Normal
0
s s
a)
180 360 0
b)
180 360
ω ω
P_PL_0009_SW
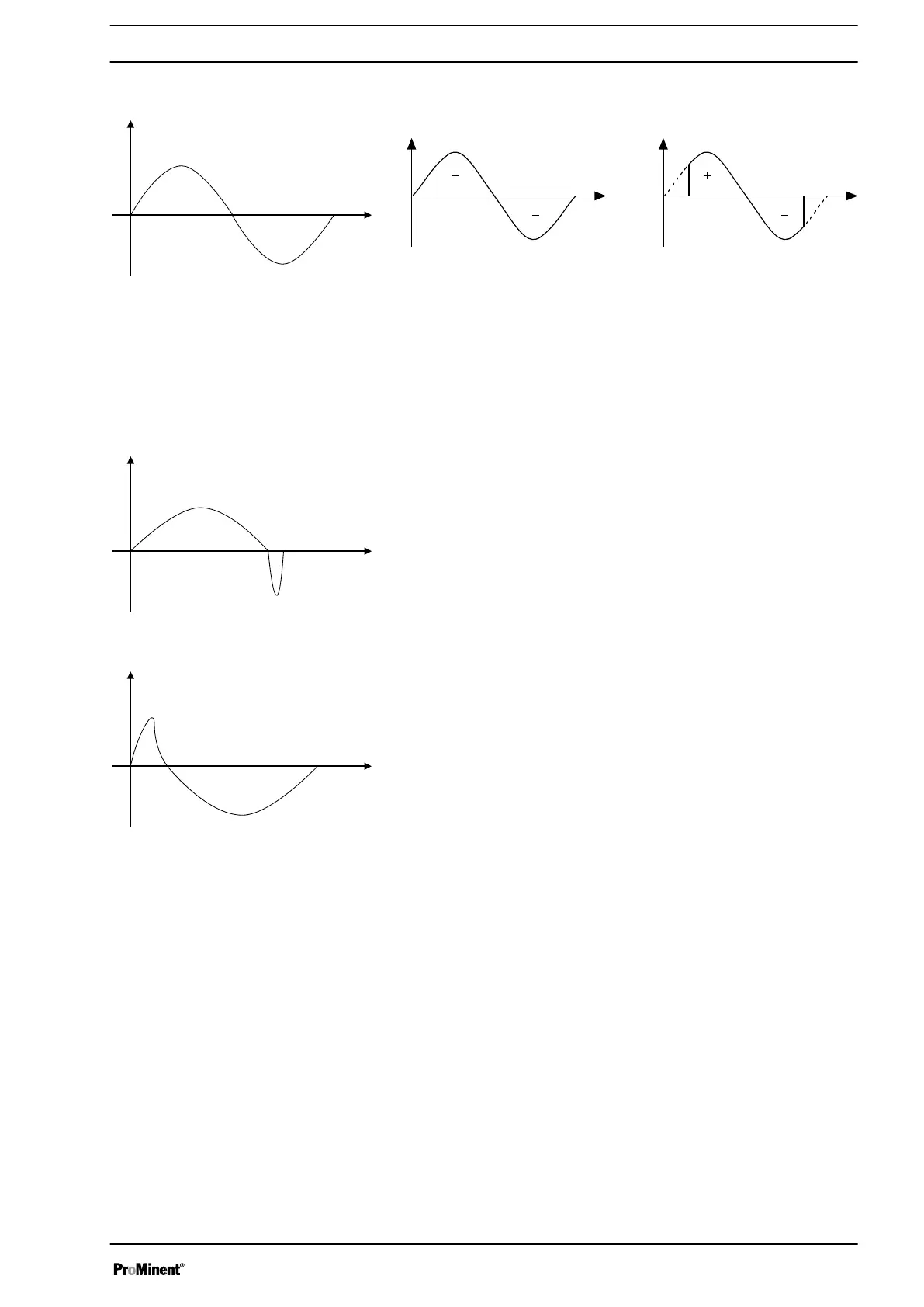
Fig. 7: Stroke movement at a) maximum stroke length and b) reduced
stroke length.
t Stroke velocity
⍵ Cam rotational angle
+ Discharge stroke
- Suction stroke
Discharge opti.
With a discharge optimised dosing profile, the discharge stroke is elon‐
gated, the suction stroke is executed as quickly as possible. This setting is
for example suitable for those applications that require optimum mixing
ratios and as continuous as possible chemical mixing.
Suction opti.
With a suction optimised dosing profile, the suction stroke is elongated as
much as possible, which makes possible a precise and problem-free
dosing of viscous and gaseous media. This setting should also be chosen
to minimise the NPSH value.
5.2
Liquid end
The diaphragm (2) hermetically shuts off the pump volume of the dosing
head (4) towards the outside. The suction valve (1) closes as soon as the
diaphragm (2) is moved in to the dosing head (4) and the feed chemical
flows through the discharge valve (3) out of the dosing head. The dis‐
charge valve (3) closes as soon as the diaphragm (2) is moved in the
opposite direction due to the vacuum pressure in the dosing head and
fresh feed chemical flows through the suction valve (1) into the dosing
head. One cycle is thus completed.
Functional description
21
 Loading...
Loading...