PART 1
GENERAL INFORMATION
Page 16
Section 1.3
Preparation Before Use
INTRODUCTION
It is the responsibility of the installer to ensure that the Generator
installation was performed properly. A careful inspection
must be performed when the installation is complete. All
applicable codes, standards, and regulations pertaining to
such installations must be strictly complied with. In addition,
regulations established by the Occupational Safety and Health
Administration (OSHA) must be complied with as well.
Prior to initial startup of the unit, the installer must ensure
that the Generator has been properly prepared for use. This
includes the following:
•An adequate supply of the correct fuel must be available for
Generator operation.
•The engine must be properly serviced with the recom-
mended oil.
•With liquid propane (LP), use only the “vapor withdrawal”
system. This type of system uses the vapors formed above
the liquid fuel in the storage tank.
The engine has been fitted with a fuel carburetion system that
meets the specification of the 1997 California Air Resources
Board for tamper-proof dual fuel systems. The unit will run
on natural gas or LP, but it has been factory set and tested to
run on natural gas. When the change from natural gas to LP is
needed, the fuel system needs to be re-configured. See Section
1.4 “Reconfiguring the Fuel System” for further information.
Recommended fuels should have a British Thermal Unit (BTU)
content of at least 1,000 BTU’s per cubic feet for natural gas; or
at least 2,520 BTU’s per cubic feet for LP. Ask the fuel supplier
for the BTU content of the fuel.
Recommended fuel pressures for natural gas and liquid propane
vapor (LPV) are as follows:
LPV NG
Minimum Water Column 10 inches 5 inches
Maximum Water Column 12 inches 7 inches
Note: All pipe sizing, construction and layout must comply
with NFPA 54 for natural gas applications and NFPA 58 for
liquid propane applications. After installation, verify that
the fuel pressure NEVER drops below five (5) inches water
column for natural gas or ten (10) inches water column for
LPV.
Prior to installation of the Generator, the installer should
