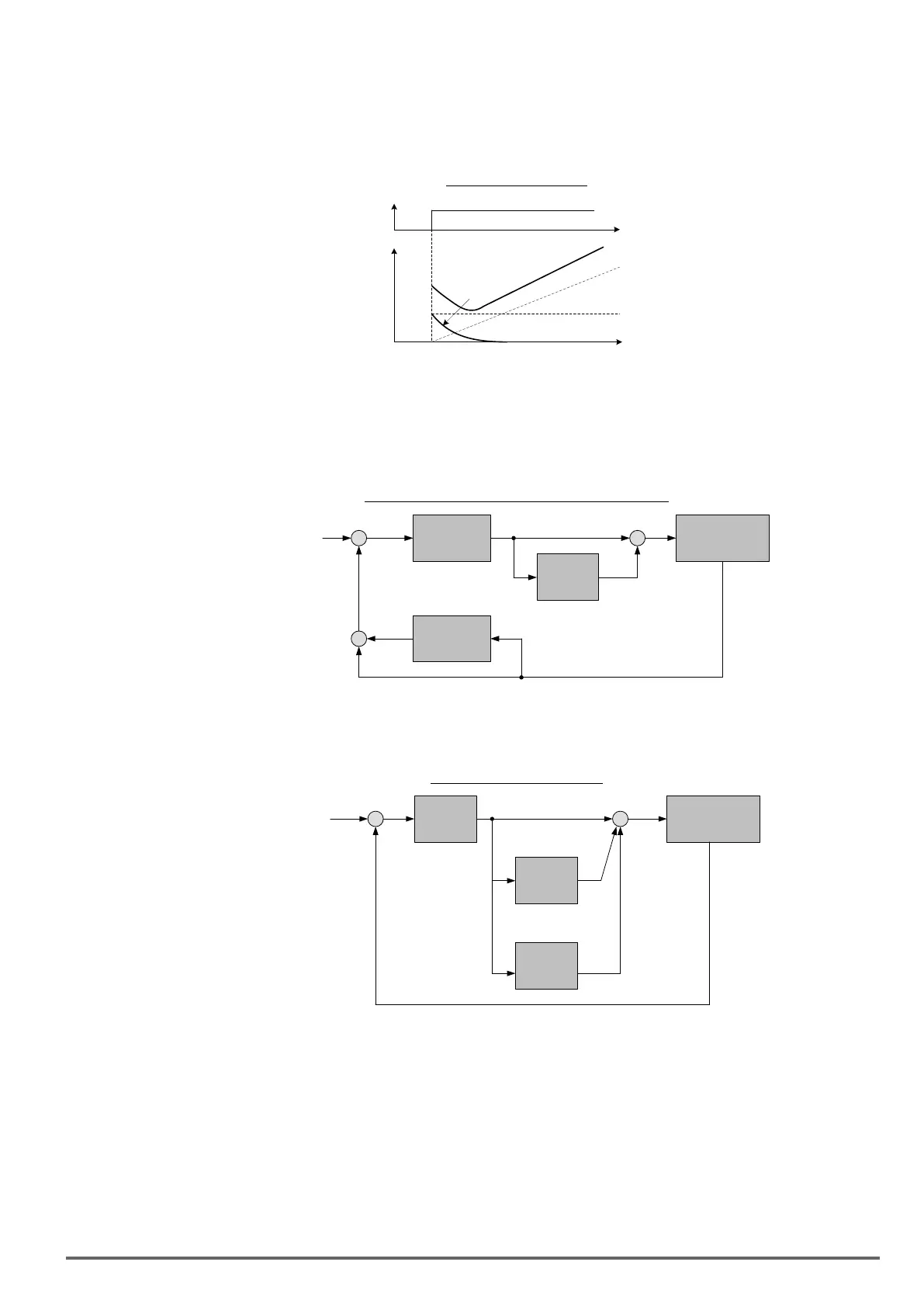
Differential control: This control is the inverse from integral control and tries to guess the behavior of the error
signal by multiplying the error with the differential time. The result is added to the PID input. Differential control
slows down the PID controller response and may reduce system oscillation. Note: Most applications that PID
control (fan and pump) do not require differential control.
Refer to Figure 4.4.77 for PID control operation
Figure4.4.77PIDControl
Control
Deviation
t
PID Control
t
I Control
P Control
D
PID Control Type
The inverter offers two types of PID control:
(a)PIDcontrolwithdifferentialfeedback: (10-03 = x1xxb)
Make sure to adjust the PID parameters without causing system instability. Refer to Figure 4.4.78 for PID con-
trol for feedback value differential.
Figure4.4.78PIDcontrolforfeedbackdifferentialvalue
P
I
Control
D
+
-
+
+
+
+
Feedback
Set Value
(b)BasicPIDcontrol:(10-03 = x0xxb)
This is the basic type of PID control. Refer to the gure 4.4.79.
Figure4.4.79BasicPIDcontrol
P
I
D
Control
+
+
+
+
-
Feedback
Set Value
PID Setup
Enable PID control by setting parameter 10-03, PID target value (10-00) and PID feedback value (10-01).
To use PID control set frequency command selection 00-05 to 4.
(1) Select PID target value (10-00):
10-00: PID target value
=1: analog AI1 given (default)
=2: analog AI2 given
=3: Pulse given
=4:10-02
=6 frequency command (00-05)
VDI100 • Instruction manual
215

 Loading...
Loading...











