1
Introduction
Scan Modes
10 TSQ Quantum XLS Series User Guide Thermo Scientific
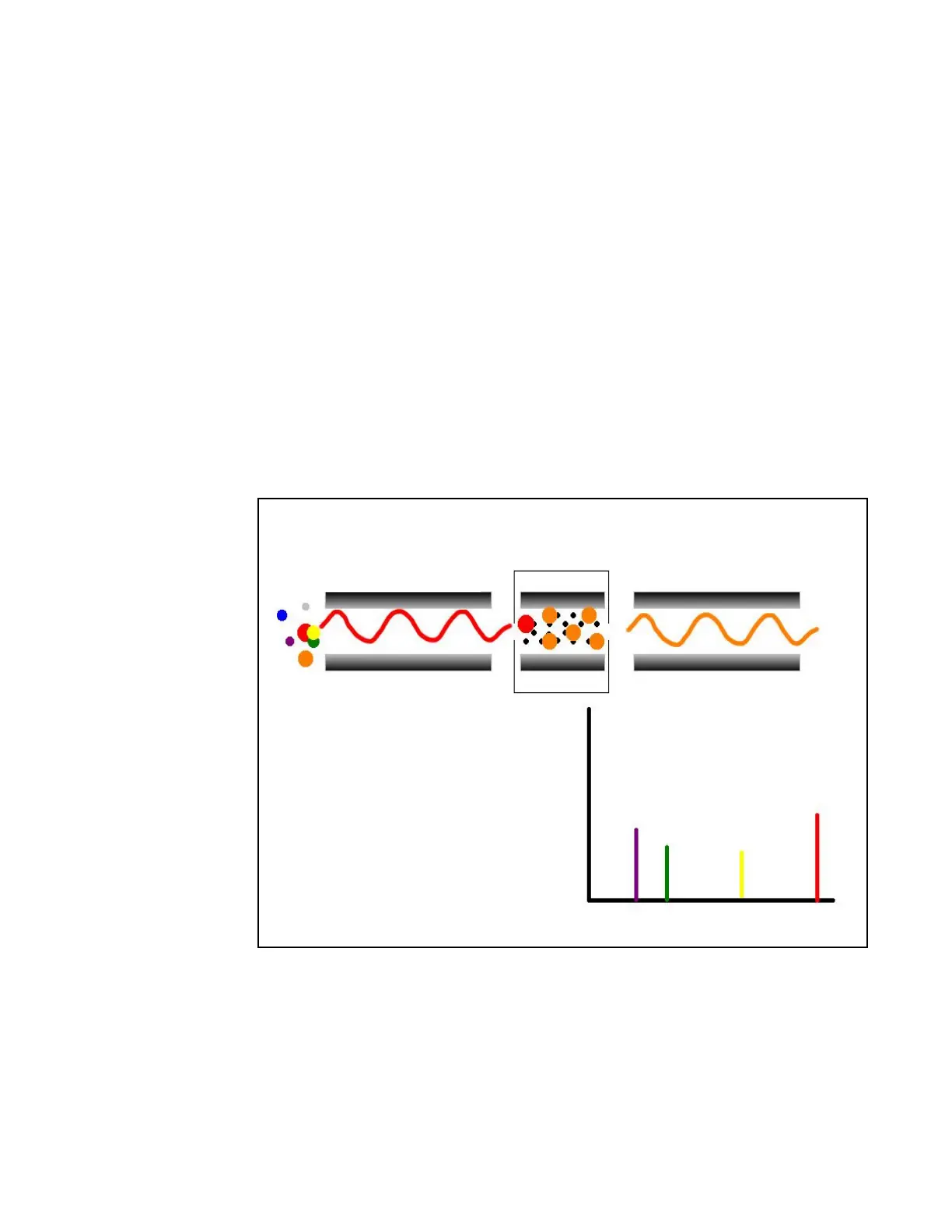
To detect an ion, between the time the ion leaves Q1 and enters Q3, it must lose a neutral
moiety whose mass (the neutral loss mass) is equal to the difference in the mass ranges that the
two mass analyzers scan. A neutral loss mass spectrum, then, is a spectrum showing all the
parent ions that lose a neutral species of a selected mass.
Note that you can also perform a neutral gain (or association) experiment in which the mass
range scanned by Q3 is offset by a selected mass above the mass range scanned by Q1.
For a neutral loss (or neutral gain) mass spectrum, as for a parent mass spectrum, data for the
mass-to-charge ratio axis is obtained from Q1 (the parent ion), whereas data for the ion
intensity axis is obtained from Q3 (the product ion being monitored).
You can perform experiments that use the Neutral Loss scan mode (neutral loss experiments)
when a large number of compounds are being surveyed for common functionality. Neutral
moieties are frequently lost from substituent functional groups (for example, CO
2
from
carboxylic acids, CO from aldehydes, HX from halides, and H
2
O from alcohols).
Figure 5. Illustration of the Neutral Loss scan mode
Q1
m/z

 Loading...
Loading...











