5050 CONTROL UNIT
Technical Manual & Cabling Instructions
19.10.2012
Epec Oy reserves all rights for improvements without prior notice
Epec Oy Postiosoite/Postal address Puhelin/Phone Fax Internet
Tiedekatu 6 PL/P.O.Box 194 +358-(0)20-7608 111 +358-(0)20-7608 110 www.epec.fi
FIN-60320 Seinäjoki FIN-60101 Seinäjoki, Finland
I
o
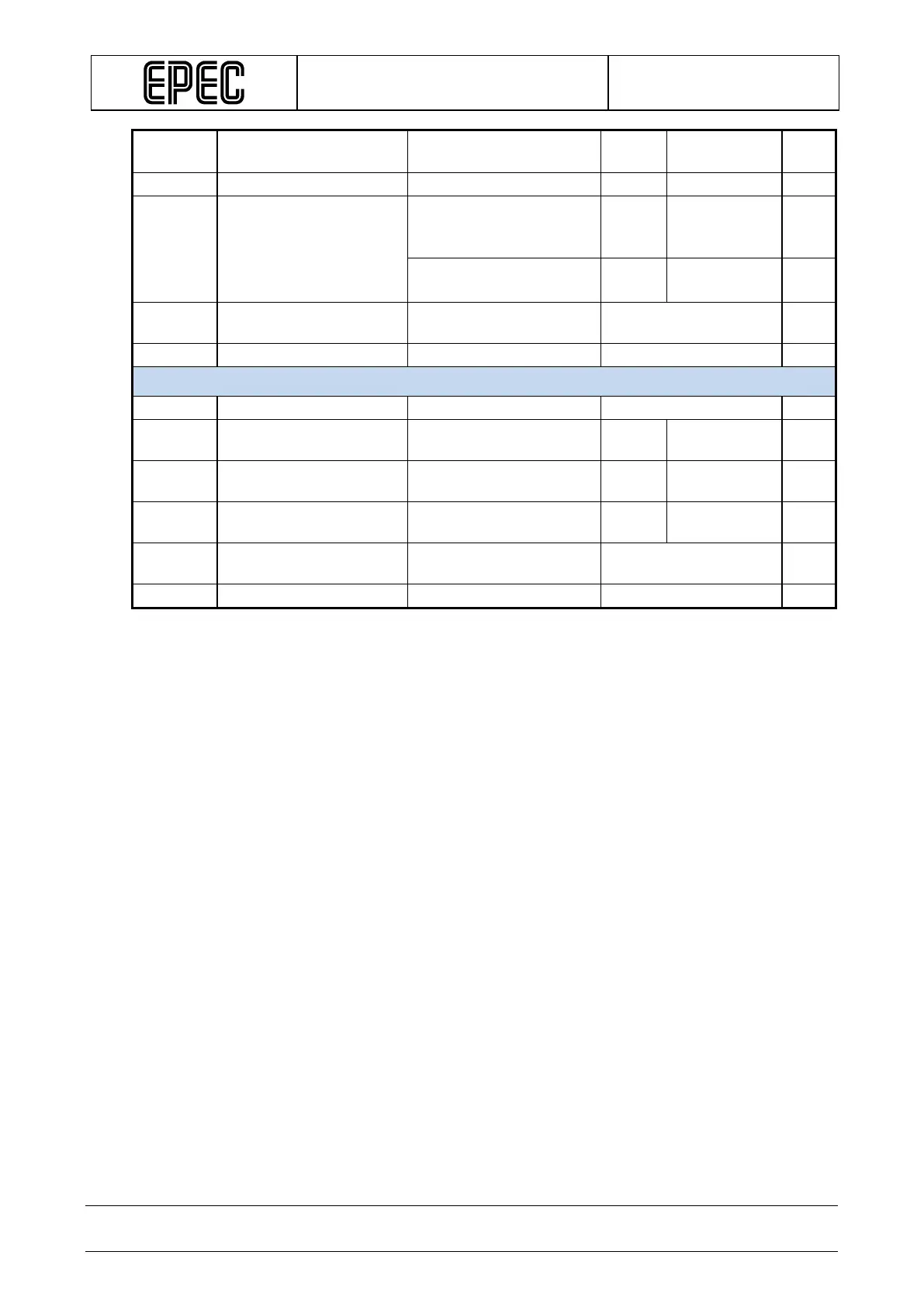
Nominal Output Current
Output On
0 2,5 A
Internal current limitation
f
PWM
PWM Frequency
In current measurement
mode
50 200 Hz
In PWM mode
10 3000 Hz
Duty
PWM
PWM
(Note 2, 10) 0 to 100 %
Digital status input
V
IH
Digital status input
Output Off (Note 5) 3,2 V
V
IL
Digital status input
Output Off
1,9 V
V
I-range
Input voltage range (Note 11) -0,5
VDCPOWERx
V
t
I
Digital Status Input
(Note 2, 4, 8)
tC + 25% ms
Note 1: Frequency of a (PWM) Pulse Width Modulation is = 1 / Period
Note 2: The duty cycle is defined as the percentage of digital ‘high’ to digital ‘low’ signals present
during a PWM period.
Note 3: The PWM resolution is defined as the maximum number of pulses that you can pack into a
PWM period.
Note 4: tC denotes software cycle time.
Note 5: Exceeding the max value might cause damage to input.
Note 6: The maximum output current depends on the load, PWM frequency and temperature.
Note 7: The firmware limits the maximum current to 2,5 A. When the current exceeds the value more
than 200 ms, the output is switched off. The current can be adjusted to be less than 2,5 A by software.
Note 8: Pulse width must be greater that the software cycle time. For example with 50/50 pulse ratio,
the pulse frequency is 1 / (2*pulse width)
Note 9: When both outputs in the pair are used, the total power output can be up to 4A. For example if
output1 continuous load is 2,5A then continuous max load for output2 is 4A – 2,5A = 1,5A.
Note 10: When the frequency increases, the actual duty cycle may be bigger than the value that has
been set.
Note 11: Overload conditions
 Loading...
Loading...