H - I - J PROGRAMMER’S MANUAL V8.94.11-
- 22 -
The modifying signals of variable value (analogue IN or motorised potentiometer) can modify he reference signal
according to the following relationship
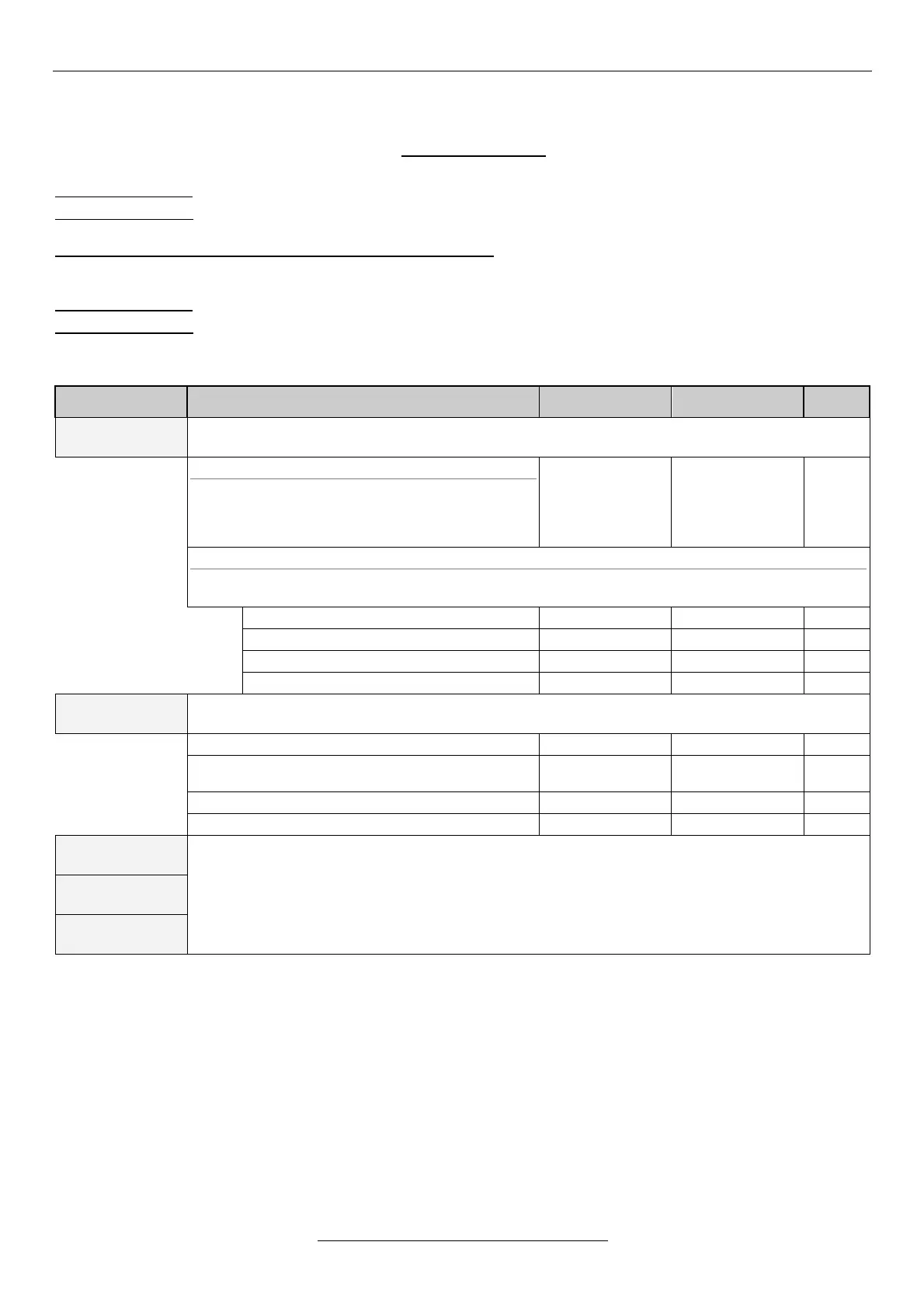
K=
lower
%
+upper
%
100 %
Normal modification: modified reference signal [%] = reference signal [%] - lower [%] + modification [%] x K
Inverse modification: modified reference signal [%] = reference signal [%] + lower [%] - modification [%] x K
Discrete modification (digital input, virtual input or PID extender):
n = number of the active units
Normal modification: modified reference signal [%] = reference signal [%] + n x discrete value [%]
Inverse modification: modified reference signal [%] = reference signal [%] - n x discrete value [%]
PID regulation
Explanation, further submenus
Serves for selecting the PID parameter set to be used.
1-10-1 selection
In regulation mode this PID parameter setting will
be valid.
PID1
PID2
PID3
PID4
frequency-dep.
1-10-2 change-over points
The change-over frequencies of the PID regulators, if frequency depending PID regulation has
been selected. The change-over is implemented with hysteresis to avoid possible swingings.
1-10-2-1 switch-over to PID2
1-10-2-2 switch-over to PID3
1-10-2-3 switch-over to PID4
Setting of the regulation parameters
(Proportional regulation can be implemented if Ti is programmed to “N”)
1-11-1 Ap proportional gain
1-11-2 Ti integration time
1-11-3 Td differentiation time
1-11-4 Ad diff. element overdriving factor
The setting is the same as that of item 1-11 PID 1 data
 Loading...
Loading...