UD70
Issue code: 70nu2
6-4 Serial communications
6.3 ANSI communications
Using the standard ANSI slave protocol
The standard built-in protocol which defines the message structure used to
read and write parameters on the UD70 is ANSI x3.28-2.5-A4. This section
explains this protocol.
The user may also create his own protocol by writing it in a DPL program,
using low-level port commands such as
GETCHAR and PUTCHAR (refer to
Chapter 7 Reference).
ANSI slave protocol is enabled when the RS485-mode set-up parameter is set
at 1 (4-wire) (which is the default setting), or 5 (2-wire). See Serial
communications modes later in this chapter for details of other
communication modes.
Fundamentals of data transmission
Data is transmitted at a fixed speed or baud rate in the form of a character.
A character may typically comprise seven or eight bits.
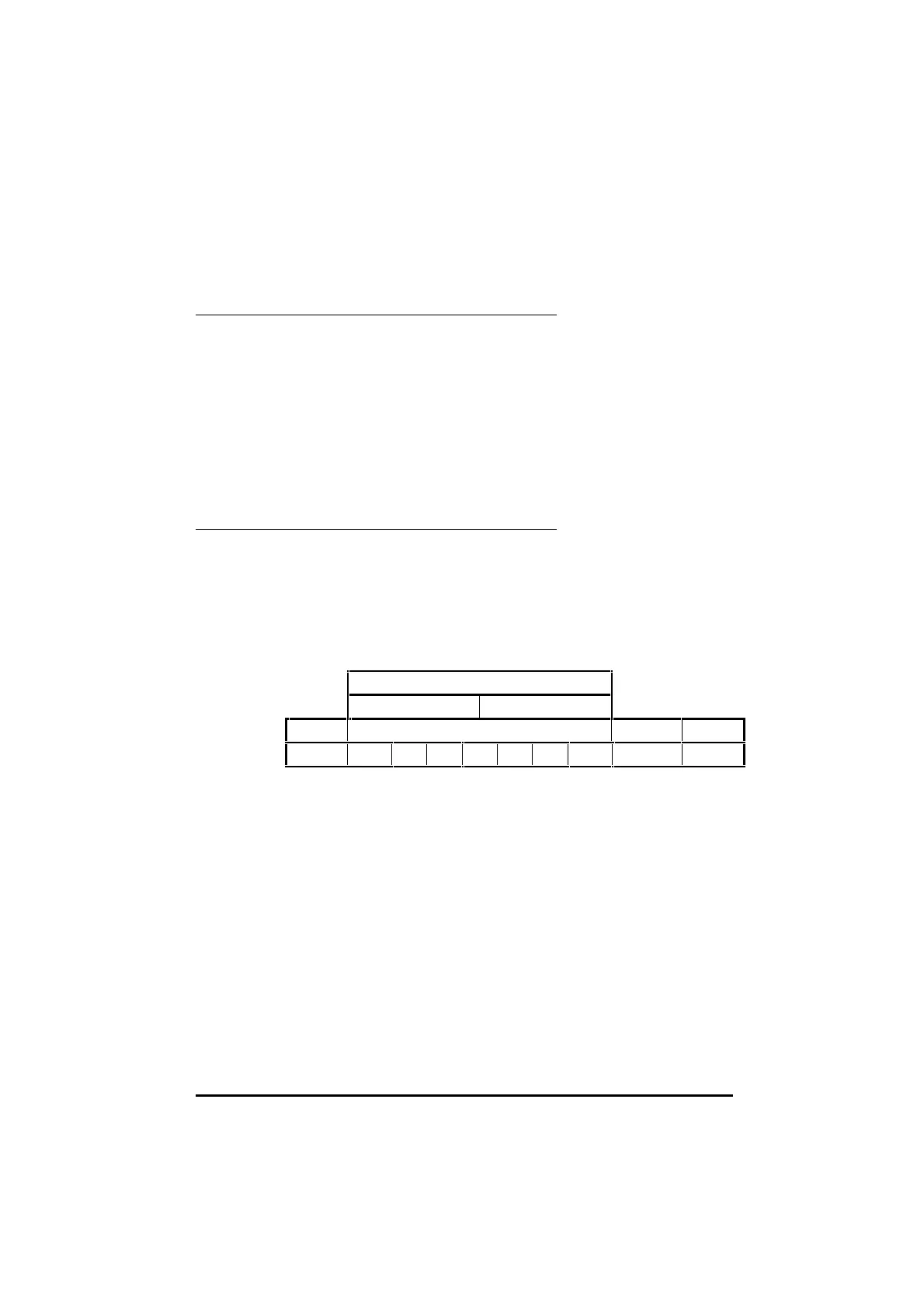
In order for a receiver to recognize valid data, a frame is placed around each
character. This frame contains a start bit, a stop bit, and an optional parity
bit. Without this frame, the receiver will be unable to synchronize itself
with the transmitted data.
A frame is shown below:
Low ASCII character byte
1st hex character 2nd hex character
Start bit Seven data bits Parity bit Stop bit
0LSB MSB 1
This is known as a 10-bit frame, since there are 10 bits transmitted in total.
The format is often described as follows:
1 start bit, 7 data bits, even/odd/no parity, 1 stop bit.1 start bit, 7 data bits, even/odd/no parity, 1 stop bit.
lsb refers to the least significant bit (ie. bit 0)
msb refers to the most significant bit (bit 6)
The Parity bit is used by the receiver to check the integrity of the data
it has received
 Loading...
Loading...