Section 4 1MAC309294-MB F
Protection functions
108 RER620
Technical Manual
Self-polarizing as polarizing method
Table 129: Equations for calculating angle difference for self-polarizing method
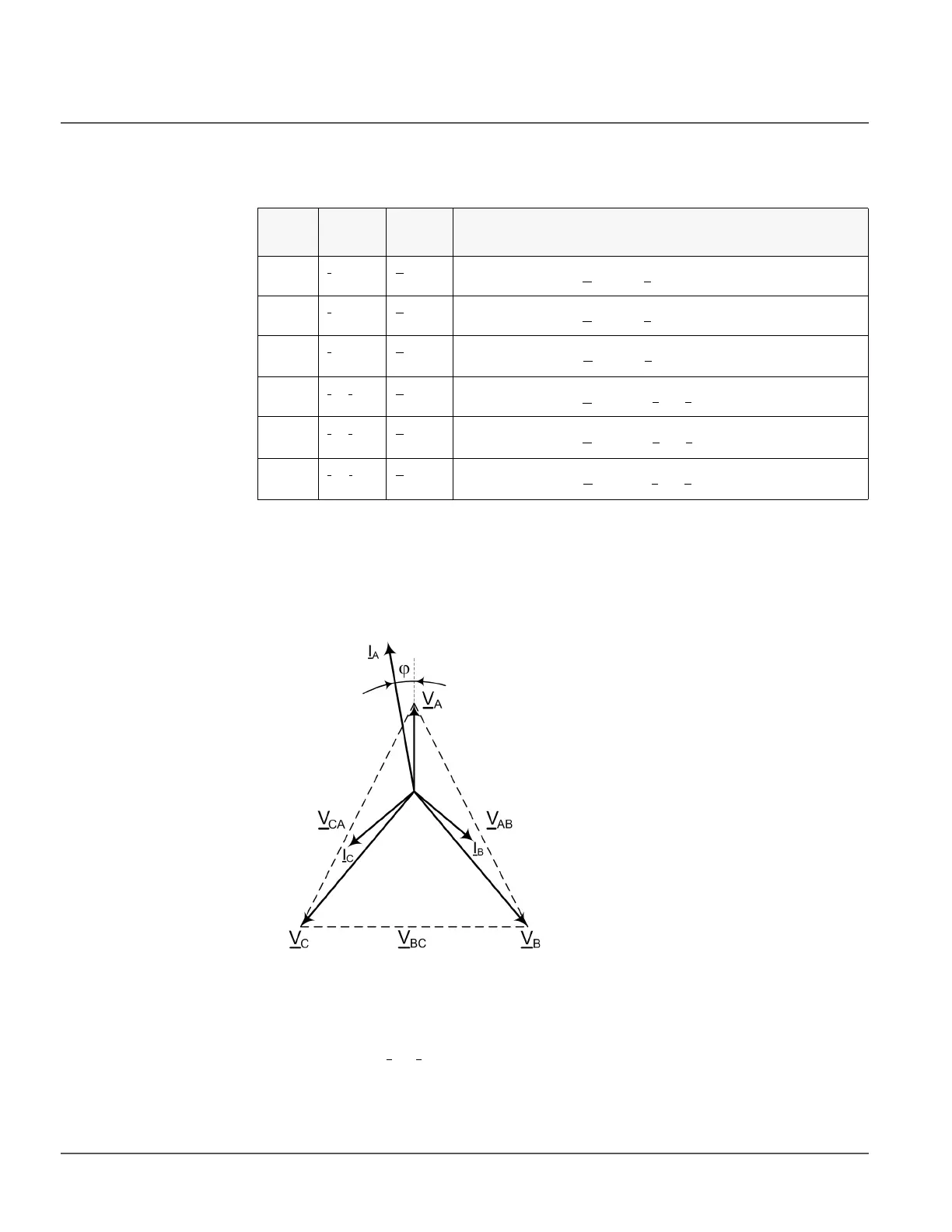
In an example case of the phasors in a single-phase ground fault where the faulted phase
is phase A, the angle difference between the polarizing quantity V
A
and operating quantity
I
A
is marked as φ. In the self-polarization method, there is no need to rotate the polarizing
quantity.
Figure 45: Single-phase ground fault, phase A
In an example case of a two-phase short-circuit failure where the fault is between phases
B and C, the angle difference is measured between the polarizing quantity V
BC
and
operating quantity I
B
- I
C
in the self-polarizing method.
Faulted
phases
Used
fault
current
Used
polarizing
voltage
Angle difference
AI
A
V
A
BI
B
V
B
CI
C
V
C
A - B I
A
- I
B
V
AB
B - C I
B
- I
C
V
BC
C - A I
C
- I
A
V
CA
ANGLE A V I
A
A
RCA
_()-()- =
ANGLE B V I
B
B
RCA
_()-()- =
ANGLE C V I
C
C
RCA
_()-()- =
ANGLE A V I I
AB
AB
RCA
_ ( )- ( - )- =
ANGLE B V I I
BC
BC
RCA
_ ( )- ( - )- =
ANGLE C V I I
CA
CA
RCA
_ ( )- ( - )- =
 Loading...
Loading...











