38
4.3.1 Using one sensor to monitor for Carbon
Monoxide and Hydrogen Sulfide
Carbon monoxide and hydrogen sulfide are the two
most common toxic gases associated with confined
space entry. Biosystems offers two different sensors,
the Duo-Tox and the CO Plus, which allow the user to
monitor for both of these hazards while utilizing only one
sensor port.
4.3.1.1 Biosystems Duo-Tox dual purpose Carbon
Monoxide/Hydrogen Sulfide sensor
The Duo-Tox sensor is a substance-specific, dual-
channel, electrochemical sensor designed to directly
detect both carbon monoxide and hydrogen sulfide
without cross interference. When the Duo-Tox sensor is
installed in the PhD Lite, it provides two independent
channels of monitoring information while using only one
sensor port. This allows the instrument to provide four
channels of detection with only three sensors installed.
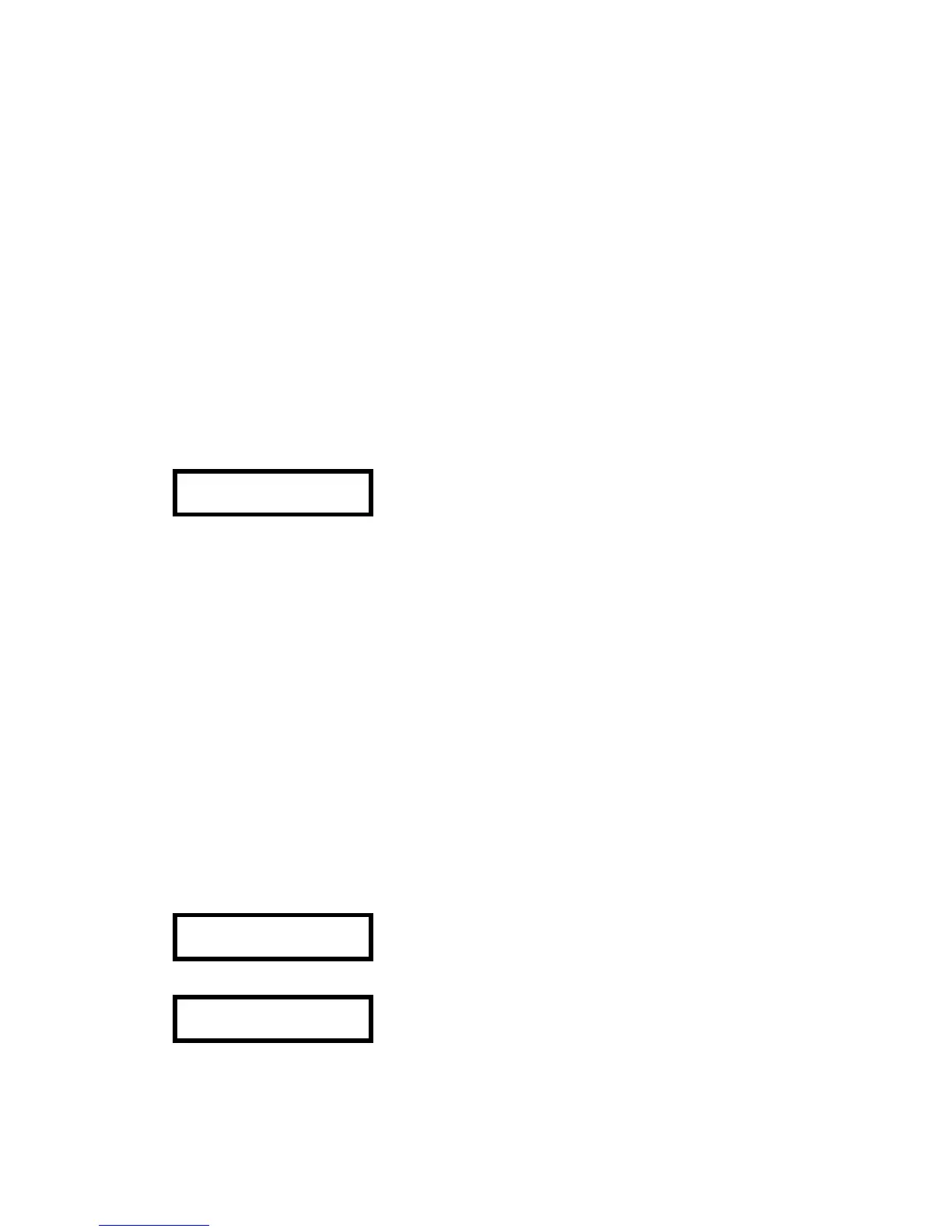
A PhD Lite equipped with a Duo-Tox sensor will show
both CO and H
2
S on the current gas readings screen.
