Wireless LAN – WLAN
26
3.1
What is a Wireless LAN?
BAT54-Rail/F..
Release
7.54
06/08
D Simple direct connections between terminals without base station (ad-hoc
mode, only with 2.4 GHz)
D Larger Wireless LANs, connection to LANs with one or more base sta-
tions (infrastructure network)
D Connecting two LANs via a direct radio link (point-to-point mode, point-to-
multipoint)
D Connecting of devices with Ethernet interface via base stations (client
mode)
D Extending an existing Ethernet network with WLAN (bridge mode)
D Multiple radio cells with one access point (Multi-SSID)
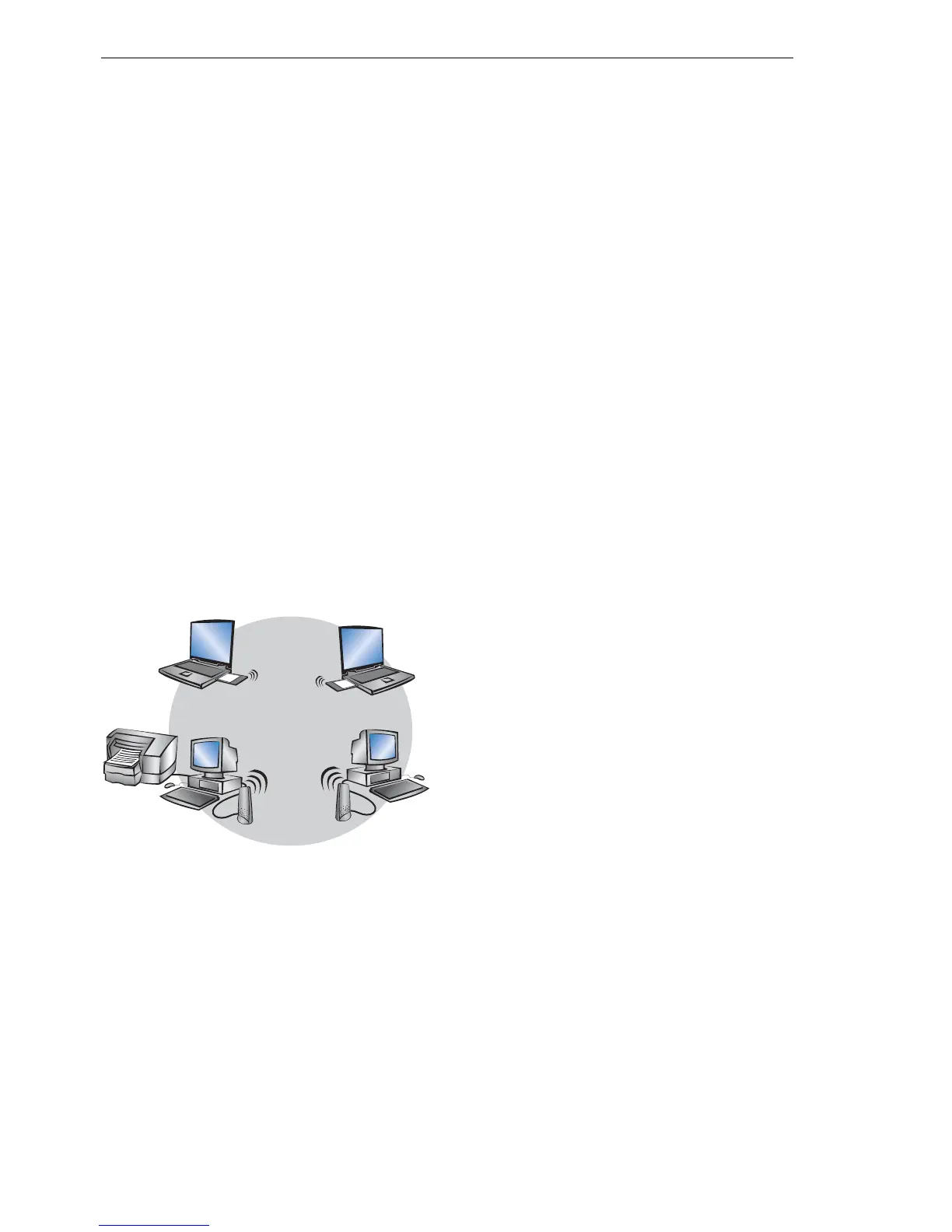
U The ad-hoc mode
When two terminals are equipped with compatible wireless interfaces, they
both can communicate directly via radio. This simplest use is the so-called
ad-hoc mode.
Only in IEEE 802.11b or IEEE 802.11g standard
In ad-hoc networks you connect two or more PCs with own wireless interfac-
es directly together for building a Wireless LAN.
This operation mode is generally called peer-to-peer network (spontaneous
network). PCs can immediately get in touch and exchange data.
U The infrastructure network
By use of one or more base stations (also called access point), a Wireless
LAN becomes more comfortable and more efficient. A Wireless LAN with one
or more base stations is referred to as an infrastructure network in Wireless
LAN terminology.
Note: In some devices the access point is built in, so called WLAN router.

 Loading...
Loading...