Operation 150821/A4 Page 25 of 110
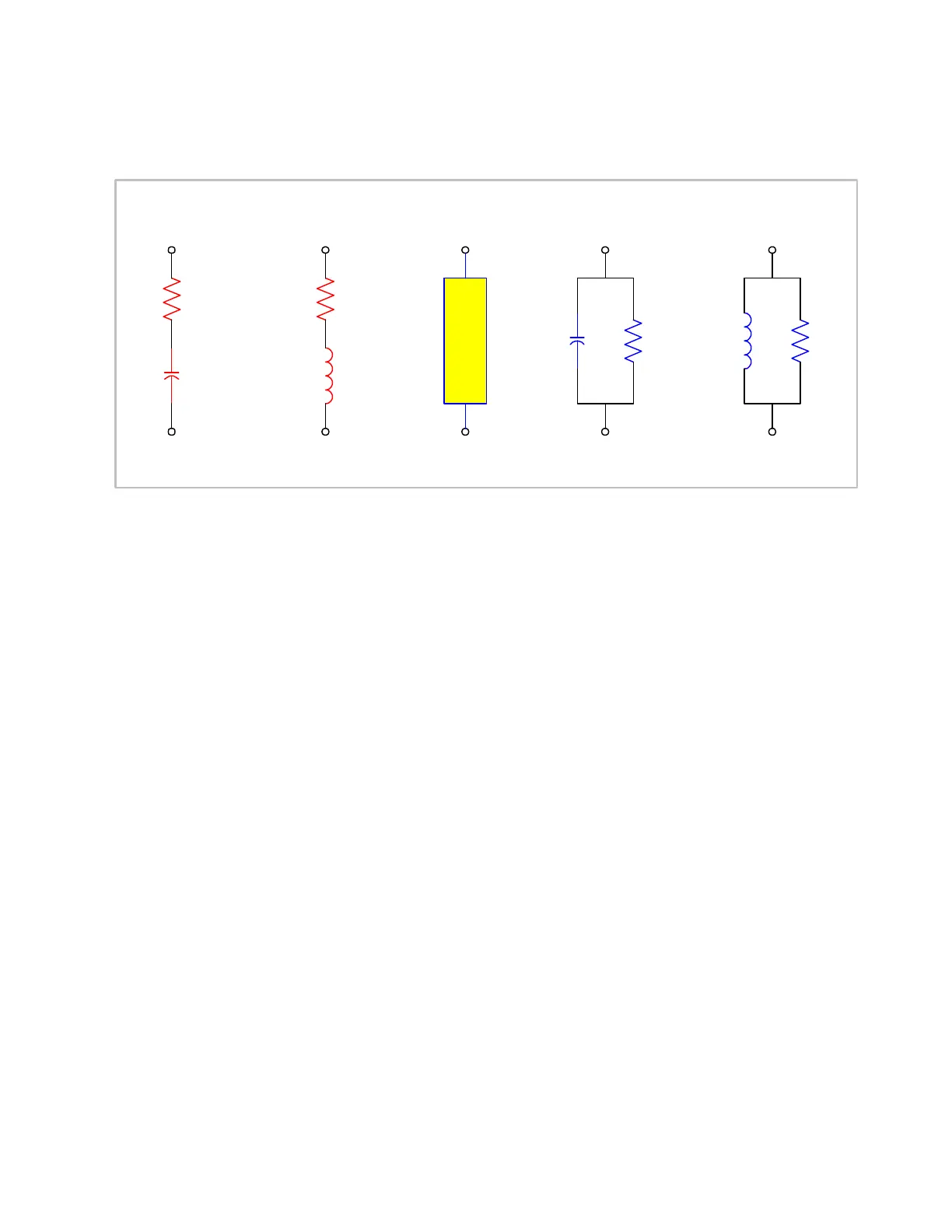
Equivalent Circuit: The configuration of the device under test. Is it a series or parallel
equivalent circuit?
R
S
R
S
R
P
R
P
C
P
L
S
C
S
L
P
IMPEDANCE ADMITTANCE
InductiveCapacitive InductiveCapacitive
G
P
G
P
or or
DUT
Series Parallel
Frequency: The rate at which current or voltage reverses polarity and then
back again completing a full cycle, measured in Hertz (Hz) or
cycles/second. AC Line Frequency = 50/60 Hz.
Ground: The base reference from which voltages are measured, nominally
the same potential as the earth. Ground is also the side of a circuit
that is at the same potential as the base reference.
Impedance: The AC resistance of the DUT. Impedance (Z) is a vector
summation of resistance R and reactance X.
For capacitors reactance is defined as XC = 1/jωC
For inductors reactance is defined as XL = jωL
For resistors resistance is defined as R
Impedance is defined as Z = √(X2 + R2)
Inductor: Abbreviated L (as in LCR). An inductor is a coil of wire. It is used
to create electromagnetic induction in a circuit.
Inductance: The property of a coil to oppose any change in current through it.
If the turns (coils) of the wire are stretched out, the field intensity
will be less and the inductance will be less. Unit of measure is the
Henry (H).
Inductive Reactance: A measure of how much the counter electro-magnetic force (emf)
of the coil will oppose current variation through the coil. The
amount of reactance is directly proportional to the current
variation: X
L
= 2πfL.
 Loading...
Loading...