Page 52 of 110 150821/A4 Operation
Two of the most common methods of sorting results into bins are using nested limits or
sequential limits.
Nested Limits
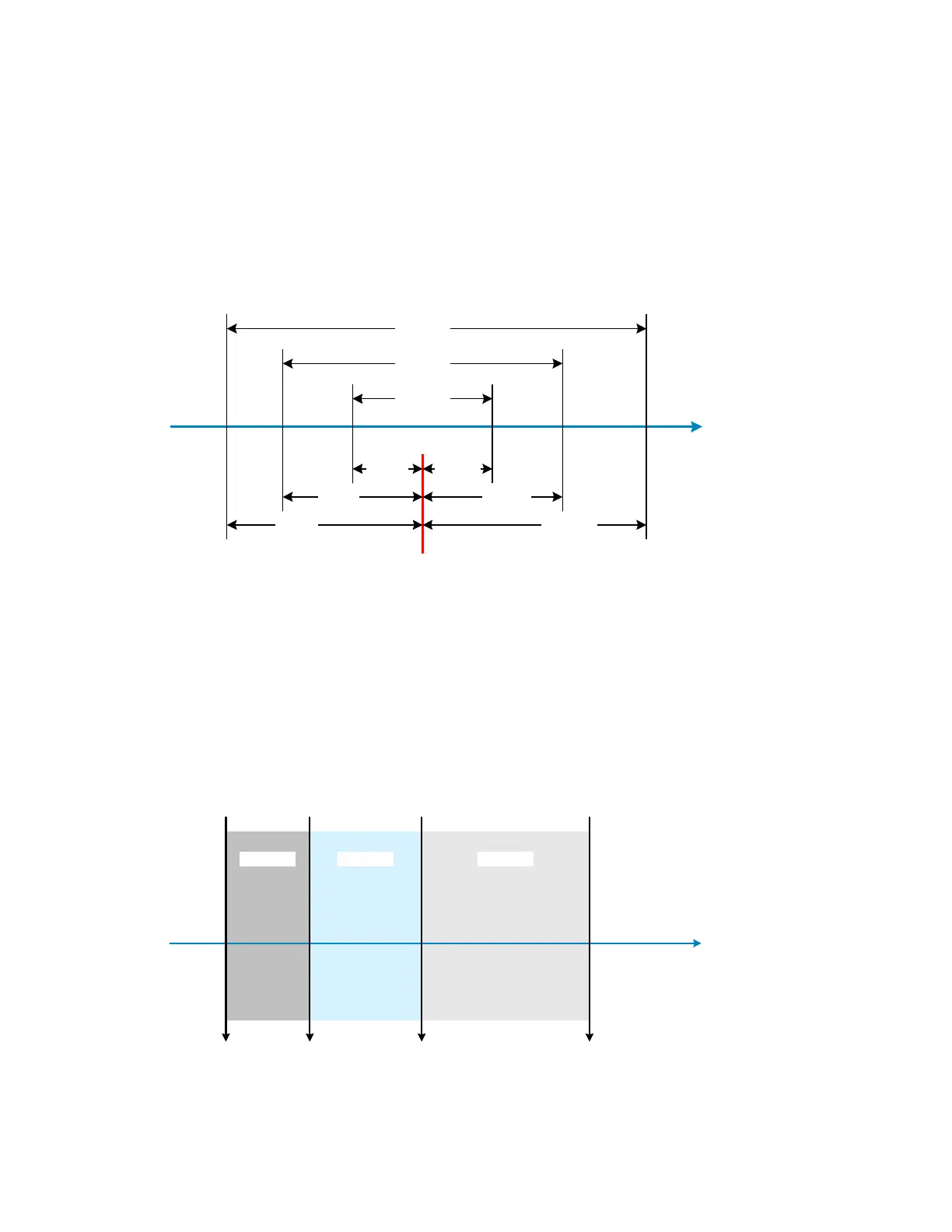
Nested limits are a natural choice for sorting components by % tolerance around a single
nominal value with the lower bins narrower than the higher numbered bins. Nested limits for
three bins are illustrated in Figure 2-5. Note that the limits do not have to by symmetrical (Bin 3
is –7% and +10%).
N
Bin 1
Bin 3
Bin 2
Measured
Value
Nominal Value
100.00k
Ω
-7%
-5%
-1% +1%
+5%
+10%
Figure 2-5: Nested Limits
Sequential Limits
Sequential limits are a natural choice when sorting components by absolute value. Figure 2-6
illustrates the use of sequential limits for a total of three bins. Sequential bins do not have to be
adjacent. Their limits can overlap or have gaps depending upon the specified limit. Any
component that falls into an overlap between bins would be assigned to the lower numbered bin
and any component that falls into a gap between bins would be assigned to the overall fail bin.
Measured
Value
Bin 3Bin 2Bin 1
85k
Ω
100k
Ω
90k
Ω
120k
Ω
Figure 2-6: Sequential Limits
 Loading...
Loading...