IEEE 32-bit Floating Point Register Information
IEEE Floating Point Data Format
Revision 13 HC900 Process Controller Communications User Guide 7
April 2017
2. IEEE 32-bit Floating Point Register Information
The Modbus interface supports IEEE 32-bit floating point information for several of the function codes.
2.1 IEEE Floating Point Data Format
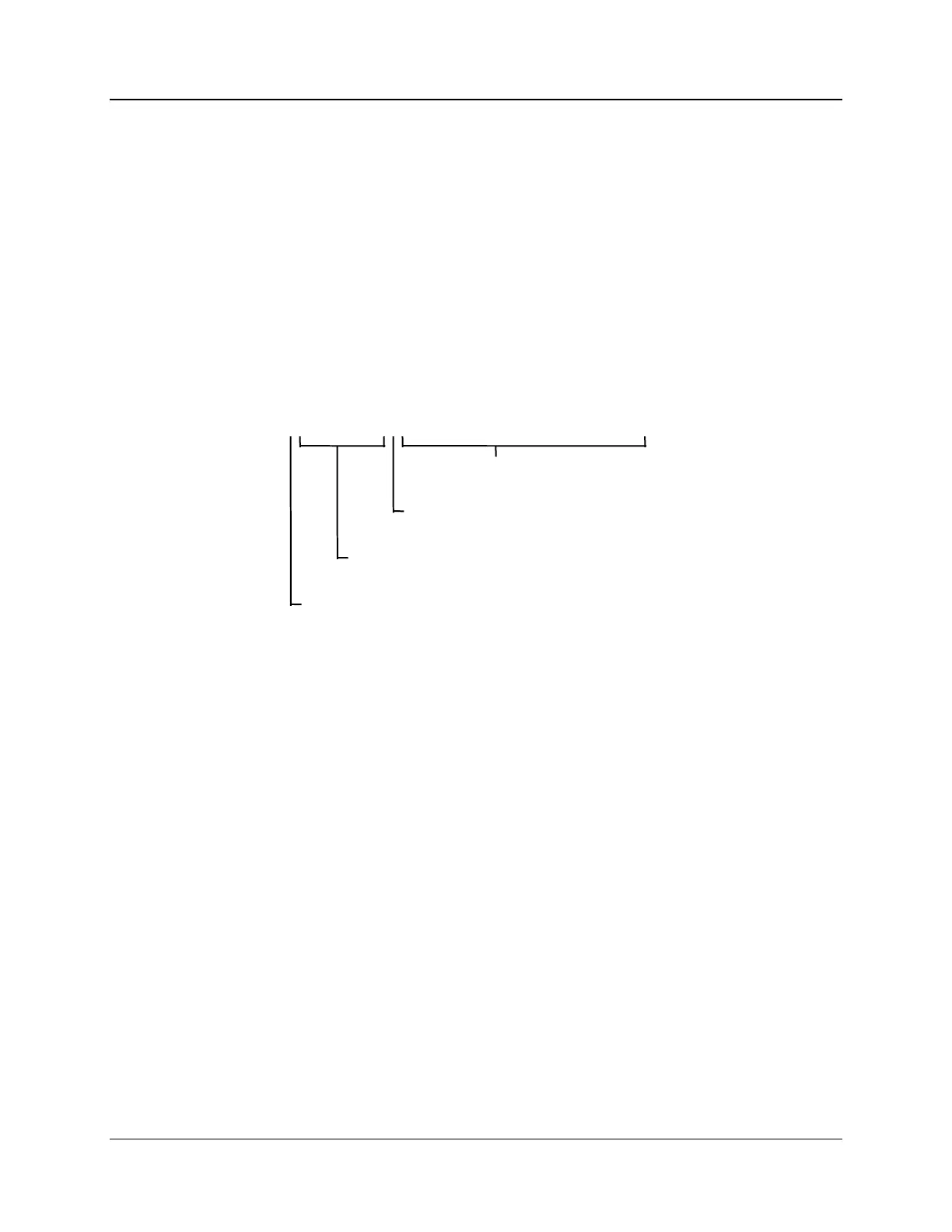
The formula for calculating the floating point number is:
mantissa x 2
(exponent -127)
byte 4 byte 3 byte 2 byte 1
3 2 2 1 1
1 4 3 6 5 8 7 0
xxxxxxxx x.xxxxxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxx
mantissa (23 bits)
implied binary point for mantissa
exponent (8 bit unsigned value)
sign of the mantissa 0 = positive, 1 = negative
(23 bit signed binary with 8 bit biased binary exponent)
Figure 2-1 IEEE Floating Point Data format
Mantissa and Sign
The mantissa is defined by a sign bit (31) and a 23-bit binary fraction. This binary fraction is combined with
an “implied” value of 1 to create a mantissa value, which is greater than or equal to 1.0 and less than 2.0.
The mantissa is positive if the sign bit is zero (reset), and negative if the sign bit is one (set). For example:
01000010 11001000 00000000 00000000
The sign bit (31) is zero, indicating a positive mantissa. Removing the sign bits and exponent bits, the
mantissa becomes:
xxxxxxxx x1001000 00000000 00000000
Add an “implied” value of one to the left of the binary point:
1.1001000 00000000 00000000
Using positioned notation, this binary number is equal to:
10 1 0 0 1 10 05 0 0 0 0 0 0625 15625. ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) . . . . . . x2 x2 x2 x2
-1 -2 -3 -4

 Loading...
Loading...