NX-ID3317 Current Consumption = Current consumption from I/O power supply + (Input
current × Number of inputs used) + Total current con-
sumption of connected input devices
=
0 mA + (6 mA × 4 points) + (50 mA × 4 points)
= 224 mA
NX-OD3121 Current Consumption = Current consumption from I/O power supply + Total load
current of connected loads + Total current consumption
of connected output devices
=
10 mA + (125 mA × 4 points) + (50 mA × 4 points)
= 710 mA
The required power supply capacity for the I/O power supply is calculated as follows.
Power supply capacity of I/O power sup-
ply
= (Current consumed by NX-PF0730) + (Current con-
sumed by NX-ID3317) + (Current consumed by NX-
OD3121)
= 10 mA + 224 mA +710 mA
= 944 mA
Calculating the Voltage Drop in the I/O Power Supply
Voltage drop occurs in the CPU Units and NX Units due to the contact resistance at the points where
Units are connected to each other
. Design the I/O power supply system to maintain the voltage specifi-
cations of the NX Unit I/O circuits and connected external devices even if the voltage of the I/O power
supply drops.
As shown in the following table, the voltage drop per Unit depends on the total current consumption
from the I/O power supply
.
In this case, the total current consumption from the I/O power supply must not exceed the maximum
I/O power supply current of the Unit that supplies the I/O power.
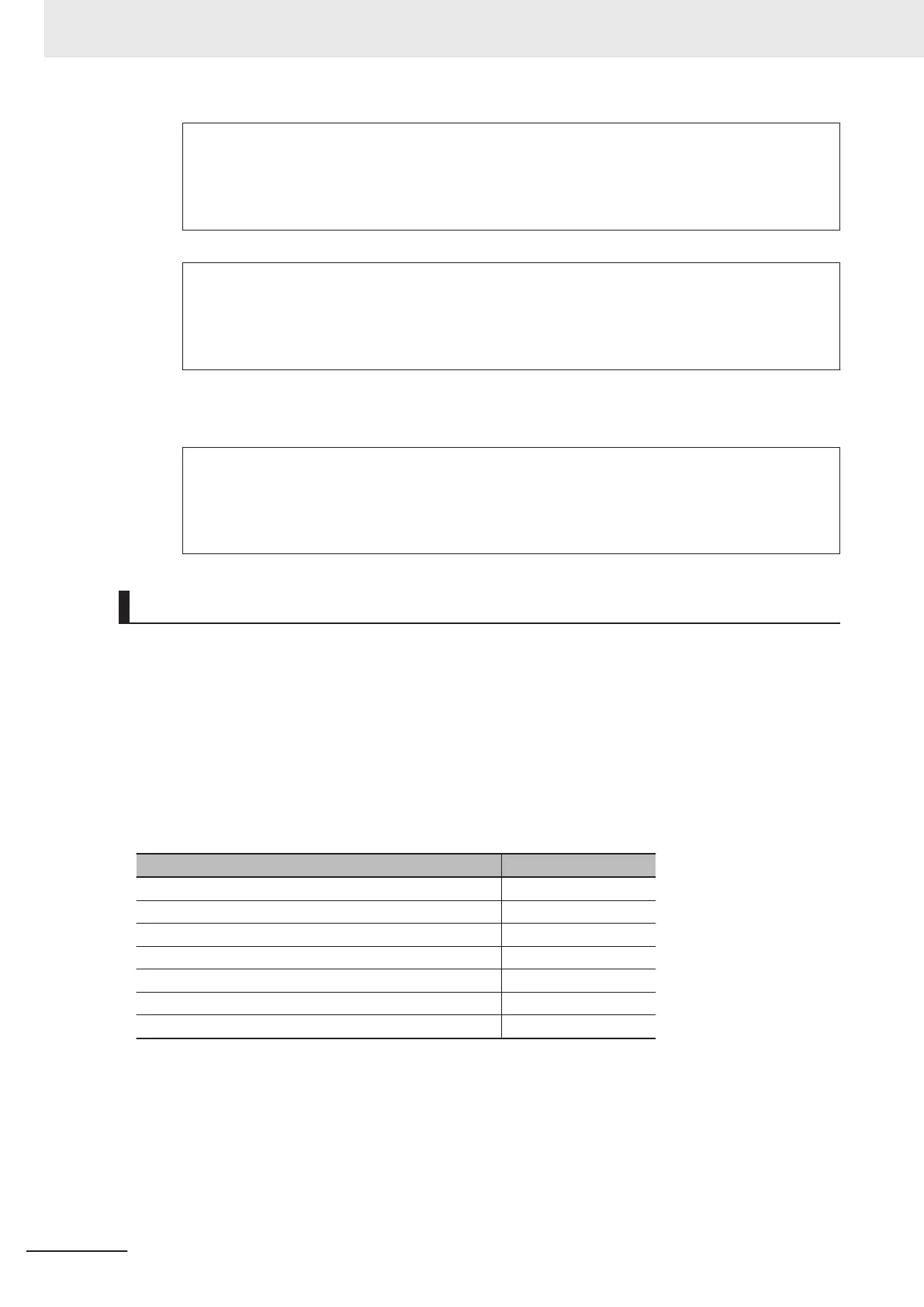
Total current consumption from the I/O power supply Voltage drop per Unit
10 A 0.20 V
8 A 0.16 V
6 A 0.12 V
4 A 0.08 V
3 A 0.06 V
2 A 0.04 V
1 A 0.02 V
The following is a calculation example of the I/O power supply range applicable to the additional I/O
power supply unit that is located on the right side of CPU Unit based on a unit configuration example
shown below
. You can also use the same calculation procedure to calculate the I/O power supply
range after you add more I/O power supply units in addition to the first one.
Example:
4 Designing the Power Supply System
4-18
NX-series NX502 CPU Unit Hardware User's Manual (W629)

 Loading...
Loading...

















