89
Polyend Synth Manual
88
Polyend Synth Manual
NOTESNOTES
5.14 Filter
Most Synth voices operate with a lter section. A variety of lter models and
applications exist. Polyend Synth is inspired by many classic lters as well
as standard lter models. Synth has a lter section with models dened for
each engine and accessible using the dedicated [Filter] button.
Filter Concepts
A lter typically operates over a 20Hz to 20kHz range, which matches the
range of human hearing. A lter carves out frequencies in order to shape
the sounds character and timbre. Used as a standard in subtractive
synthesis but increasingly used in other synth models.
Synths
5
Synths
5
2
2
4
4
1
1
3
3
Attenuation
Frequency
Cutoff Frequency
Point at which frequencies
are attenuated.
Low Cut / High Pass
State Variable Filter (SVF)
24dB / Octave
Filter Models Filter Slopes
HPF LPF 4-Pole
BPF N 2-Pole
Attenuates frequencies
below the cutoff point
A state Variable Filter can consist of an integration of models,
typically HPF, LPF and BP which operate within a single model.
Aggressive slope to cut
frequencies sharply.
Attenuates frequencies
above the cutoff point
Attenuates frequencies
above and below cutoff
Attenuates more
frequencies, moderately.
Attenuates frequencies
within a narrow cutoff
Hi Cut / Low Pass
Bandpass 12dB / OctaveNotch
Resonance
Frequency is emphasised
at the cutoff point.
Slope
Affects how aggressive or
moderate the attenuation.
Example: 24dB / Octave.
Filter Model
Designs perform various
functions. Example: Low Cut.
20Hz 20kHz
Other than the PMD Synth model, the lter parameters follow a similar
setup within each engine. The lter is also controlled by default using an
ADSR Envelope which shapes the lter Behavior.
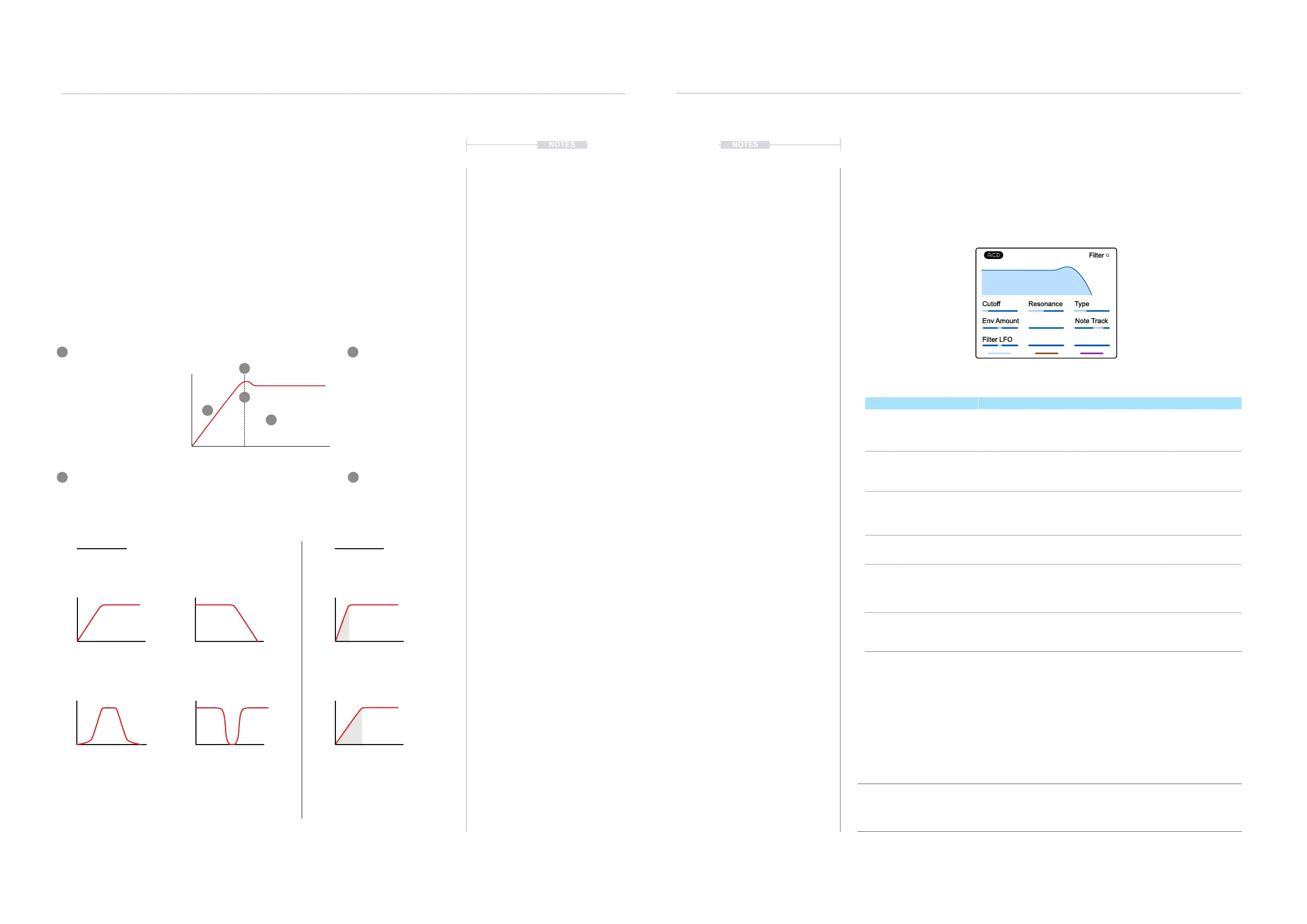
Filter
Cutoff Resonance Type
Env Amount Note Track
Filter LFO
Parameter Description
Cutoff
Cutoff frequency. The point in the frequency range where the
attenuation begins. The amount of frequency attenuation is based
on the cutoff frequency as well as the models slope.
Resonance
Resonance emphasises and boosts the small range of
frequencies at the cutoff point. This introduces a unique shrill
sound to the audio signal ideal for percussive sounds.
Type
A selection of synth models. These include low pass, high pass,
band pass, notch or state variable, also with various slopes. These
models are also inspired in their design from classic synth lters.
Env Amount
The amount of ADSR - Attack, Decay, Sustain and Release
envelope that is applied to shape the lter.
Note Track
Sets note tracking on or off. Tracking links the application of the
modulation envelope to the note pitch played over a keyboard
range. The higher the note played the more the lter will open and
therefore sound brighter.
Filter LFO
Adjusts the amount of the LFO applied to the lter cutoff. This is
only available on certain models by default.
MG24 Filter Model & Modulation:
Due to the nature of the classic MG24 lter type it is not recommended to use a
square wave source when modulating the lter to avoid audio artefacts.
 Loading...
Loading...