34 Troubleshooting
3 Chromatographic Symptoms
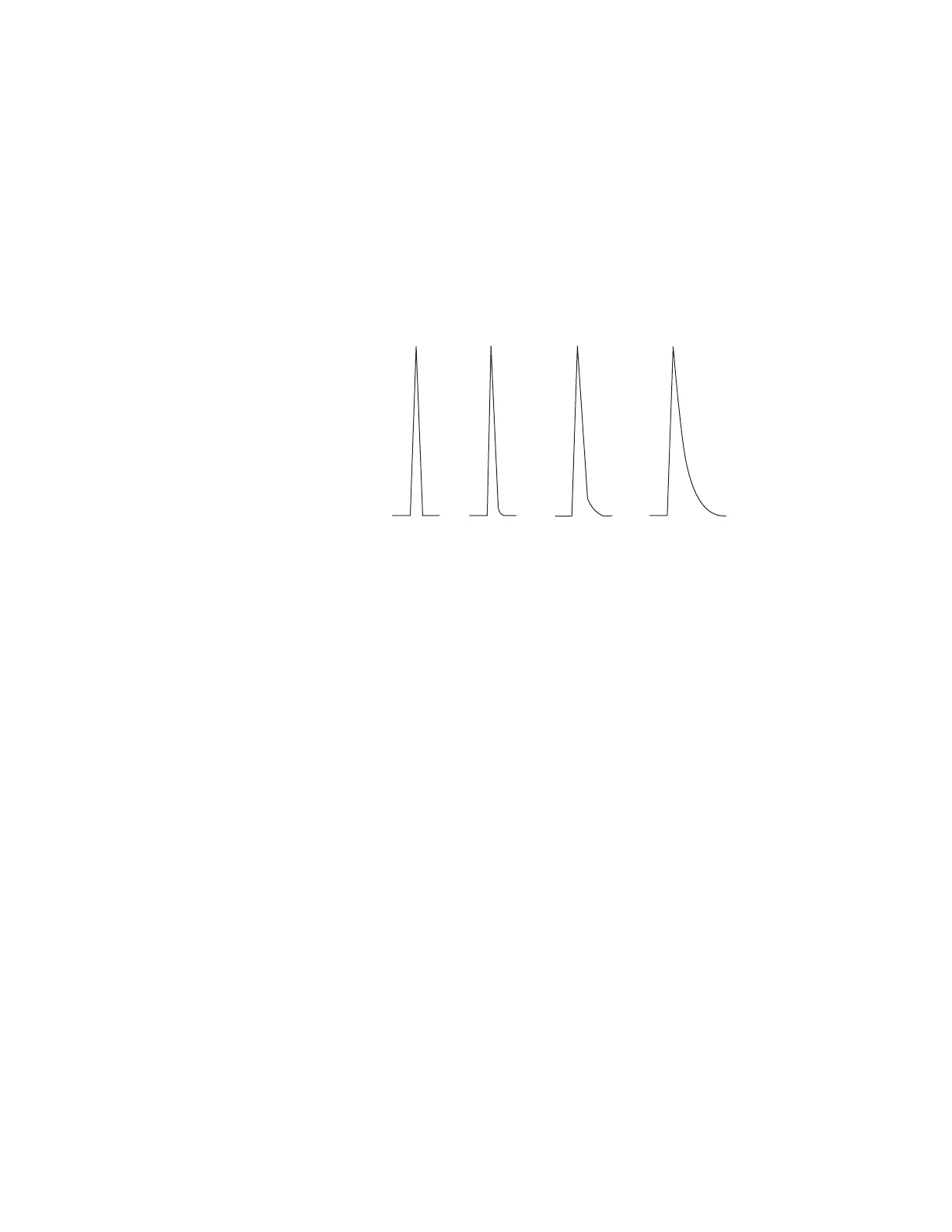
Peak Tailing
The figure below shows an example of tailing peaks. When
troubleshooting tailing peaks, consider:
• Which peaks are tailing?
• Are the tailing peaks active compounds, all compounds, or
are there trends (such as early eluters or late eluters)?
• Check the column for severe contamination.
• Consider the column stationary phase (active column).
• Verify that the column was cut and installed properly.
• Consider the type of adapter, liner, and inlet seal being
used. One or all of these may be contaminated or active.
• Check adapters (if installed) and liner for solid particles.
• For capillary splitless injection, consider compatibility
between the solvent and column.
• Verify that the injection technique is adequate.
• Verify the inlet temperature.
• Check for dead volume in the system. Check for correct
column installation at both ends.
• Inspect any transfer lines for cold spots.
NPD
For NPD, do the following:
• Verify that you are using the correct bead for the sample
being run. If you are analyzing phosphorus, install a black
bead. White beads can cause peak tailing when
phosphorus is being analyzed.
• Verify that the correct jet is installed. Use an extended
jet.
• Replace the ceramic insulators.

 Loading...
Loading...











