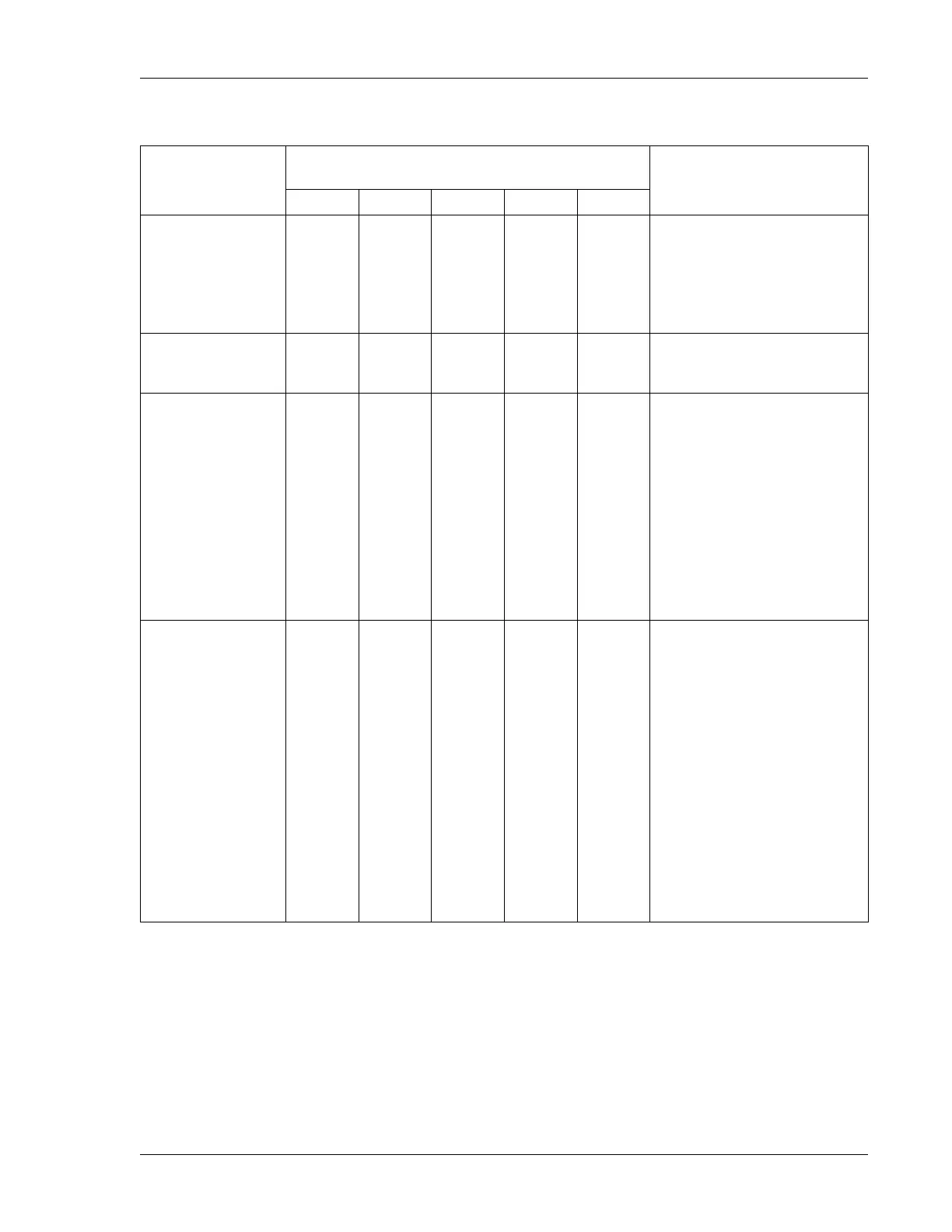
Table 8.1. Scenarios with power readings between 31V and 35V
Current could be in these ranges depending on
the number of connected stations:
(Less than -15%)
It is possible that one or more
stations are not connected
correctly. Try running the test
program (Se
e Section 7.1.2,
“Running the Electrical
Test” [39]).
(-15% - +20%)
Everything is fine - the system
is looking healthy.
(+20% - +50%)
somewhere on the two-wire
causing an excess
consumption.
The Ranger Converter 3000
can handle this, but you could
be looking at problems that
dramatically increase under
wetter conditions. See
8.1.1, “Problems on the
Two-wire” [45].
(More than +50%)
This is a risky situation that can
interfere with the functionality
of the Ranger Converter 3000
and you should locate the
problem in the field right away.
It will typically be a bad
connection or a cable left
open-ended in the field.
Troubleshooting is identical to
when locating short circuits in
the field (see (See Section 8.4,
“When there is a Short Circuit
in the Field”
[50])), but the
current will not be as
as when a short occurs.
8.1.1.
Problems on the Two-wire
It only takes seemingly innocent cracks in the cable insulation or connections to cause big problems: If you
remove the insulation on just 1/3 of an inch on a AWG14 cable (both wires) and immerse the cable in water
the current can increase by 30mA. If you immerse into salt water the current increases by as much as
170mA.

 Loading...
Loading...