O
2
LEL CO H
2
S
20.9 0 0 0
Current gas readings screen with O
2
, LEL and Duo-Tox
sensor installed.
Calibration gas containing known concentrations of both
CO and H
2
S must be used to properly calibrate the Duo-
Tox sensor.
4.3.1.2 Biosystems “CO Plus” dual purpose carbon
monoxide/hydrogen sulfide sensor
The “CO Plus” sensor is ideal for situations requiring the
use of a single sensor to monitor simultaneously for
both CO and H
2
S, in which the user does not need to
definitively know which hazard is being encountered.
While the “CO Plus” sensor will simultaneously detect
both carbon monoxide and hydrogen sulfide, it is only
possible to directly monitor for one of these hazards.
The PhD Lite offers a choice of two different calibration
gas settings for the CO Plus sensor. Calibration gas
setting determines whether the PhD Lite is configured
for the direct detection of CO or H
2
S. When the
calibration gas value is set to CO, the PhD Lite will show
CO+ on the current gas readings screen. Alternately,
when the calibration gas value is set to H
2
S, the PhD
Lite will show H
2
S+ on the current gas readings screen.
O
2
LEL CO+
20.9 0 0
Current gas readings screens with CO Plus sensor;
calibration gas value set to CO.
O
2
LEL H
2
S+
20.9 0 0
Current gas readings screens with CO Plus sensor;
calibration gas value set to H
2
S.
Note: The procedure for changing the calibration
gas value setting for the CO Plus sensor is covered
below in section 4.7.2.2.
4.3.1.2.1 Relative response of the CO Plus sensor
to carbon monoxide and hydrogen sulfide
The “CO Plus” sensor will accurately and directly
measure the gas type to which it has been successfully
calibrated. OSHA has assigned an 8-hour TWA of 35
PPM as the permissible exposure limit for carbon
monoxide. If the “CO Plus” sensor is successfully
calibrated to carbon monoxide, and then exposed to 35
PPM carbon monoxide, the display will show 35 PPM.
Appendix A discusses Permissible Exposure Limit
alarm calculations in greater detail.
Regardless of the calibration gas selection, the “CO
Plus” sensor will also show a “relative response” to
other interfering gases. When calibrated with carbon
monoxide, the “CO Plus” sensor responds to hydrogen
sulfide in a ratio of about 3.5 to 1.0. This means a
concentration of about 10 PPM hydrogen sulfide would
produce a reading of 10 X 3.5 or 35 PPM in an
instrument that has been calibrated to CO.
This is a very convenient relative response. The 8-hour
TWA permissible exposure limit for hydrogen sulfide is
10 PPM. This means that even when configured for the
direct reading of CO, the CO Plus gas alarms will be
activated any time the concentration of hydrogen sulfide
exceeds the permissible exposure limit.
Note: The procedure for changing the calibration
gas value setting for the CO Plus sensor is covered
below in section 4.7.2.2.
4.3.2 Cl
2
and ClO
2
Non-Specific sensors
Four different sensors are currently available for the
PhD Lite for the detection of chlorine (Cl
2
) and chlorine
dioxide (ClO
2
). The non-specific versions of the Cl
2
and
ClO
2
(part numbers 54-25-08 and 54-25-12) have built-
in cross-sensitivity as follows:
4.3.2.1 Cl
2
Non-Specific
The 54-25-08 Cl
2
non-specific sensor is cross sensitive
to ClO
2
at a rate of 3.1 to 1. This means that when a
properly calibrated PhD Lite with a Cl
2
non-specific
sensor encounters 1PPM ClO
2
, it will respond by giving
a reading of 3.1PPM Cl
2
.
4.3.2.2 ClO
2
Non-Specific
The 54-25-12 ClO
2
non-specific sensor is cross
sensitive to Cl
2
at a rate of 1 to 3.1. This means that
when a properly calibrated PhD Lite with a ClO
2
non-
specific sensor encounters 1PPM Cl
2
, it will respond by
giving a reading of approximately 0.3PPM ClO
2
.
Note: For more information on cross sensitivity for
any of the sensors available in the PhD Lite, see
Appendix B.
 Loading...
Loading...