CHAPTER 3
IPv4 Communication Fundamentals
This chapter describes IPv4 Communication operating principles.
DHCP Versus Manual Network Settings
The following methods can be used to set the network settings:
£ Manually set network settings allow precise control over the network’s configuration. This option may require an in-
depth understanding of arcane networking details – much of which is covered in this guide. See Networking Basics.
£ Use the router’s DHCP setting to automatically connect devices to the network by negotiating the appropriate settings
with the device. This option may not be applicable to all networks; for example, the network administrator does not
want to use DHCP and has supplied information to manually configure the device’s IP interface.
No matter which option is chosen, it will be necessary to coordinate with Information Technology (IT) department person-
nel the use of shared network resources.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a router feature that dynamically allocates configuration parameters
to connected devices such as IP, DNS, and default gateway addresses. Enabling DHCP on a router normally eliminates
the need to manually configure network settings on connected devices. The implementation of DHCP on most routers al-
lows a device to be assigned a fixed IP address by associating a specific IP address to a device’s MAC address.
Devices that use ECLYPSE’s internal router with the DHCP option (Hotspot/AP mode) cannot be assigned fixed IP addresses
according to the device’s MAC address.
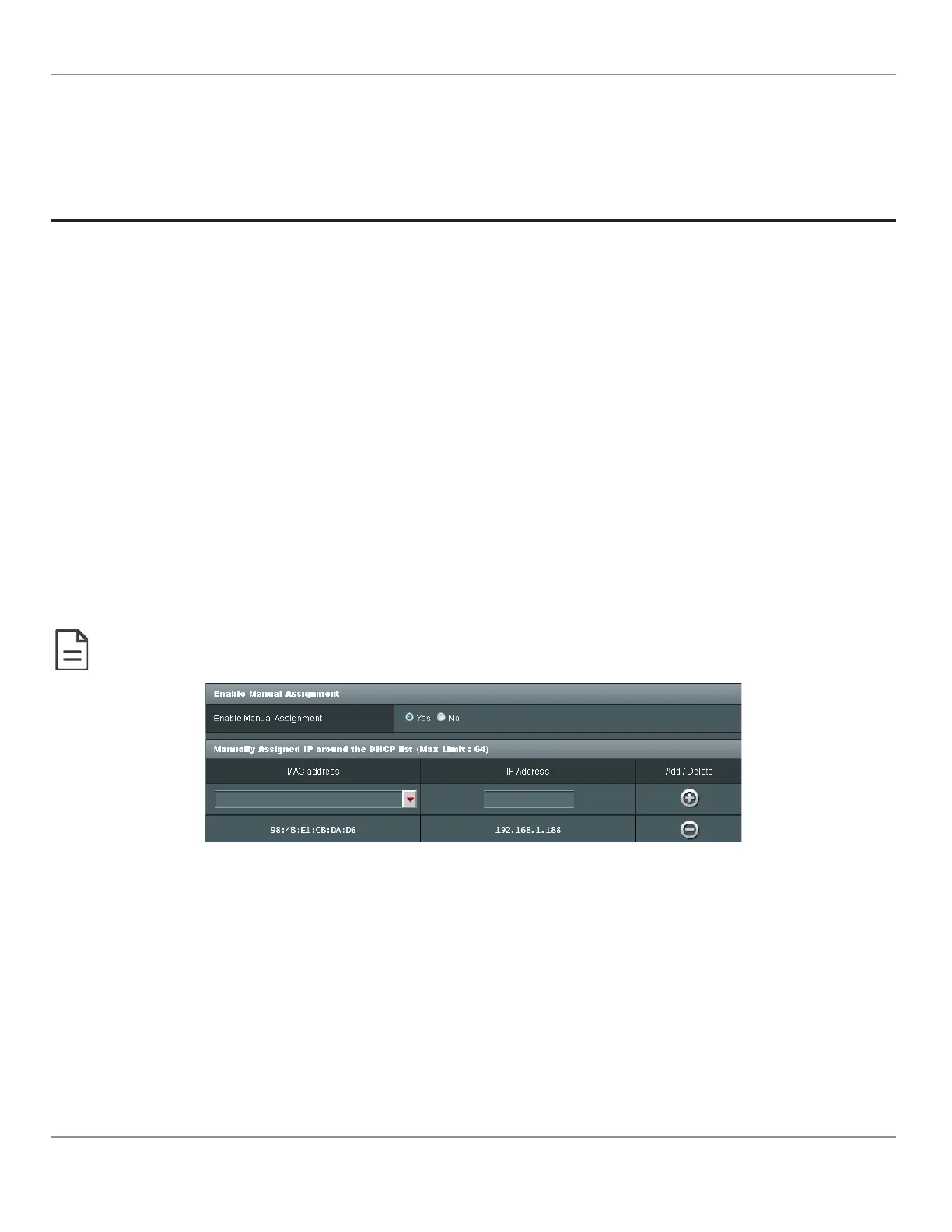
Figure1: Typical Router Configuration to Assign a Device’s MAC Address to a Fixed IP Address
If your router supports DHCP and you have access to the router’s configuration interface, this is the most straight-forward
way to configure your network. Ensure that all devices that require a fixed IP address use a manually assigned IP address.
Fixed IP Address or Hostname Management
Why Should ECLYPSE IP controllers use a fixed IP address or use hostname Management? To program or to access an
IP controller, you must be able to connect to it. Like a postal address, a fixed IP address that is always assigned to the
same device allows you to consistently connect to and work with the same device.
An alternative to using a fixed IP address is to use the controller’s Hostname Management which allows a controller to be
identified by a nickname such as
Office_205
instead of the controller’s IP address. The hostname can be used in a Web
browser.
IPv4 Communication Fundamentals
13
nLight ECLYPSE

 Loading...
Loading...