AMT-70/AMT-73/AMT-75 Installation and Operation
The calculated uncoded size is thus reduced to the nearest multiple of 8.
8
8
)32)((
int ×
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
−××
=
zYX
bits
UUU
U
In 2D cases, U
z
is 1. The code rate is then determined as the ratio of the two values:
E
U
CodeRate =
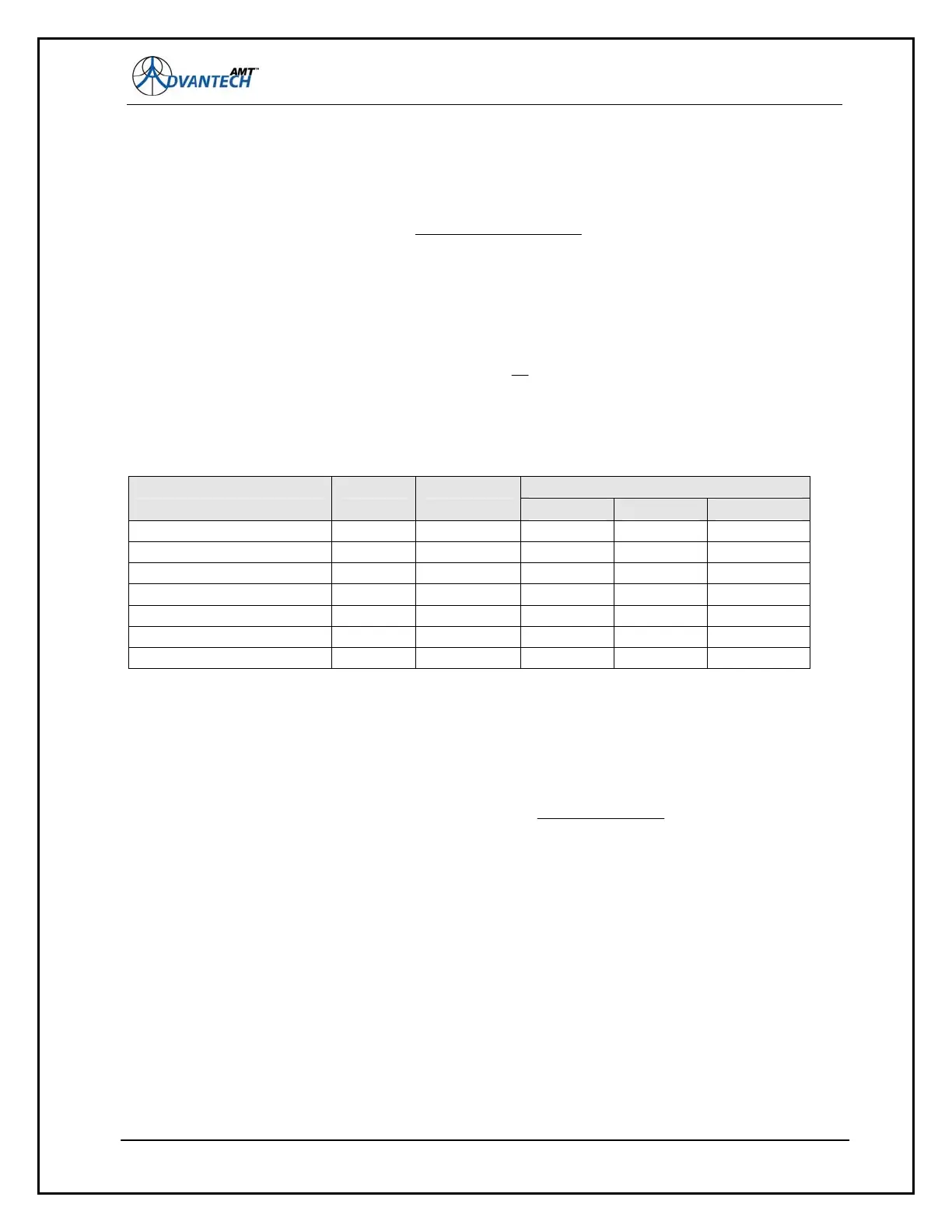
For each of the supported code, the rates are:
Eb/No (10 Mbps data rate & 10
-7
BER) Code Rate TPC Code
QPSK 8PSK 16QAM
eH(32, 26) eH(32,26) eH(16,11) 2.4 dB 0.44815891 TPC16K-2/5
eH(64, 57) eH(64, 57) P(4,3) 0.58817829 TPC16K-3/5 2.9 dB 5.8
eH(64, 57) eH(64, 56) 0.76550388 TPC4K-3/4 3.9 dB 7.0 7.9
eH(128, 120) eH(128, 119) 0.86288760 TPC16K-8/9 4.2 dB 7.3 8.3
eH(128, 120) P(128, 126) 0.91375969 TPC16K-19/20 5.1 dB 8.6 9.6
0.75 TPC-4k 3.9 dB 7.0 7.9
7.3 0.875 TPC-16k 4.2 dB 8.3
Figure 58: eTPC Code Rates and Eb/No Values
The code rate can then be used to calculate the transmitted symbol rate from the input bit rate (and
visa versa):
ssymbols
sbits
symbolbits
BaudRate
BitRate
ModulationCodeRate
/
/
/
=×
The ratio of the raw data (base-band) bit rate and the transmitted symbol rate is the product of the
code rate and the modulation order in bits/symbol: BPSK has order 1; QPSK and Offset QPSK have
order 2; 8PSK has order 3 and 16QAM order 4.
119
 Loading...
Loading...