Utility Requirements
74 / 120 H157654_9_011
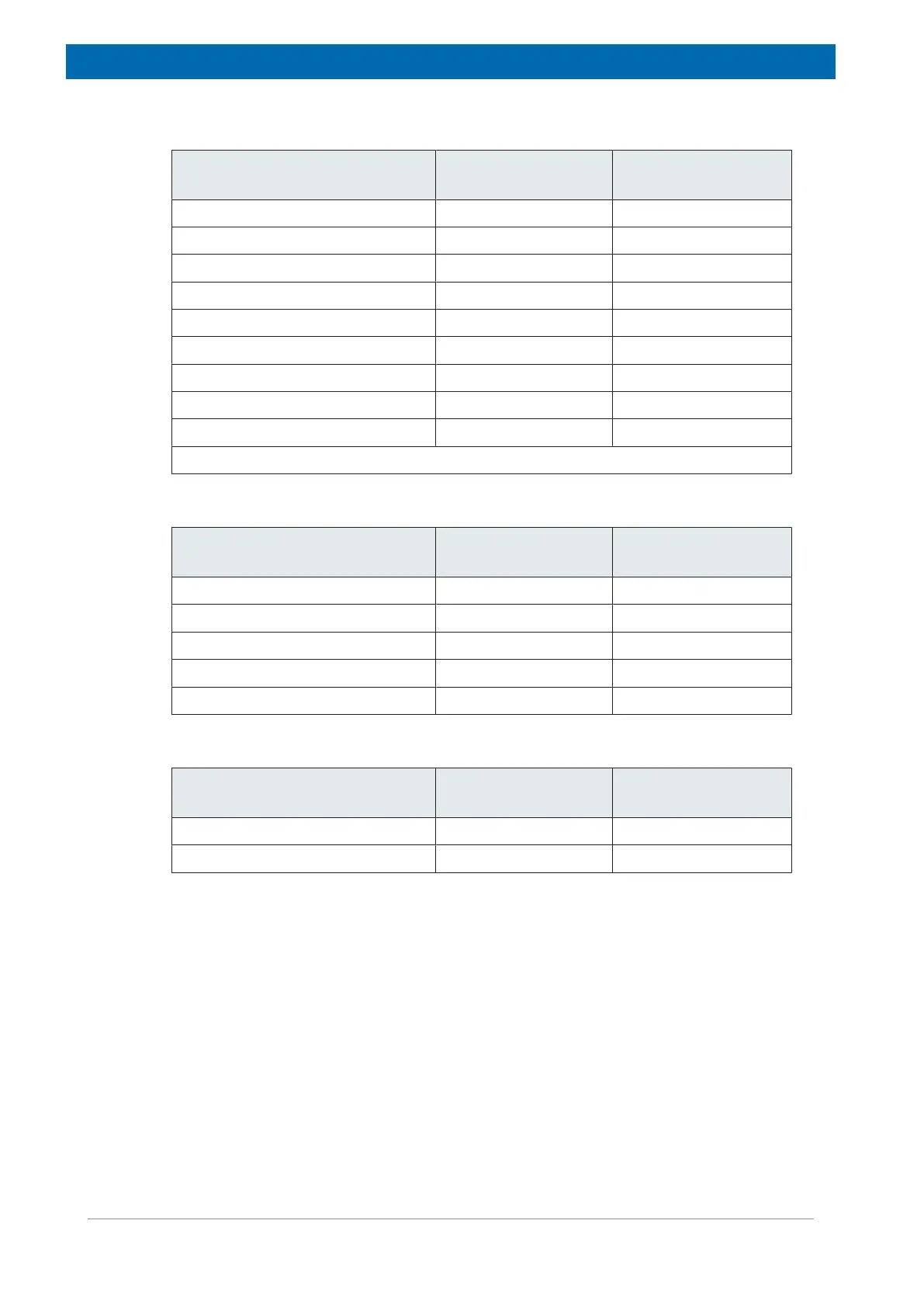
Total Volume of Gas and Maximum Helium Gas Flow
Magnet Type Total Volume of He
Gas (m
3
)
Maximum He Gas
Flow (m
3
/min.)
300/54 Ascend ULH 83.6 41.8
400/54 Ascend 75.5 37.8
400/54 Ascend ULH 101.4 50.7
500/54 Ascend 62.9 31.5
500/54 Ascend ULH 162.8 81.4
600/54 Ascend 65.2 32.6
600/54 Ascend ULH 261.3 130.6
700/54 Ascend 97.7 48.9
800/54 Ascend 244.2 122.1
ULH = Ultra Long Hold.
Table8.6: Total Gas Volume and Maximum He Gas Flow: Standard Bore 54 mm
Magnet Type Total Volume of He
Gas (m
3
)
Maximum He Gas
Flow (m
3
/min.)
300/89 Ascend 99.9 50.0
400/89 Ascend 75.5 37.8
500/89 Ascend 75.5 37.8
600/89 Ascend 96.2 48.1
700/89 Ascend 153.0 76.3
Table8.7: Total Gas Volume and Maximum He Gas Flow: Wide Bore 89 mm
Magnet Type Total Volume of He
Gas (m
3
)
Maximum He Gas
Flow (m
3
/min.)
200/154 Ascend 40.4 20.2
300/154 Ascend 74.8 37.4
Table8.8: Total Gas Volume and Maximum He Gas Flow: Super Wide Bore 154 mm
Regarding the emergency gas exhaust, important considerations include, but are not limited
to, the following:
• Amount of liquid helium: Taking the 700/89 Ascend magnet as an example, the total
amount of liquid helium is 218 liters. In case of a quench, the liquid transforms into gas
and expands by a factor of 740. Therefore, the total amount of helium evaporated gas in
case of a quench will be ca. 76.3 m
3
(2,695 ft
3
).
• Maximum helium gas flow: The maximum flow of helium gas is calculated on the as-
sumption that half of the volume of liquid evaporates in 1 minute, thus the maximum flow
would be 175 m
3
(6,180 ft
3
) for the 750 WB US
2
magnet. The gas should be removed
from the room immediately through an emergency exhaust system.

 Loading...
Loading...










