14
8303460000 Rev A IA672-04-01-Rev. I
4.4. IP Addresses
The simplest and most reliable way to open a network connection is with the power
supply’s IP address. This is a group of four numbers separated by periods (for example:
10.1.15.123). This IP address may be viewed from its front panel (see section 5.1).
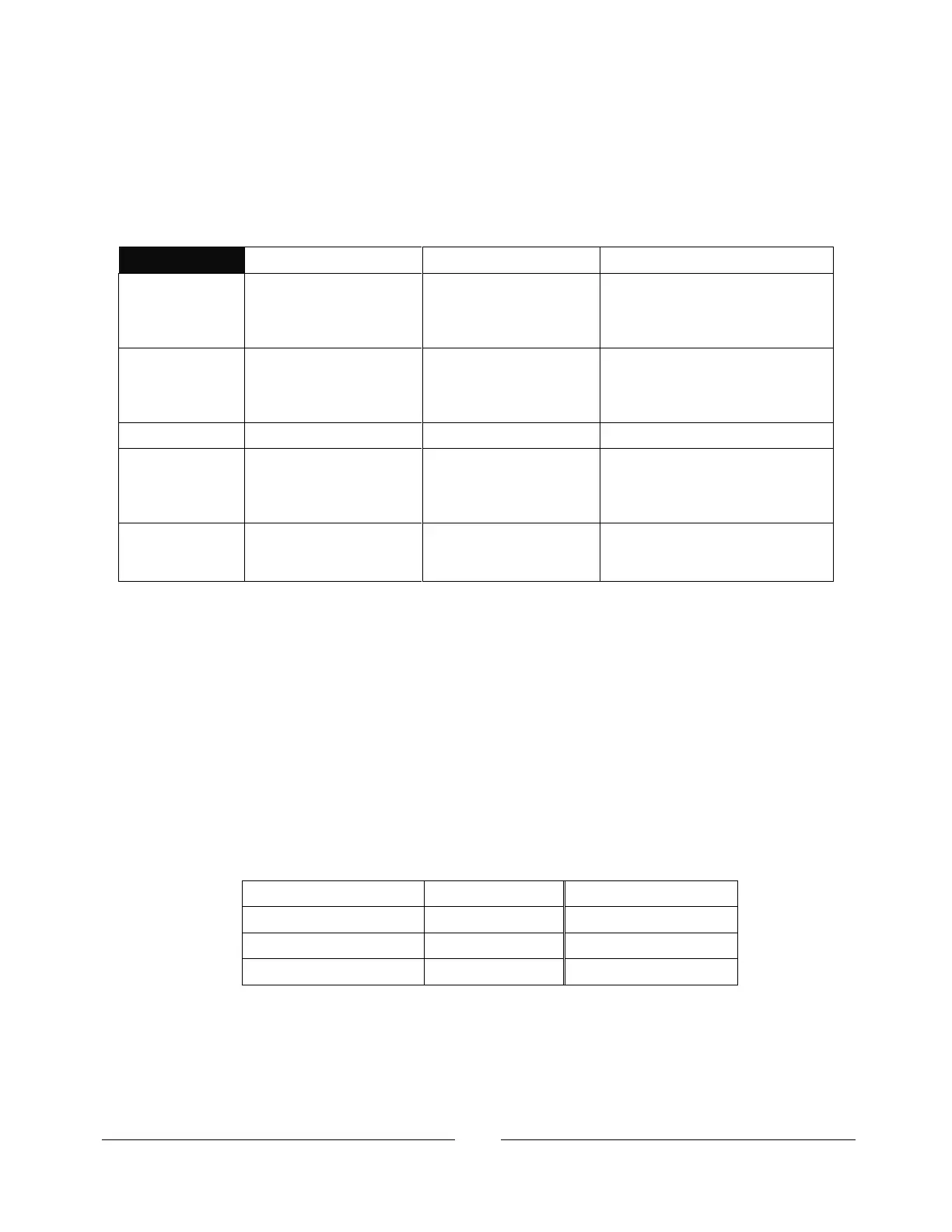
There are three modes which the power supply can get an IP address, as show in this
table:
Note: Static IP numbers (octets) may not be set to zero when setting from the front panel,
but they may be set to zero when using the web page.
4.5. Hostnames
The hostname is a way to address the supply using a name instead of an IP address.
The power supply’s hostname can be seen on its web Home page. Using the hostname
requires a network with naming service such as NetBIOS or DNS.
The factory default hostname is in the format:
< Product > < Voltage or Current rating > – < last 3 digits of serial number >
The default hostname will use the larger number from the voltage or current rating and then
append a V or A. The last three digits of the serial number will skip over any letters.
Example factory default hostnames:
DHCP is default after
“LAN Reset”
Default after “LAN Reset”
if no DHCP server is
used
May be set in the “LAN Modify”
web page (see 6.6.2) or by setting
the IP-4 address on the front
panel (see note below and 5.2)
Assigned by the network
server
Assigned by the power
supply
Assigned in the “LAN Modify” web
page (see 6.6.2) or by setting the
IP-4 address on the front panel
(see 5.2)
Address may change as
the DHCP server assigns
addresses dynamically to
many instruments
Fixed for the power
supply, except if an
address collision is
detected
Always fixed for the power supply
The DHCP server should
prevent duplicate IP
addresses
Finds another available
auto-IP address
Disconnect from the network and
the LAN Status LED stays red
 Loading...
Loading...











