MSTP
MSTP divides a network into several MST regions. The CST is generated between these MST
regions, and multiple spanning trees can be generated in each MST region. Each spanning tress
is called an instance. As well as STP, MSTP uses BPDUs to generate spanning tree. The only
difference is that the BPDU for MSTP carry the MSTP configuration information on the switches.
Port States
In an MSTP, ports can be in the following four states:
Forwarding: In this status the port can receive/forward data, receive/send BPDU packets as
well as learn MAC address.
Learning: In this status the port can receive/send BPDU packets and learn MAC address.
Blocking: In this status the port can only receive BPDU packets.
Disconnected: In this status the port is not participating in the STP.
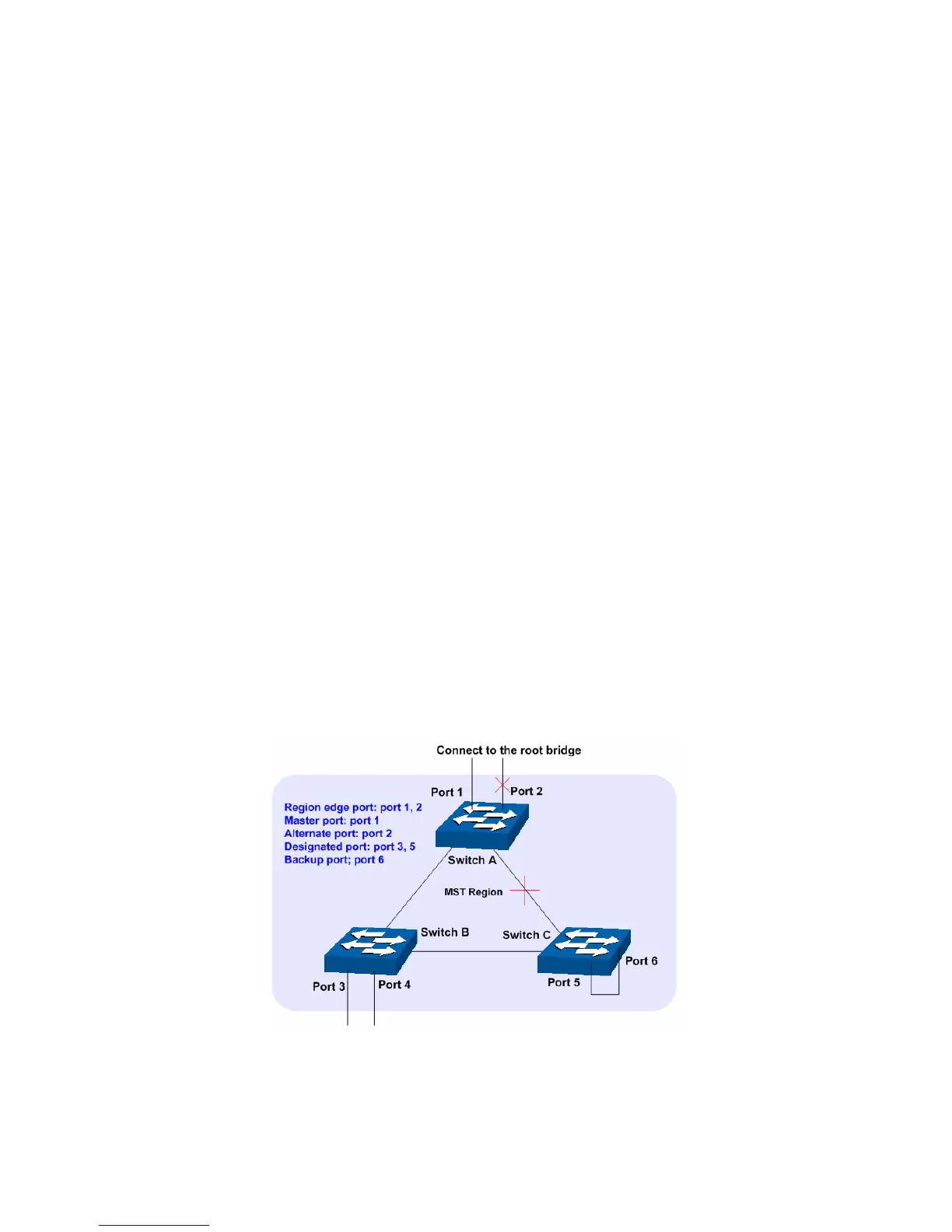
Port Roles
In an MSTP, the following roles exist:
Root Port: Indicates the port that has the lowest path cost from this bridge to the Root
Bridge and forwards packets to the root.
Designated Port: Indicates the port that forwards packets to a downstream network
segment or switch.
Master Port: Indicates the port that connects a MST region to the common root. The path
from the master port to the common root is the shortest path between this MST region and
the common root.
Alternate Port: Indicates the port that can be a backup port of a root or master port.
Backup Port: Indicates the port that is the backup port of a designated port.
Disabled: Indicates the port that is not participating in the STP.
The following diagram shows the different port roles.
Figure 7-3 Port roles
The Spanning Tree module is mainly for spanning tree configuration of the switch, including four
submenus: STP Config, Port Config, MSTP Instance and STP Security.
82

 Loading...
Loading...











