7-28
7.3.3.1 Pressure Calibration Principles
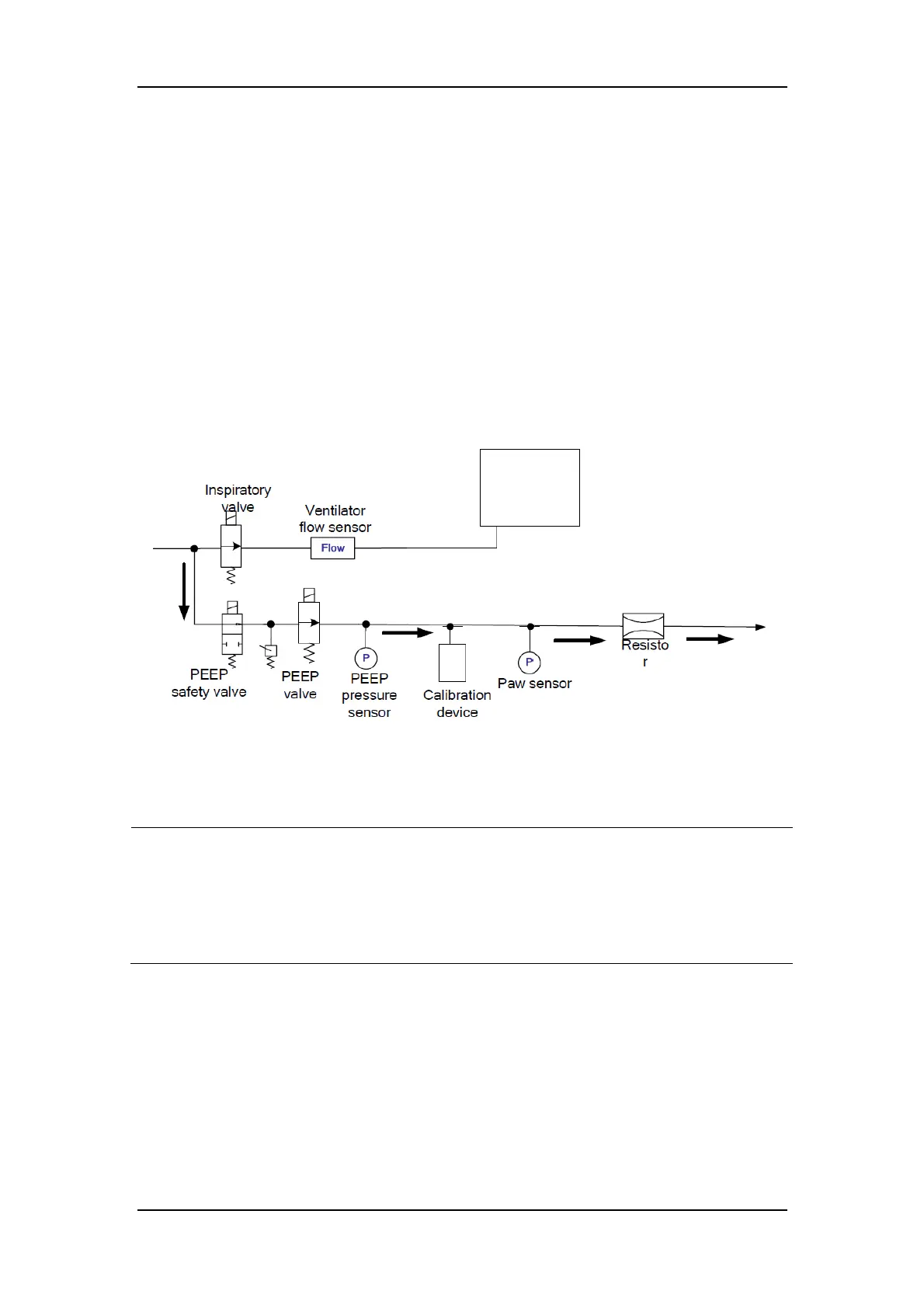
In pressure calibration (service), the anesthesia machine calibration device specified by the
manufacturer needs to be used to calibrate the PEEP valve, Paw sensor, and PEEP pressure sensor.
The calibration principles are as follows: The anesthesia machine calibration device can
communicate with the VCM, which controls the tight closing of the inspiration valve. The VCM
opens the PEEP valve based on a certain DA value to make the circuit pressure reach a certain
value. The Paw sensor, PEEP pressure sensor, and anesthesia machine, calibration device collect
the circuit pressure. The calibration device sends the collected pressure to the VCM. The VCM
uses the pressure measured by the calibration device and AD values collected by the pressure
sensors as the data of one calibration point for the pressure sensors, and uses the pressure
measured by the calibration device and DA value of the PEEP valve as the data of one calibration
point for the PEEP valve. The VCM controls the PEEP valve to change the DA value to obtain
calibration data under a series of pressures, forming a pressure calibration data table. The gas
pressure should be in the range from 0 cmH20 to 100 cmH20 when the VCM opens the PEEP
valve.
FIGURE 3 Schematic Diagram of Pressure Calibration (Service)
7.3.3.2 Precautions
NOTE
Before pressure calibration, ensure tube tightness during connection. Ensure that
no leakage occurs.
Do not move or press the tube during the calibration process.
You can use the anesthesia machine calibration device VT, Fluke VT Plus or
FPMfor automatic calibration. You can also use a pressure calibration device that
meets the precision requirement in manual calibration.

 Loading...
Loading...