49
5–5–2 AND Load and OR Load
Ladder Symbol
AND Load – AND LD
0002
0003
0000
0001
Ladder Symbol
OR Load – OR LD
0000 0001
0002 0003
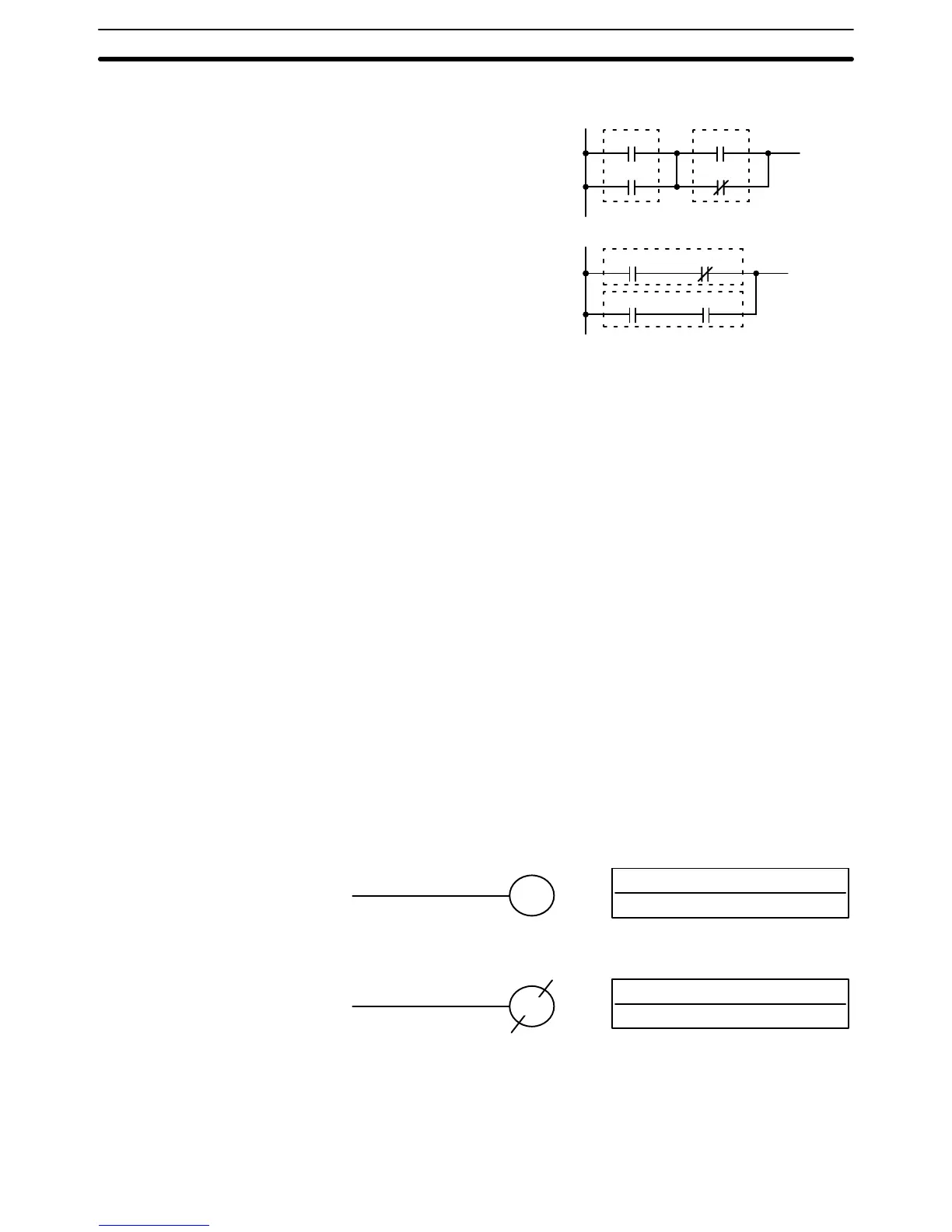
When the above instructions are combined into blocks that cannot be logi-
cally combined using only OR and AND operations, AND LD and OR LD are
used. Whereas AND and OR operations logically combine a bit status and an
execution condition, AND LD and OR LD logically combine two execution
conditions, the current one and the last unused one.
AND LD and OR LD instruction are not necessary to draw ladder diagrams,
nor are they necessary when inputting ladder diagrams directly, as is possi-
ble from the GPC. They are required, however, to convert the program to and
input it in mnemonic form. The procedures for these, limitations for different
procedures, and examples are provided in
7–5 Inputting, Modifying and
Checking the Program
.
In order to reduce the number of programming instruction required, a basic
understanding of logic block instructions is required. For an introduction to
logic blocks, refer to
7–2–3 Logic Block Instructions
.
There are no flags affected by these instructions.
5–6 Bit Control Instructions
There are five instructions that can be used generally to control individual bit
status. These are OUT, OUT NOT, DIFU(13), DIFD(14), and KEEP(11).
These instructions are used to turn bits ON and OFF in different ways.
5–6–1 Output and Output NOT – OUT and OUT NOT
B: Bit
IR, HR, TR
Ladder Symbol Operand Data Areas
Output – OUT
B
B: Bit
IR, HR, TR
Ladder Symbol Operand Data Areas
Output NOT –
OUT NOT
B
Any output bit can be used in only one instruction that controls its status. See
3–3–1 I/O Words
for details.
OUT and OUT NOT are used to control the status of the designated bit ac-
cording to the execution condition.
Description
Flags
Limitations
Description
Bit Control Instructions Section 5–6

 Loading...
Loading...











