Routing and WAN connections
370
11.4
IP masquerading
BAT54-Rail/F..
Release
7.54
06/08
11.4.1 Simple masquerading
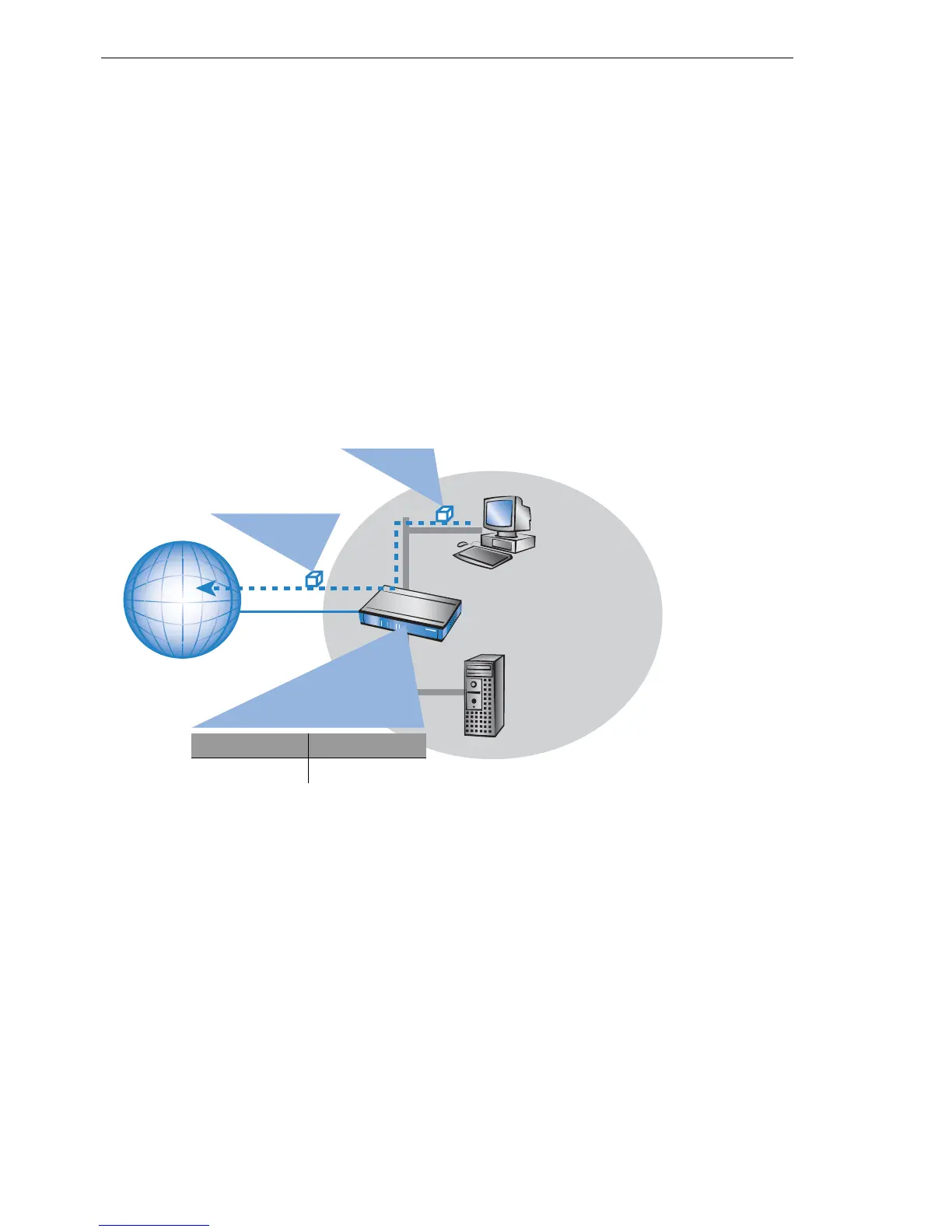
U How does IP masquerading work?
Masquerading makes use of a characteristic of TCP/IP data transmission,
which is to use port numbers for destination and source as well as the source
and destination addresses. When the router receives a data packet for trans-
fer it now notes the IP address and the sender's port in an internal table. It
then gives the packet its unique IP address and a new port number, which
could be any number. It also enters this new port on the table and forwards
the packet with the new information.
The response to this new packet is now sent to the IP address of the router
with the new sender port number. The entry in the internal table allows the
router to assign this response to the original sender again.
Internet
Source: 10.0.0.100
Target: 80.123.123.123
IP: 10.0.0.100
Source: 80.146.74.146, Port 3456
Target: 80.123.123.123
internal IP: 10.0.0.1
public IP: 80.146.74.146
Source IP Port
10.0.0.100 3456

 Loading...
Loading...