Network Synchronization
Page 224 7750 SR OS Basic System Configuration Guide
Network Synchronization
This section describes network synchronization capabilities available on SR and ESS product
platforms. These capabilities involve multiple approaches to network timing; namely SDH/
SONET, Synchronous Ethernet, and Adaptive clocking.. These features address barriers to entry
by:
• Providing synchronization quality required by the mobile space; such as radio operations
and circuit emulation services (CES) transport.
• Augmenting and potentially replacing the existing (SONET/SDH) timing infrastructure
and delivering high quality network timing for time sensitive applications in the wireline
space.
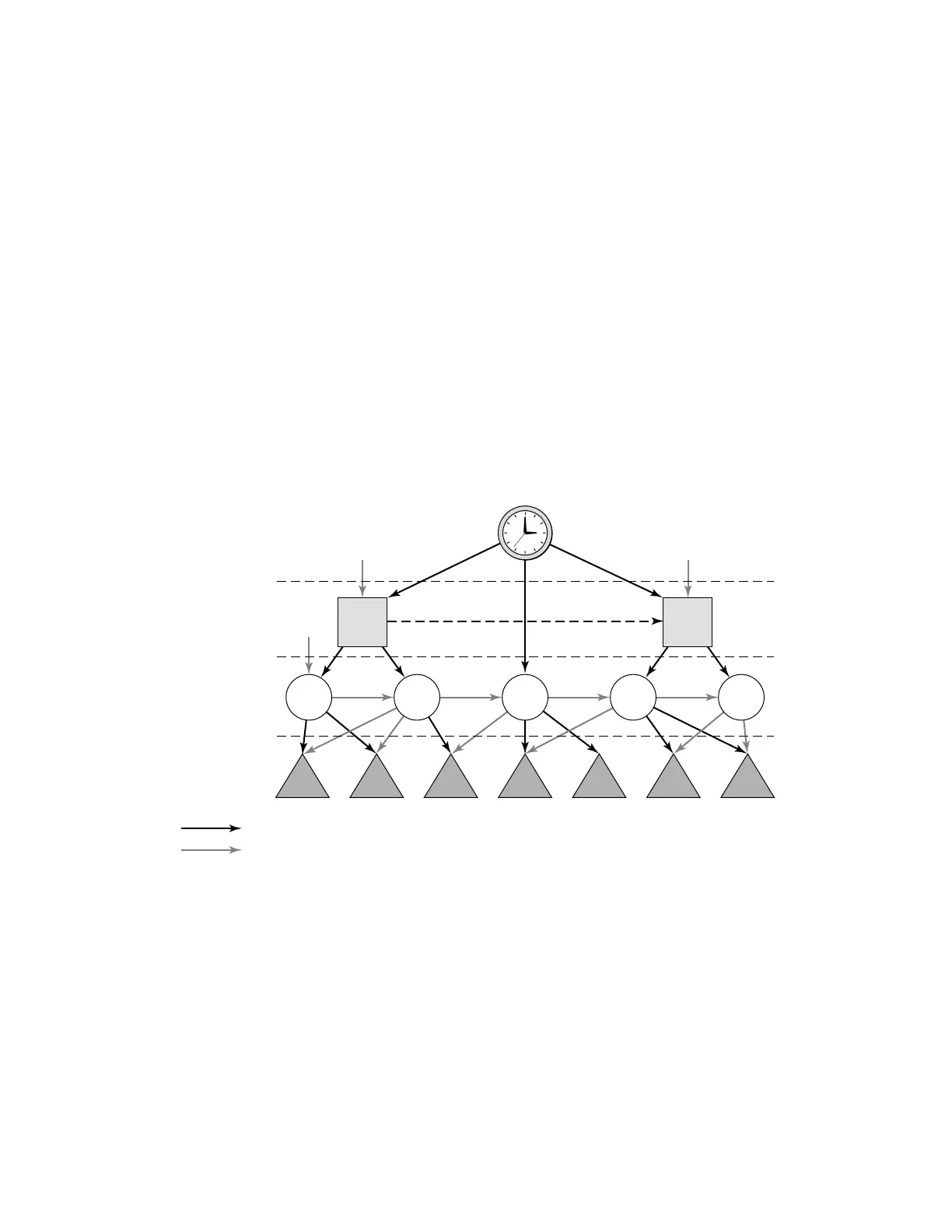
Network synchronization is commonly distributed in a hierarchical master-slave topology at the
physical layer as shown in Figure 9.
Figure 9: Conventional Network Timing Architecture (North American Nomenclature)
The architecture shown in Figure 9 provides the following benefits:
• Limits the need for high quality clocks at each network element and only requires that
they reliably replicate input to remain traceable to its reference.
• Uses reliable physical media to provide transport of the timing signal; it doesn't consume
any bandwidth and requires limited additional processing.
OSSG287
ST 2
ST 3 ST 3 ST 3 ST 3 ST 3
ST 2
Primary Reference Clock
Stratum 1
Gateway
Class 1 or 2 CO
ST 4 ST 4 ST 4ST 4 ST 4 ST 4 ST 4
Stratum 2
Class 2 or 3
Central Office
Stratum 3
Class 4 or 5
Toll/End Office
Stratum 4
Customer
Prem
Primary Reference
Secondary Reference

 Loading...
Loading...











