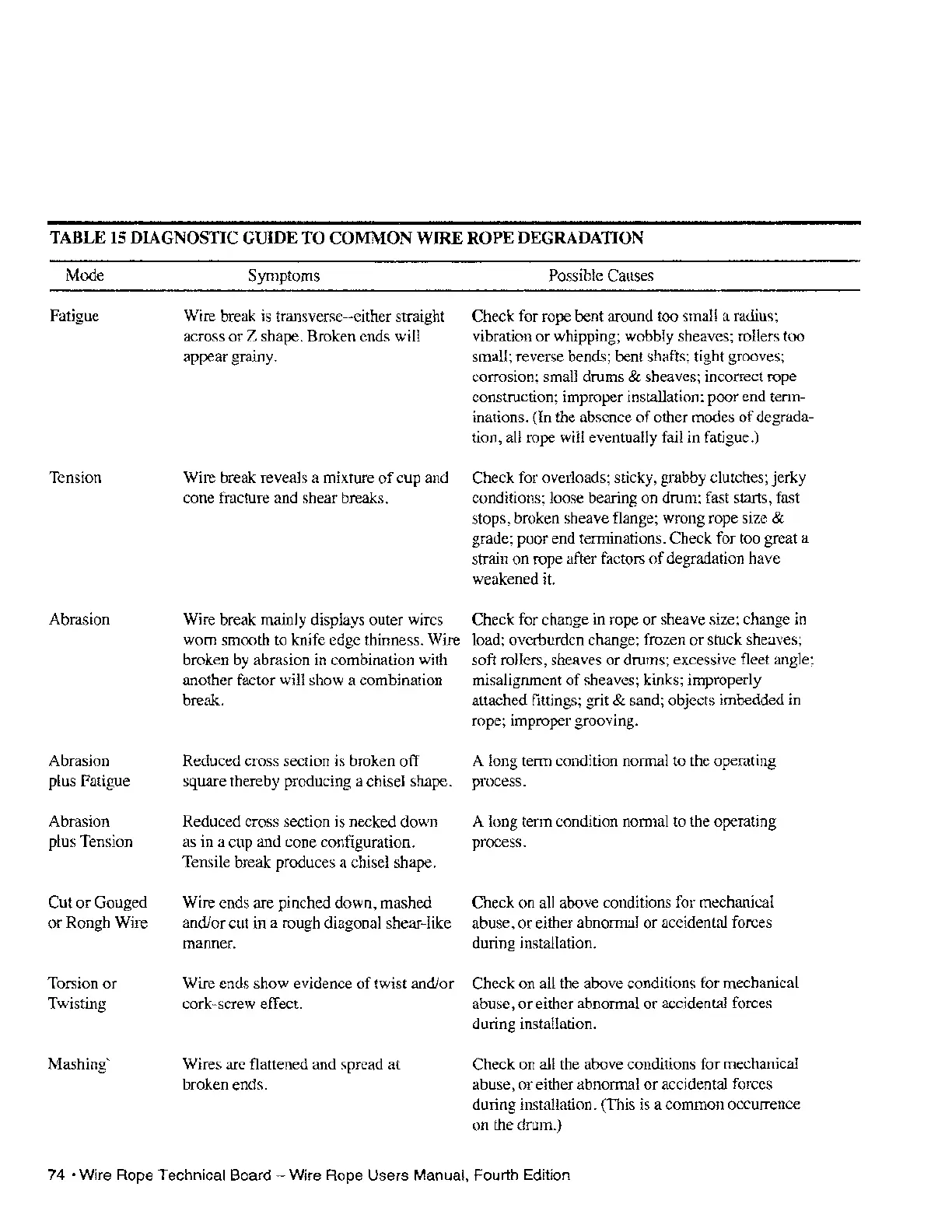
TABLE
15
DIAGNOSTIC
GUIDE
TO
COMMON
WIRE
ROPE
DEGRADATION
Mode
Fatigue
Tension
Abrasion
Abrasion
plus Fatigue
Abrasion
plus Tension
Cut
or
Gouged
or
Rough Wire
Torsion
or
Twisting
Mashing'
Symptoms
Wire break is transverse--either straight
across
or
Z shape. Broken ends will
appear grainy.
Wire break reveals a mixture
of
cup and
cone fracture and shear breaks.
Wire break mainly displays outer wires
worn smooth to knife edge thinness. Wire
broken by abrasion in combination with
another factor will show a combination
break.
Reduced cross section is broken
off
square thereby producing a chisel shape.
Reduced cross section is necked down
as in a cup and cone configuration.
Tensile break produces a chisel shape.
Wire ends are pinched down, mashed
and/or cut in a rough diagonal shear-like
manner.
Possible Causes
Check for rope bent around too small a radius;
vibration
or
whipping; wobbly sheaves; rollers too
small; reverse bends; bent shafts; tight grooves;
corrosion; small drums
& sheaves; incorrect rope
construction; improper installation; poor end term-
inations. (In the absence
of
other modes
of
degrada-
tion, all rope will eventually fail in fatigue.)
Check for overloads; sticky, grabby clutches; jerky
conditions; loose bearing
on
drum; fast starts, fast
stops, broken sheave flange; wrong rope size
&
grade; poor end terminations. Check for too great a
strain
on
rope after factors
of
degradation have
weakened
it.
Check for change in rope
or
sheave size; change in
load; overburden change; frozen
or
stuck sheaves;
soft rollers, sheaves
or
drums; excessive fleet angle;
misalignment
of
sheaves; kinks; improperly
attached fittings; grit
& sand; objects imbedded in
rope; improper grooving.
A long term condition normal to the operating
process.
A long term condition normal to the operating
process.
Check on all above conditions for mechanical
abuse,
or
either abnormal
or
accidental forces
during installation.
Wire ends show evidence
of
twist and/or Check
on
all the above conditions for mechanical
cork -screw effect.
Wires are flattened and spread at
broken ends.
abuse,
or
either abnormal
or
accidental forces
during installation.
Check on all the above conditions for mechanical
abuse, or either abnormal
or
accidental forces
during installation. (This is a common occurrence
on
the drum.)
74 • Wire Rope Technical Board - Wire Rope Users Manual, Fourth Edition
 Loading...
Loading...