200
Examples of Applied Control Types Section 5-2
Note 1. Before dead time compensation is performed, the dead time, time constant
and gain of the target process must be investigated.
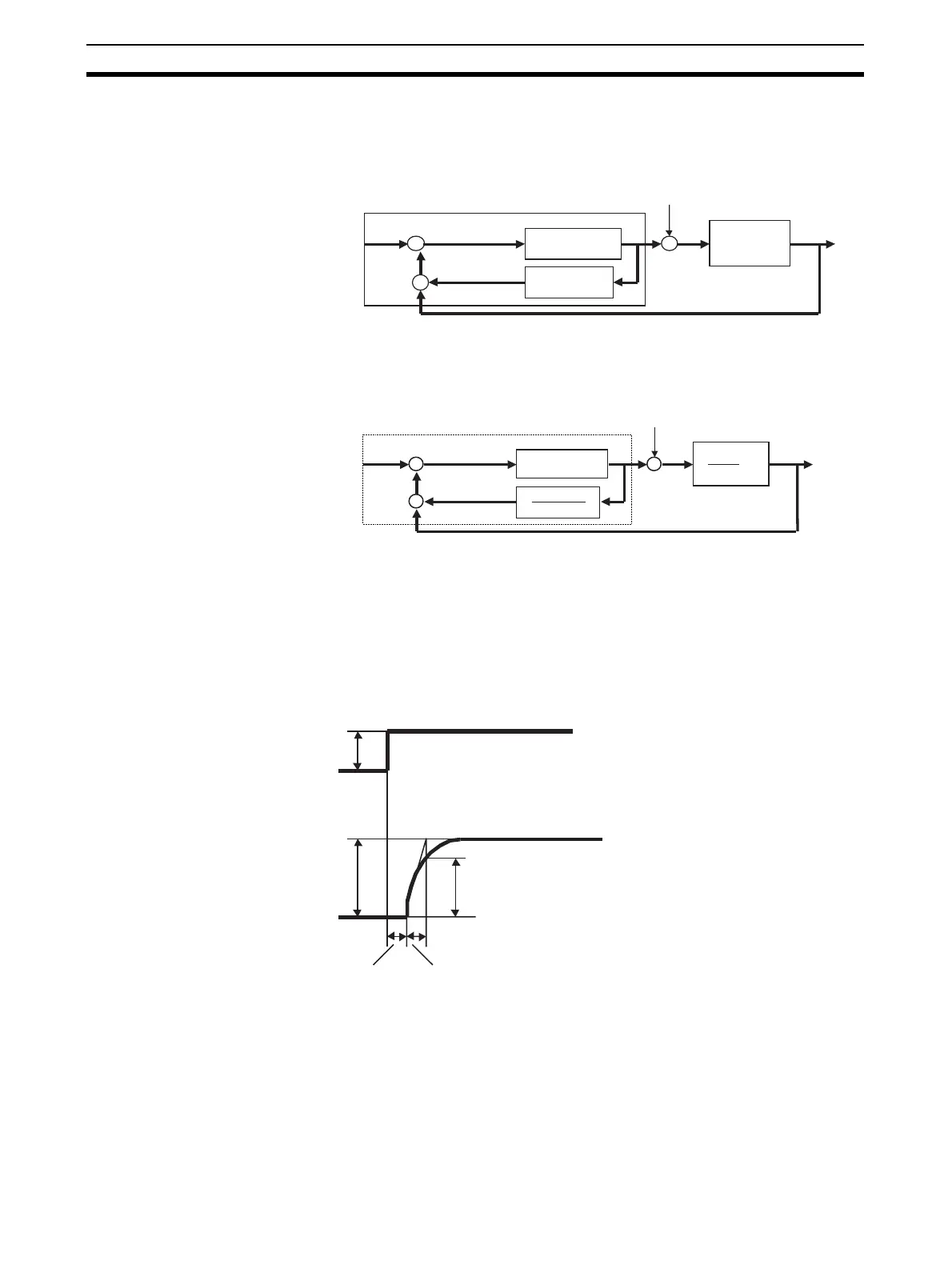
2. By dead time compensation control, dead time compensation is performed
on MV as shown below and the result is added to the PV of PID control.
As dead time L worsens controllability, control is performed on process K/
(1+Ts) not having dead time element (
e
-Ls
) by compensating the dead time
element within the PLC.
The Dead Time Compensation block (Block Model 149) inputs MV for
K (1-(
e
-Ls
) ÷ (1+Ts), and outputs the result to ITEM047 (PV compensation) of
Advanced PID block (Block Model 012). The PV compensation mode is set to
“add”. The Dead Time Compensation block (Block Model 149) sets K (pro-
cess gain), T (time constant of process) and L (dead time) to equal H (sam-
pling cycle) multiplied by N (number of samples). Set MV to manual, apply
step changes to the process, and calculate these constants from the changes
in PV.
−
PID control
Dead time
compensation
Process
characteristics
Set Point
+
PV
+
+
Disturbance
Control
output
+
+
PID control
Set Point
+
−
PV
+
+
Disturbance
Control
output
+
+
1+Ts
K (1-e
-Ls
)
1+Ts
Ke
-Ls
1
K
K
×
0.632
T (time constant)
L (dead time)
 Loading...
Loading...











