100 Epsilon EP-P Drive Reference Manual
www.controltechniques.com Revision: A4
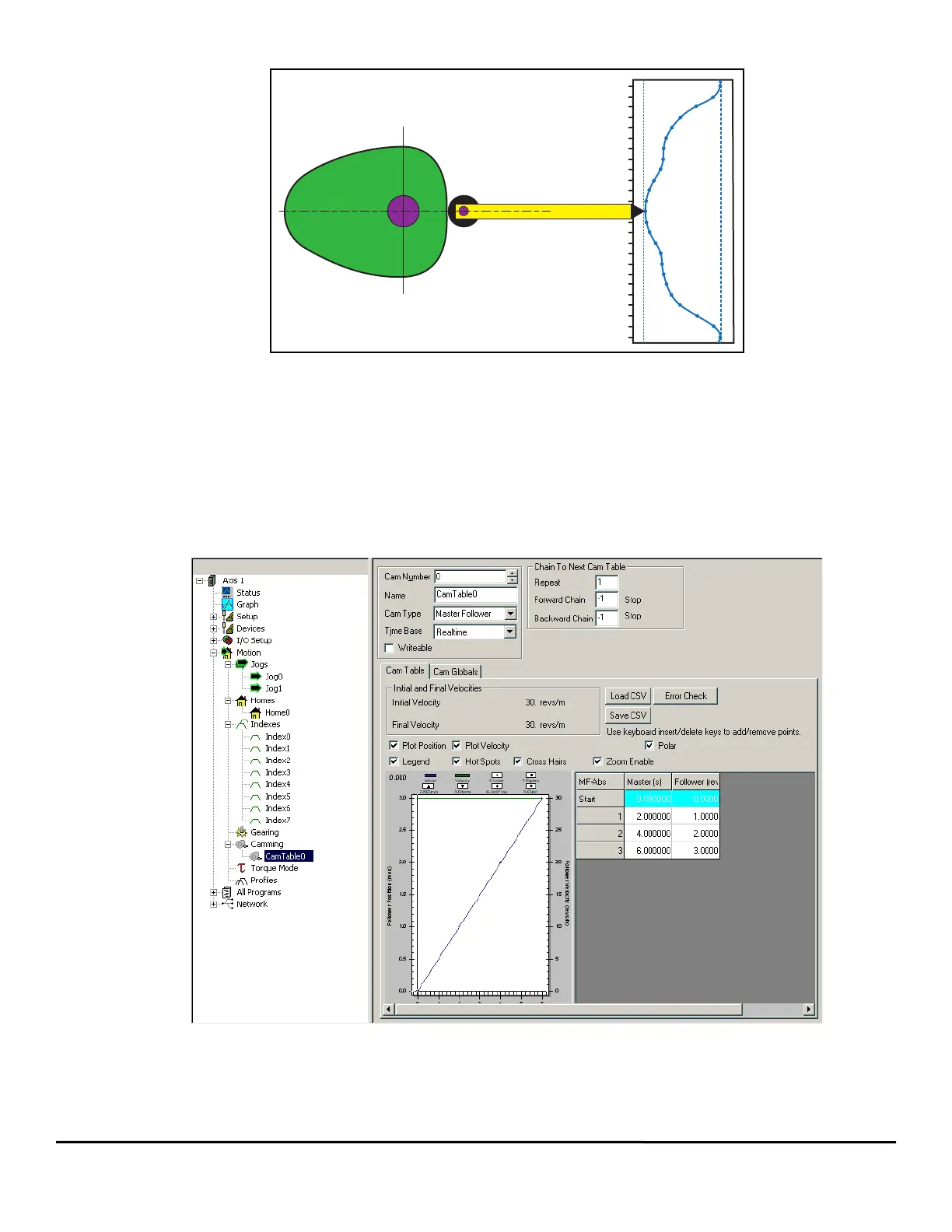
Figure 112: Mechanical Master and Slave Follower
As the master axis (the cam lobe) rotates, the follower axis produces a non-linear motion profile. This same profile can then be produced with
a single motor driving a linear axis programmed with an electronic cam.
The cam motion object uses a master/follower principal in a synchronized mode and also has a follower with Realtime mode that allows the
follower to travel through its cam table without a physical master axis moving.
Control Techniques provides a Cam as a collection of cam table(s) that can be used individually of chained together to form a full sequence of
motion. Each cam table is a user specific sequence of movements whereby the user can specify the master and follower movement along with
the interpolation type. Coupled with a user program to monitor the flow, the motion can dynamically be altered by changing the cam table
chains selecting a different sequence of tables. You can further adjust the flow by dynamically changing the cam tables themselves or using a
cam table time base index to adjust time or distance.
As an alternative, the cam is initiated in the same manor as jogs, home and indexes.
Figure 113: Camming View
Cam Number
Use the arrows of the spin box to increment or decrement the Cam Number and view the setup information for that Cam number. A maximum
of 32 different cam tables can be created.
180
135
90
45
315
270
225
180
0
MASTER
AXIS
FOLLOWER AXIS
(SLAVE)
 Loading...
Loading...