Routing and WAN connections
400
11.7
Changes in other services
BAT54-Rail/F..
Release
7.54
06/08
11.7.4 RIP
Similar to the NetBIOS proxy, the local network structure should generally
not be propagated by RIP in the DMZ. Apart from that it is sometimes desir-
able to propagate routes to a network, but not to learn routes from that net-
work (e.g. in the WAN). For this reason, the RIP function can be configured
separately for each network.
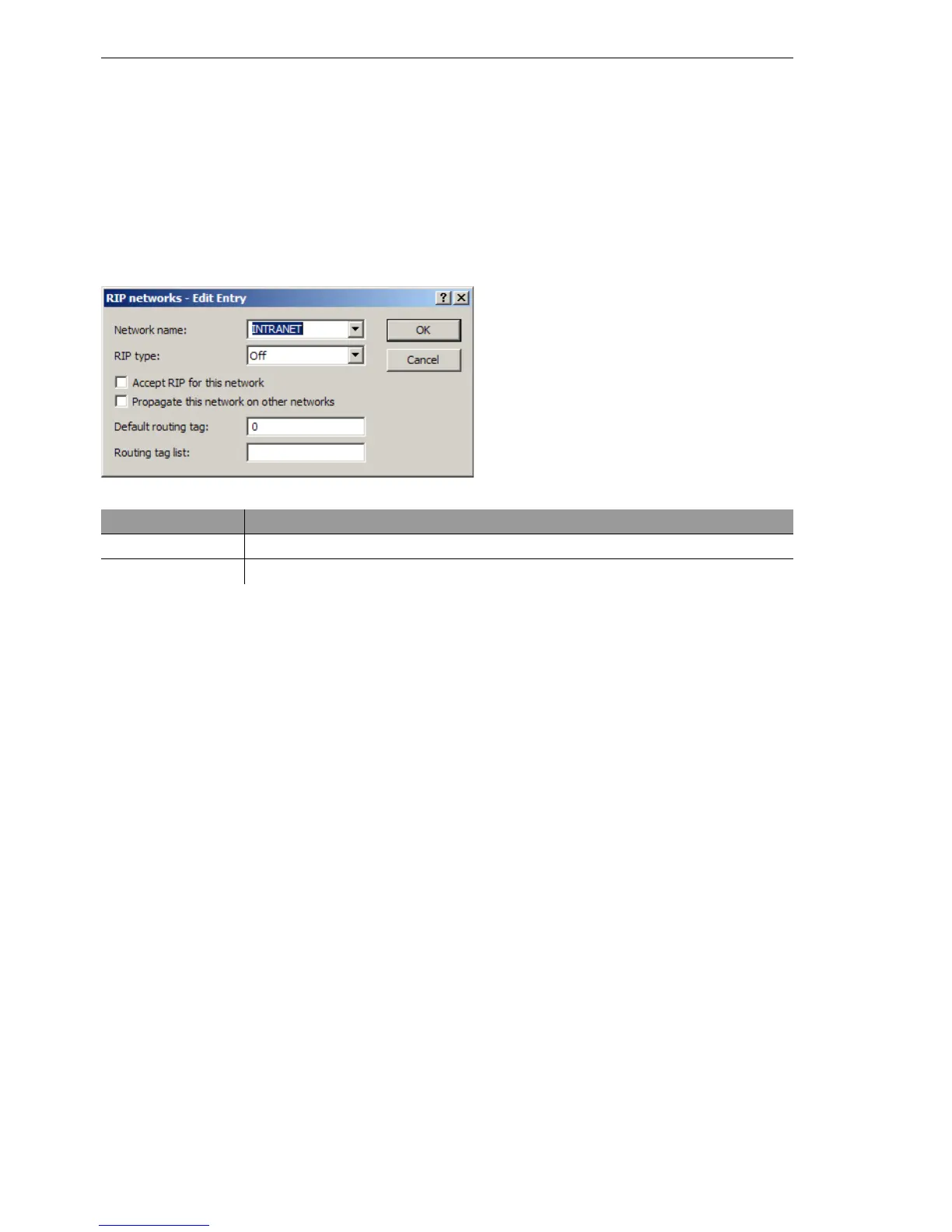
D Network name
Name of the network that the RIP support is to be activated for.
D RIP support
RIP type for propagating own routes. Values:
D Off: No routes are propagated.
D RIP-1: Routes are propagated with RIP-1 packets.
D RIP-1 compatible: Routes are propagated in RIP-1-compatible pack-
ets (RIP-2 packets as broadcast).
D RIP-2: Routes are propagated with RIP-2 packets.
D RIP accept (from these networks)
This option defines if RIP routes are to be learned in this network.
D Propagate to other networks
This option defines whether the associated network is to be propagated
to other networks.
D Default routing tag
The standard routing tag for this interface. Routes with a routing tag set
with the interface tag are propagated by the interface with the tag config-
ured here. Routes that are received at the interface with the standard rout-
Configuration tool Call
LANconfig IP router
General RIP networks
WEBconfig, Telnet Expert Configuration > Setup > IP-Router > RIP > LAN Sites

 Loading...
Loading...