28 323094 Dev Kit Manual
2 x 8 PCI Express IO (or PEG)
The 2 x 8 slots are supported through the Nowata Add-In Card. Embedded Display Port (eDP)
is supported through the Eaglemont 2 add-in card.
The usage model of the processor‟s PCI Express interface needs to be configured through the
following hardware straps:
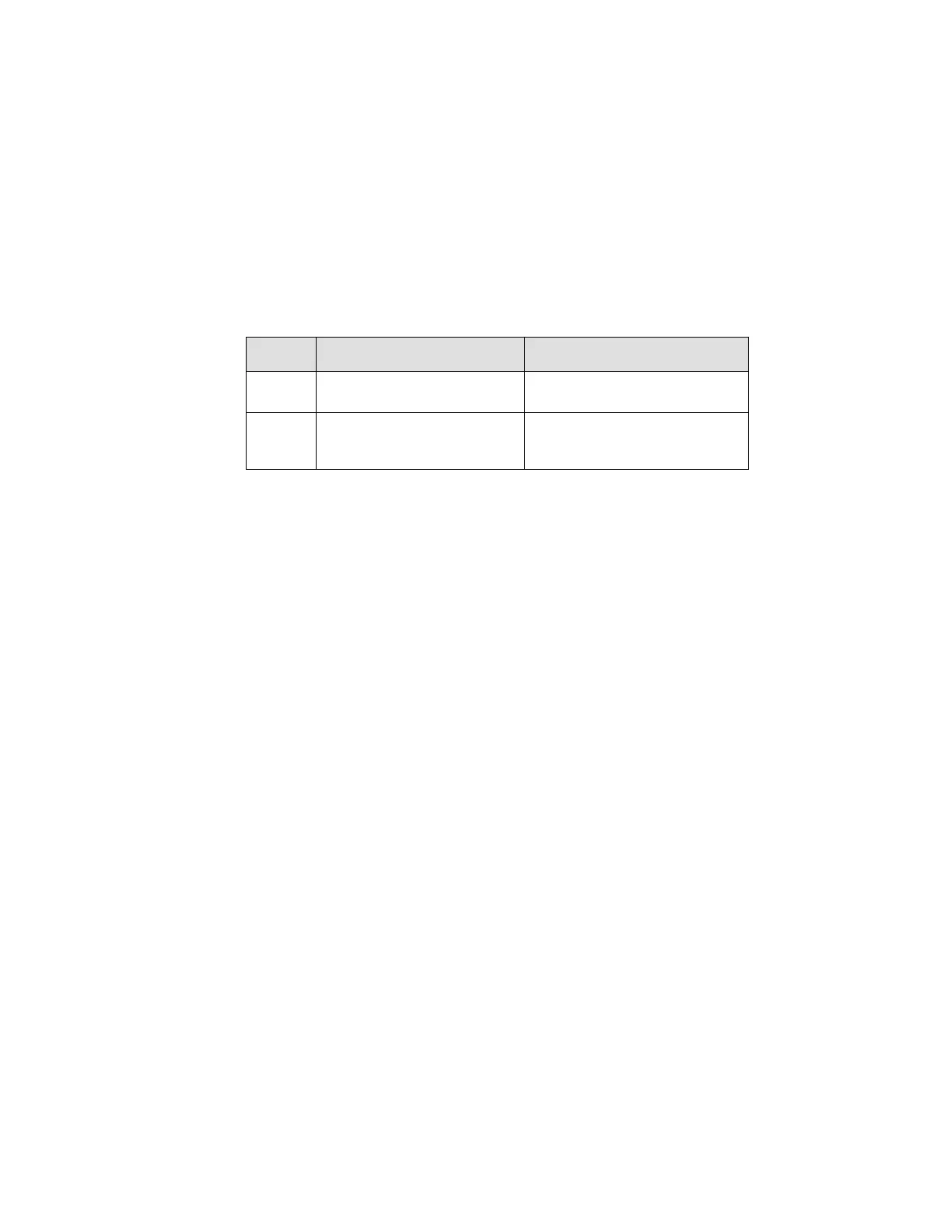
Table 7. Hardware Straps for processor PCI Express* Interface Usage
Single PCI Express*
(default)
PCI Express Bifurcation Enabled
J1D4: IN (1-2)
No Display Port connected to
eDP (default)
An External Display Port is
connected
J1D1: IN (1-2)
3.7.1.8 Embedded Display Port
Embedded Display Port (eDP) is a feature on Intel
®
Core™ Processor.
Note: When eDP is enabled, we can only have 1x8 PEG card. eDP lanes are multiplexed over PEG
12:15 lanes from the processor.
1. Insert the PCI graphics add-in-card in the PEG slot (J5C1), not the DDI slot.
2. To enable eDP, you need to “short” the Jumper pins of J1D1 (1-2) on motherboard.
3. Connect the side-band signals on J6D1 on motherboard, via a cable to J3C1 on the PCI
graphics.
4. For the Sideband signals, we have 2 options
5. Connect J6D1 (on motherboard) to J3C1 (on PCI graphics) through a 10-pin cable.
6. Use the BLI connector from LVDS Connector provided to connect it directly at the eDP
Panel.
3.7.1.9 DMI Interface
The Development kit Supports x4 DMI bi-directional lanes between the Processor and Chipset.
The transmissions happen over DMI protocol. Max speed supported is 2.5GT/s. This protocol is
different from the ones on earlier platforms, and has some instructions added.
3.7.1.10 Intel
®
Flexible Display Interface (Intel
®
FDI)
The development kit supports Intel
®
FDI, a new interface. On this platform, the GPU is in the
processor and display interfaces are supported through the chipset. The Intel
®
FDI is a
dedicated link to transmit the display related pixel information over unidirectional 2x4 lane
interfaces. The synchronization signals are directed from chipset to processor.

 Loading...
Loading...