consult local fuel suppliers or the fire marshal to check
codes and regulations for proper installation. Local codes
will mandate correct routing of gaseous fuel line piping
around gardens, shrubs and other landscaping to prevent
any damage.
Special considerations should be given when installing the unit
where local conditions include flooding, tornados, hurricanes,
earthquakes and unstable ground for the flexibility and strength
of piping and their connections.
Use an approved pipe sealant or joint compound on all threaded
fittings.
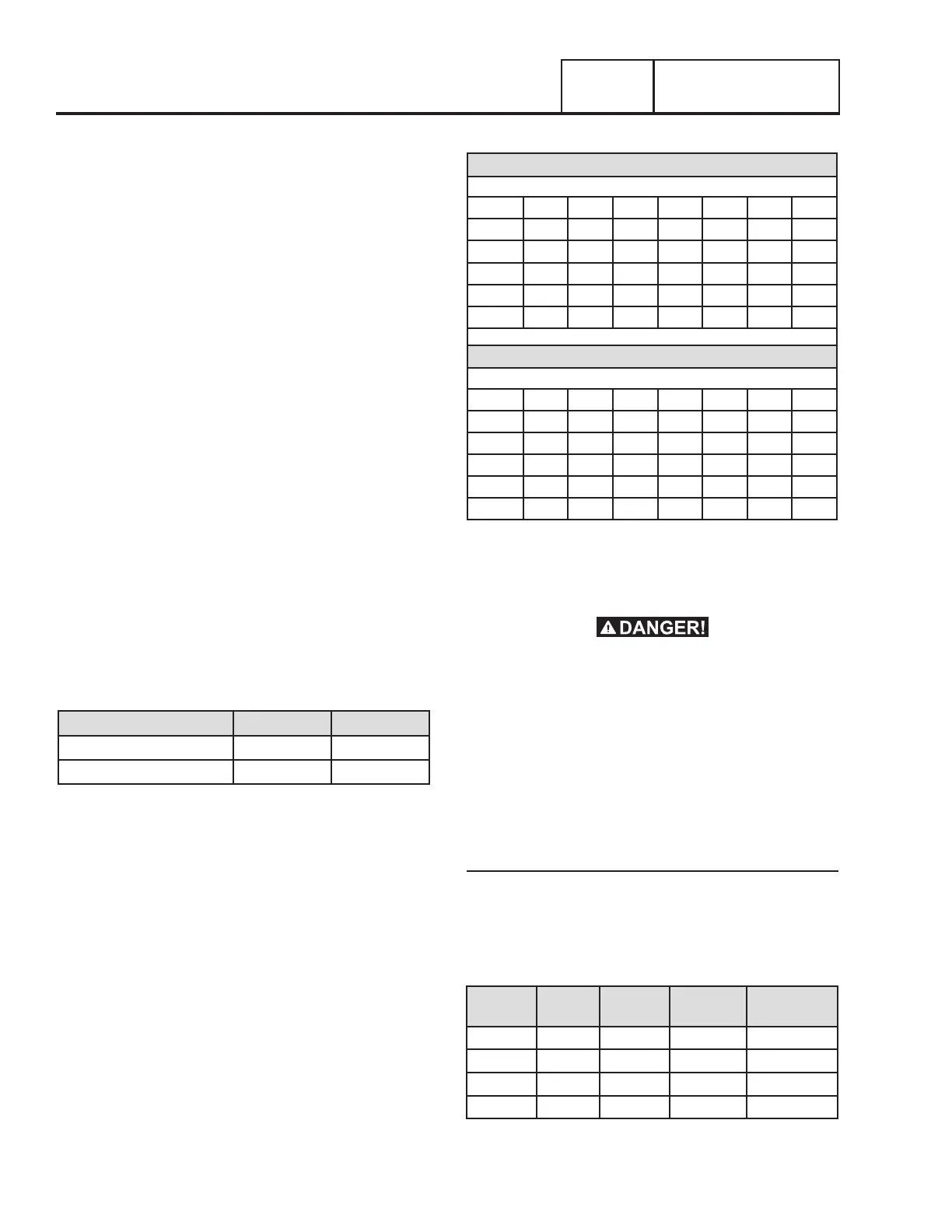
Table 2. Fuel Pipe Sizing
Natural Gas
Table values are maximum pipe run in feet
KW 0.75" 1" 1.25" 1.5" 2" 2.5" 3"
7-8 55 200 820
10 20 85 370 800
13-14 10 50 245 545
15-17 40 190 425
20 20 130 305 945
Liquid Propane Vapor
Table values are maximum pipe run in feet
KW 0.75" 1" 1.25" 1.5" 2" 2.5" 3"
7-8 165 570
10 70 255 1000
13-14 45 170 690
15-17 25 130 540
20 15 115 480
Notes:
•Pipe sizing is based on 0.5” H20 pressure drop
•Sizing includes a nominal number of elbows and tees
•Please verify adequate service and meter sizing
Gaseous fuels such as natural gas and LPV are highly
explosive. Even the slightest spark can ignite such
fuels and cause an explosion. No leakage of fuel is
permitted. Natural gas, which is lighter than air, tends
to collect in high areas. LP gas is heavier than air and
tends to settle in low areas.
Note: Code requires a minimum of one approved manual
shutoff valve installed in the gaseous fuel supply line. The
valve must be easily accessible. Local codes determine
the proper location.
Fuel Consumption
The fuel consumption rate for individual kW ranges are listed
in the Specifications section at the front of this manual. Table
3 shows standard fuel consumption rates based on 4 different
kW ranges.
Table 3. Standard Fuel Consumption Rates
Load (kW) BTU / Hr LP Gal
/ Hr
NG FT3 / Hr NG Therms
/ Hr
5 110,000 1.2 110 1.1
10 176,400 2 156 1.6
15 231,800 2.5 220 2.2
20 267,100 2.8 262 2.6
Note: Typical fuel consumption based on a Generator 100%
loaded.

 Loading...
Loading...











