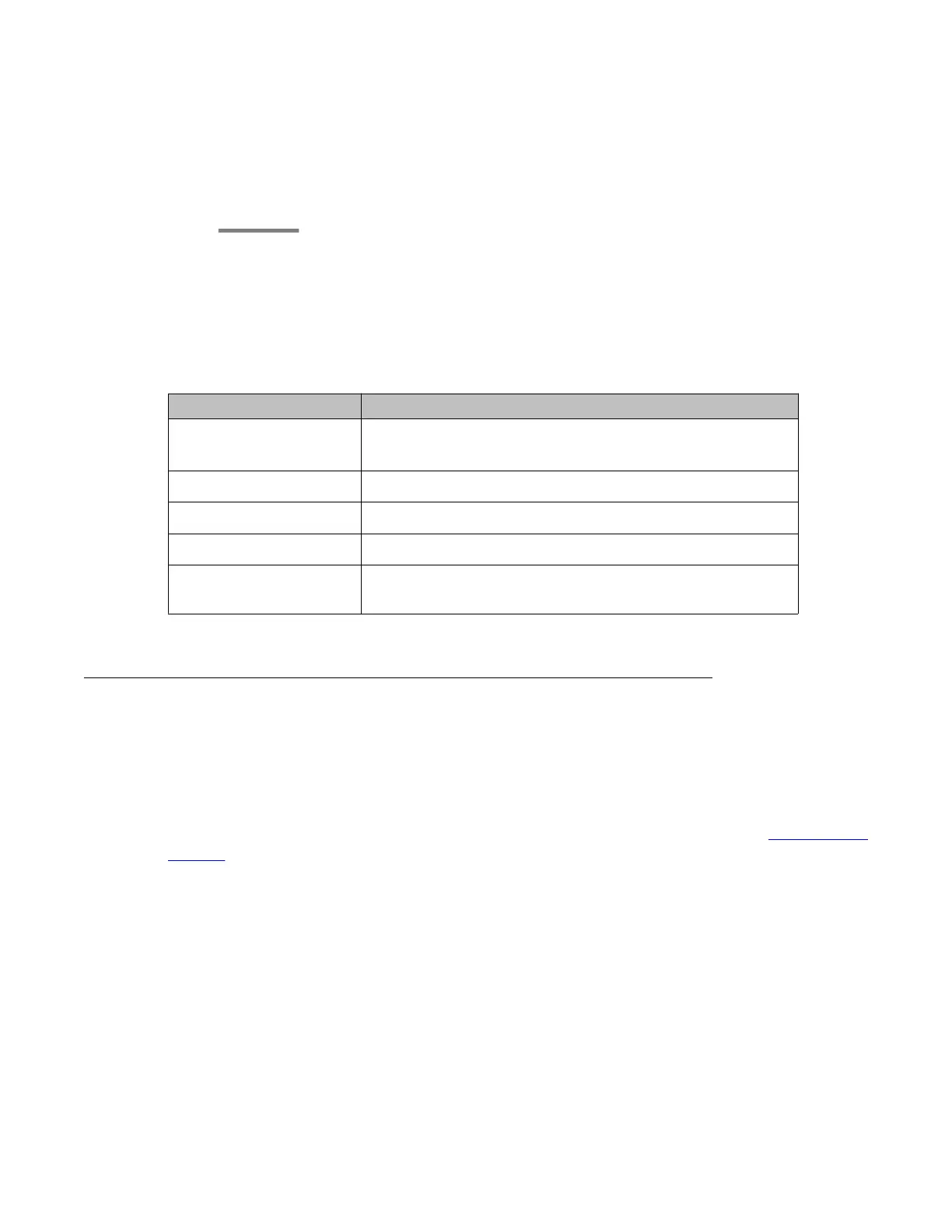
Summary of SSH configuration commands
For more information about these commands, see the Avaya Branch Gateway G430 CLI
Reference.
Command Description
crypto key
generate dsa
Generate an SSH host key pair
disconnect ssh Disconnect an existing SSH session
hostname Assign hostname identification to the Branch Gateway
ip ssh Enable or disable the Secure Shell (SSH) service
show ip ssh Display general SSH information and information about the
currently active connections that are using SSH
SCP protocol support
In addition to data transfer via an SSH session, the SSH protocol is used to support SCP for
secure file transfer. When using SCP, the Branch Gateway is the client, and an SCP server
must be installed on the management station. After users are defined on the SCP server, the
Branch Gateway acts as an SCP client.
The process of establishing an SCP session is the same process as described in SSH protocol
support on page 45, except that the roles of the Branch Gateway and the client computer are
reversed.
To perform file transfers secured by SCP, the Branch Gateway launches a local SSH client
using the CLI. This establishes a secured channel to the secured file server. The Branch
Gateway authenticates itself to the server by providing a username and password. With a
Windows-based SSH server (WinSSHD), the username provided must be a defined user on
the Windows machine with read/write privileges. The files transferred via SCP are saved in the
C:\Documents and Settings\username directory.
The network element performs file transfer in unattended mode.
Security overview
Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 47
 Loading...
Loading...




