RADIUS Server Architectures
Local Credential Authentication
Each device has its own credential database in the local credential authentication architecture. This approach is labor-in-
tensive as multiple credential database instances must be maintained.
User
Server
A
ECLYPSE
Controller B
C
ECLYPSE
Controller A
B
Key:
Credential Database
Login Credential
1 2 3
4 4
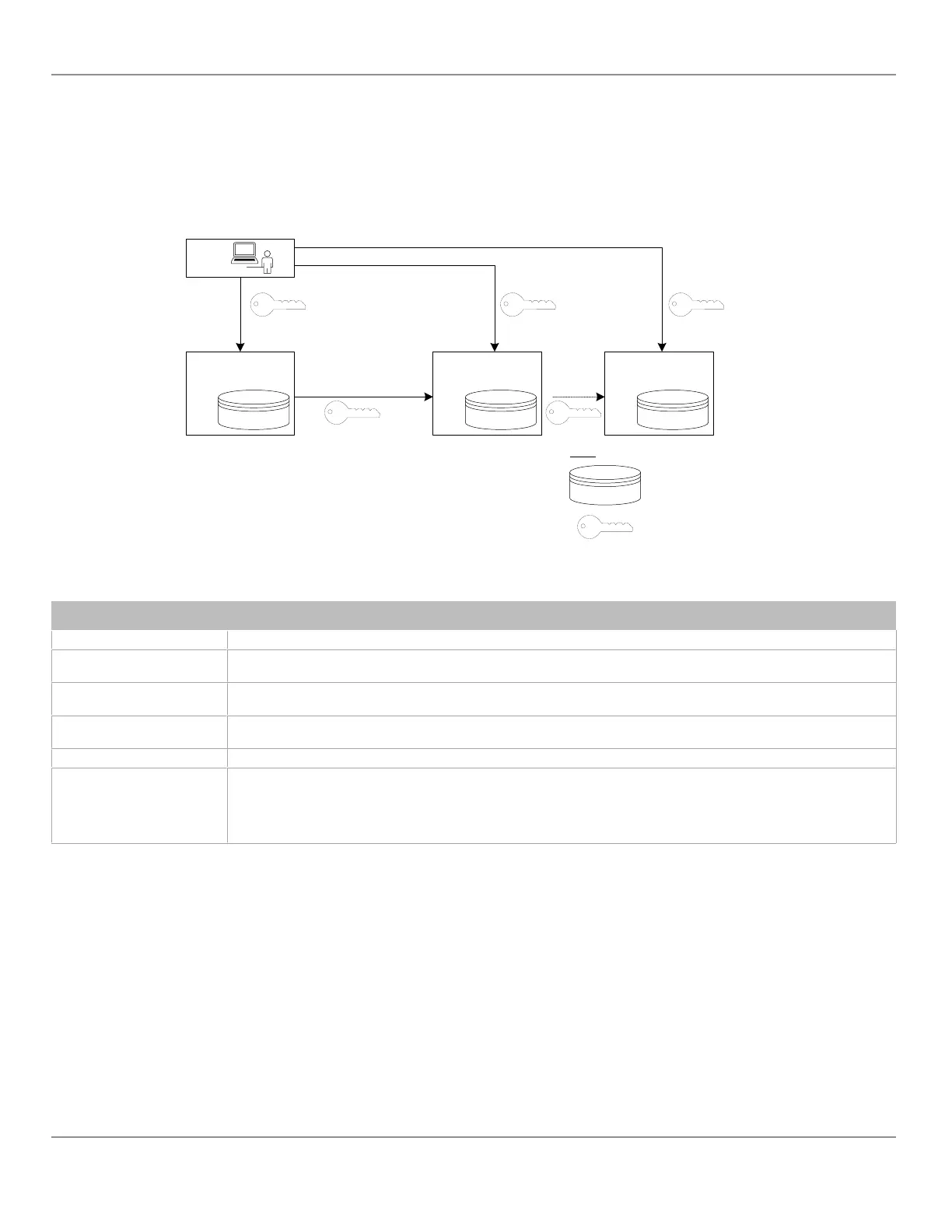
Figure29: Local Credential Authentication
This authentication method has the following components.
Component Description
Login Credential 1 This is the login credential used by a user to connect to the Server station. This credential is managed by the Server.
Login Credential 2
This is the login credential used by a user to connect to ECLYPSE controller A. This credential is managed in
controller’s A User Management credential database.
Login Credential 3
This is the login credential used by a user to connect to ECLYPSE controller B. This credential is managed in
controller’s B User Management credential database.
Login Credential 4
This is the login credential used by the Server’s Rest Service to connect to ECLYPSE controller A and B. This credential
is managed in this controller’s A and B User Management credential databases.
Credential Database A This is the Server’s user credential database.
Credential Database B and C
This is the ECLYPSE controller A’s credential database and ECLYPSE controller B’s credential database. If the User
can to connect to either of these controllers through the Server, the controller’s credential database must have the
credentials for the Server’s RestService. Each credential database must also have the credentials for each user that will
log in to ECLYPSE controller A (for example, administrators, direct connection by users, ENVYSION users, etc.). See
User Management.
Supported RADIUS Server Architectures
39
nLight ECLYPSE
 Loading...
Loading...