85
ER: The content S is not BCD
EQ: ON when 0000 is placed in R.
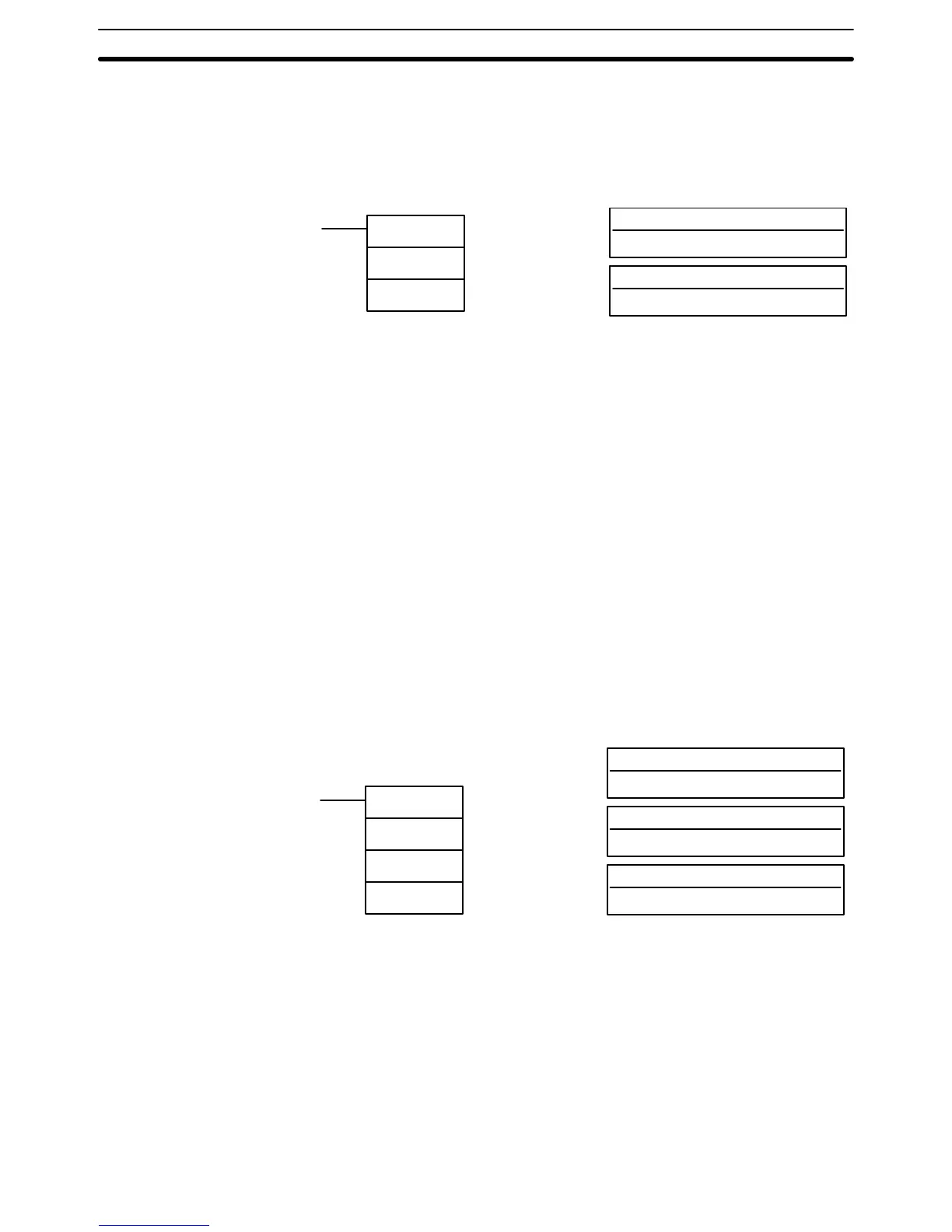
5–15–2 Binary to BCD – BCD(24)
S : Source word (binary)
IR, SR, DM, HR, TC
R : Result word
IR, DM, HR
Ladder Symbol Operand Data Areas
BCD(24)
S
R
If the content of S exceeds 270F, the converted result would exceed 9999
and BCD(24) will not be executed. When the instruction is not executed, the
content of R remains unchanged.
BCD(24) converts the binary (hexadecimal) content of S into the numerically
equivalent BCD bits, and outputs the BCD bits to R. Only the content of R is
changed; the content of S is left unchanged.
BCD(24) can be used to convert binary to BCD so that displays on the Pro-
gramming Console or any other programming device will appear in decimal
rather than hexadecimal. It can also be used to convert to BCD to perform
BCD arithmetic operations rather than binary arithmetic operations, e.g.,
when BCD and binary values must be added.
ER: S is greater than 270F.
EQ: ON when 0000 is placed in R.
5–15–3 4-to-16 Decoder – MLPX(76)
S : Source word
IR, SR, DM, HR, TC
Di : Digit designator
IR, DM, HR, TC, #
Ladder Symbol
Operand Data Areas
R : First result word
IR, DM, HR
MLPX(76)
S
Di
R
The rightmost two digits of Di must each be between D and 3.
All result words must be in the same data area.
When the execution condition is OFF, MLPX(76) is not executed and the next
instruction is moved to. When the execution condition is ON, MLPX(76) con-
verts up to four, four-bit hexadecimal digits from S into decimal values from 0
to 15, each of which is used to indicate a bit position. The bit whose number
corresponds to each converted value is then turned ON in a result word. If
more than one digit is specified, then one bit will be turned ON in each of
consecutive words beginning with R. (See examples, below.)
Flags
Limitations
Description
Flags
Limitations
Description
Data Conversion Section 5–15
 Loading...
Loading...











