Maintenance-2445A/2455A Service
Troubleshooting Charts
The
troubleshooting charts contained
in
the "Diagrams·
section are to
be
used
as
an
aid
in
locating malfunctioning
circuitry. To
use
the charts,
begin
with the Preliminary
Tests flowchart. This chart
will
help identify problem areas
and
will
direct
you
to other appropriate charts for further
troubleshooting.
Some
malfunctions, especially those involving multiple
simultaneous failures, may require more elaborate trouble-
shooting approaches with references to circuit descriptions
in
the "Theory of Operation" section of this
manual.
Component Color Coding
Information regarding color codes
and
markings of
resistors
and
capacitors
is
located
on
the color-coding
illustration
(Figure
9-1)
at
the
beginning of the "Diagrams"
section.
RESISTOR
COLOR
CODE.
Resistors
used
in
this
instrument are carbon-film, composition, or precision
metal-film types.
They
are usually color
coded
with the
EIA
color code; however, some metal-film type resistors
may
have the value printed
on
the body.
The
color code
is
interpreted starting with the stripe nearest to
one
end
of
the resistor. Composition resistors
have
four stripes;
these represent two significant digits, a multiplier,
and
a
tolerance
value.
Metal-film resistors have five stripes
representing three significant digits, a multiplier,
and
a
tolerance
value.
CAPACITOR MARKINGS. Capacitance values of
common disc capacitors
and
small electrolytics
are
marked
on
the side of the capacitor body. White ceramic
capacitors are color coded
in
picofarads, using a modified
EIA
code.
Dipped
tantalum capacitors are color coded
in
microfarads. The
cdor
dot indicates both the positive
lead
and
the voltage rating.
Since
these capacitors
are
easily
destroyed by reversed or excessive voltage,
be
careful to
observe the polarity
and
voltage rating when replacing
them.
DIODE
COLOR
CODE.
The
cathode
end
of
each
glass-
encased diode
is
indicated by either a stripe, a series
of
stripes or a dot.
For
most diodes marked with a series of
stripes, the color combination of the stripes identifies three
digits of the Tektronix Part
Number,
using the resistor
color-code system.
The
cathode
and
anode
ends
of a
metal-encased diode may
be
identified
by
the diode symbol
marked
on
its
body.
6-6
Semiconductor Lead Configurations
Figure
9-2
in
the
"Diagrams" section shows
the
lead
configurations for semiconductor devices
used
in
the
instrument. These
lead
configurations
and
case styles are
typical of those
used
at completion of the instrument
design. Vendor changes
and
performance improvement
changes may result
in
changes of
case
styles or lead
configurations. If the device
in
question does not appear to
match the configuration shown
in
Figure 9-2, examine the
associated circuitry or consult a manufacturer's data
sheet.
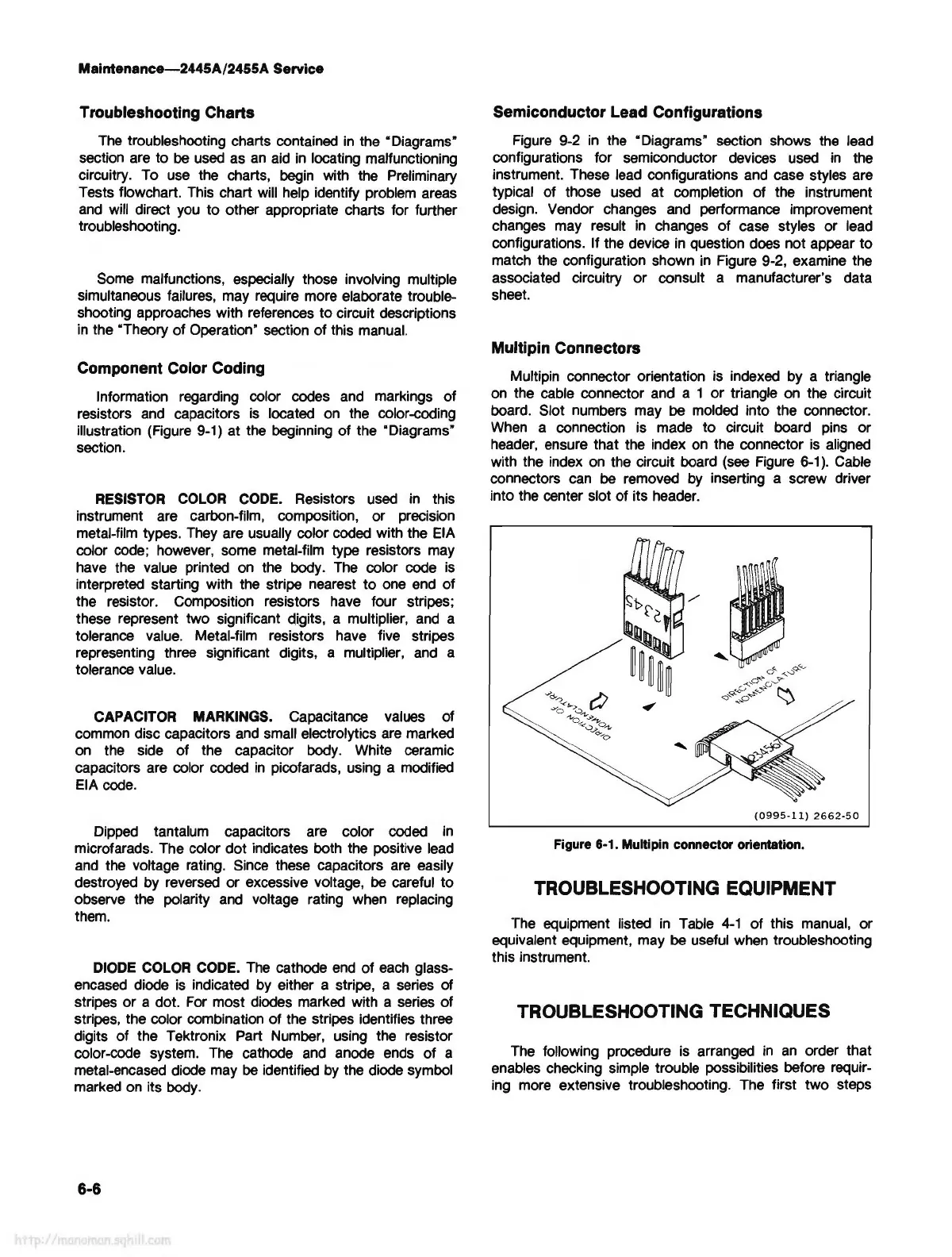
Multipin Connectors
Multipin connector orientation is indexed by a triangle
on
the cable connector and a 1 or triangle
on
the circuit
board. Slot numbers may
be
molded into the connector.
When
a connection is made to circuit board
pins
or
header,
ensure that the index
on
the connector
is
aligned
with the index
on
the circuit board
(see
Figure
6-1
).
Cable
connectors
can
be
removed
by
inserting a screw driver
into the center slot of its header.
(0995-11)
2662-50
Figure 6-1. Multipin connector orientation.
TROUBLESHOOTING EQUIPMENT
The equipment listed
in
Table
4-1
of this
manual,
or
equivalent equipment, may
be
useful
when
troubleshooting
this instrument.
TROUBLESHOOTING TECHNIQUES
The
following procedure is arranged
in
an
order that
enables checking simple trouble possibilities before requir-
ing more extensive troubleshooting. The first two steps
 Loading...
Loading...