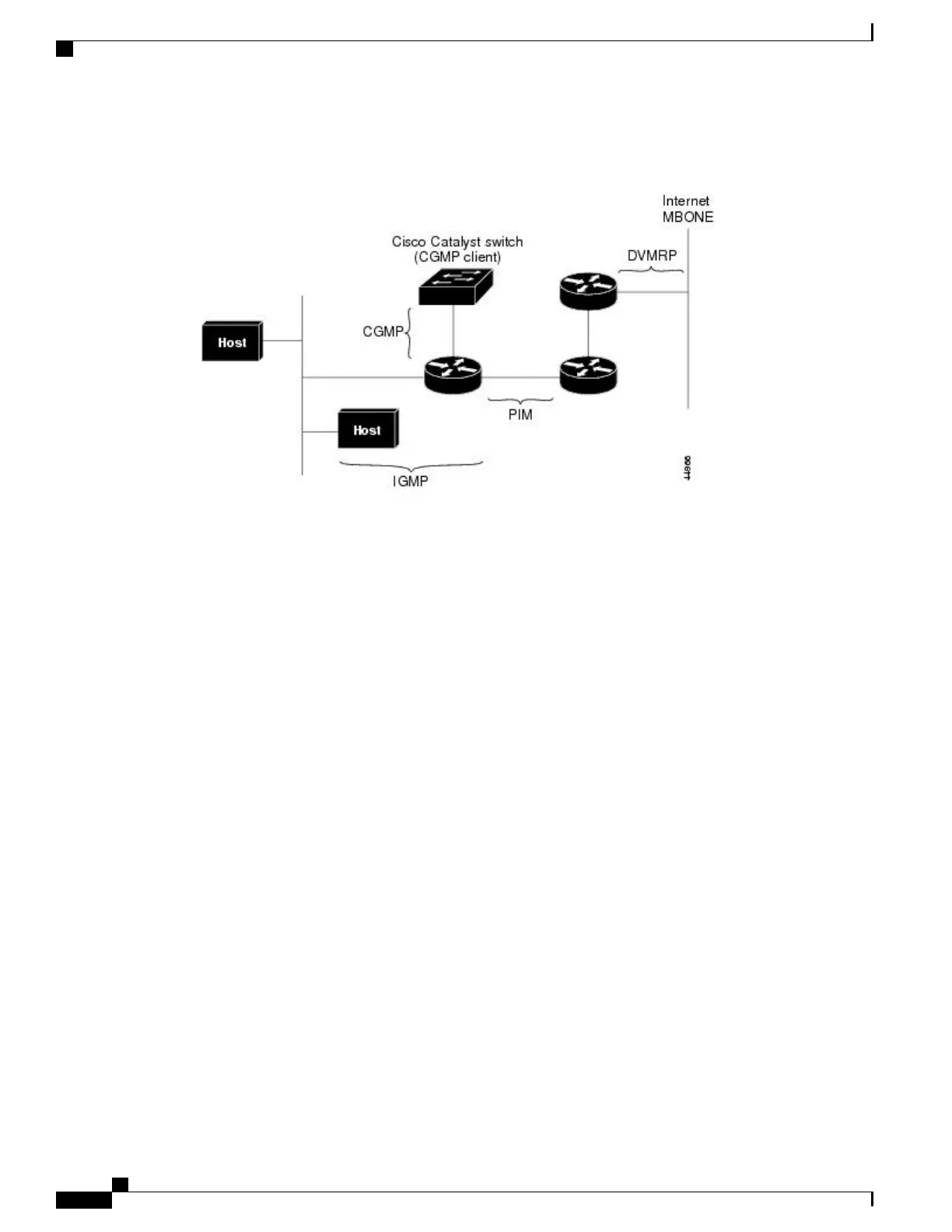
The following figure shows where these protocols operate within the IP multicast environment.
Figure 1: IP Multicast Routing Protocols
According to IPv4 multicast standards, the MAC destination multicast address begins with 0100:5e and is
appended by the last 23 bits of the IP address. For example, if the IP destination address is 239.1.1.39, the
MAC destination address is 0100:5e01:0127.
A multicast packet is unmatched when the destination IPv4 address does not match the destination MAC
address. The switch forwards the unmatched packet in hardware based on the MAC address table. If the
destination MAC address is not in the MAC address table, the switch floods the packet to the all port in the
same VLAN as the receiving port.
Information About IGMP
To participate in IP multicasting, multicast hosts, routers, and multilayer switches must have the Internet
Group Management Protocol (IGMP) operating. This protocol defines the querier and host roles:
•
A querier is a network device that sends query messages to discover which network devices are members
of a given multicast group.
•
A host is a receiver that sends report messages (in response to query messages) to inform a querier of a
host membership.
A set of queriers and hosts that receive multicast data streams from the same source is called a multicast group.
Queriers and hosts use IGMP messages to join and leave multicast groups.
Any host, regardless of whether it is a member of a group, can send to a group. However, only the members
of a group receive the message. Membership in a multicast group is dynamic; hosts can join and leave at any
time. There is no restriction on the location or number of members in a multicast group. A host can be a
member of more than one multicast group at a time. How active a multicast group is and what members it has
can vary from group to group and from time to time. A multicast group can be active for a long time, or it can
be very short-lived. Membership in a group can constantly change. A group that has members can have no
activity.
Catalyst 2960-XR Switch IP Multicast Routing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2)EX1
14 OL-29426-01
Understanding Cisco's Implementation of IP Multicast Routing
Information About IGMP
 Loading...
Loading...











