AR 2000 Operator's Manual
111
Chapter 9
AR 2000 Interfacial Accessory
Overview
At the interface between two immiscible liquids, or between a liquid and a gas, a two-dimensional phase exists
that has its own rheological properties, distinct from those of the two bulk phases [1]. Several methods of
investigating the rheology of this interfacial phase have been developed [2]. One of these methods is to use a
two-dimensional analogue of the standard concentric cylinder system, with a rotational rheometer [3]. Although
the principles of this method were first described some years ago, it is only recently that commercially available
rotational rheometers have become sufficiently sensitive to allow it to be generally used. TA Instruments has
designed an interfacial accessory for use with the AR 2000 rotational rheometer and Smart Swap
TM
connector,
which operates on these principles.
The interfacial accessory consists of a circular cup with removable lid and a thin, biconical disc geometry
(Figure 1). For chemical inertness, and to reduce the meniscus effect, the cup and lid are constructed from
poly(tetrafluoroethene), PTFE, and the geometry from stainless steel. It is important that the cup and disc are
aligned concentrically, and base with Smart SwapÔ connection into which the cup sits has been designed to
ensure this. Normally, the cup should be exactly half filled with the more dense sample fluid, and filled to the
top with the less dense fluid. The disc is placed at the interface of the two fluids. A mark has been lightly
inscribed on the inside of the cup to indicate when it is half full.
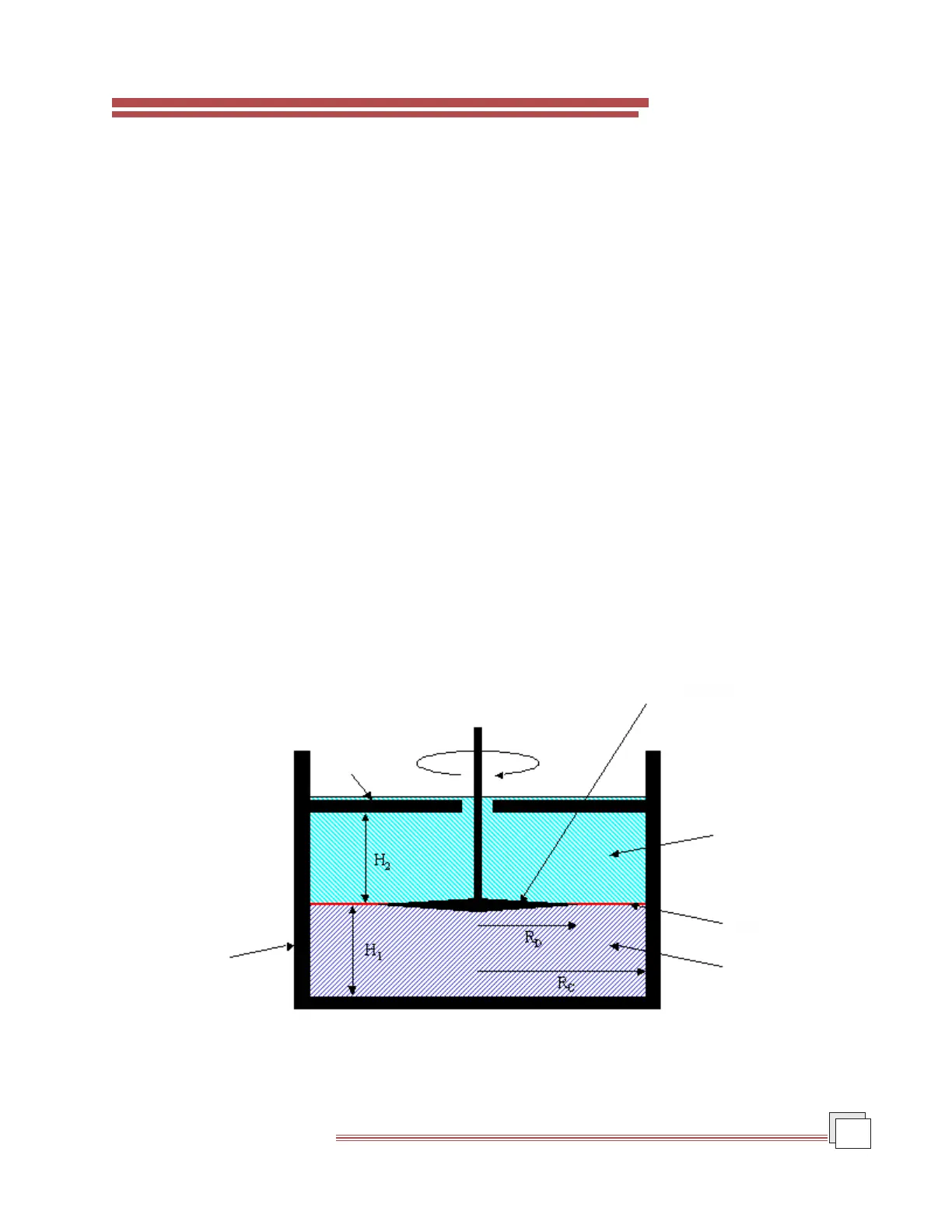
Figure 9.1 below shows a schematic of TA Instruments Interfacial Rheology Accessory. Liquid A is the more
dense fluid, Liquid B the less dense fluid, R
D
is the disc radius, R
C
is the cup inner radius, H
1
is the lower fluid
depth, and H
2
is the upper fluid depth. For correct operation H
1
should equal H
2
.
Figure 9.1
Interfacial Accessory Schematic
Cup
Lid
Biconical
Geometry
Liquid B
Interface
Liquid A

 Loading...
Loading...