4 Epsilon EP-P Drive Reference Manual
www.controltechniques.com Revision: A4
zero, index 1 may run on profile one.
Please note that Indexes and Jogs can be run simultaneously by using the two Profiles, however, Gearing or Camming can only run on one
profile at a time. This means that two indexes or two jogs can run at the same time, but gearing or camming can not be run on multiple profiles
simultaneously.
The Positive direction parameter affects all motion types by specifying which direction of motor revolution (CW or CCW) is considered motion
in the “+” direction.
2.4 How Jogging Works
Jogging produces rotation of the motor at controlled velocities in a positive or negative direction.
Assignments to jogs are level sensitive such that when the jog input is turned on, jogging begins and continues jogging until the jog input is
removed.
Each jog has its own acceleration and deceleration ramp along with a specified velocity. Jogging has no distance parameter associated with it.
If trying to move a specific distance or to a known position, then an index is used.
Jog velocity can be changed on the fly with a negative value reversing the direction. The velocity transition will use the deceleration or
acceleration parameters.
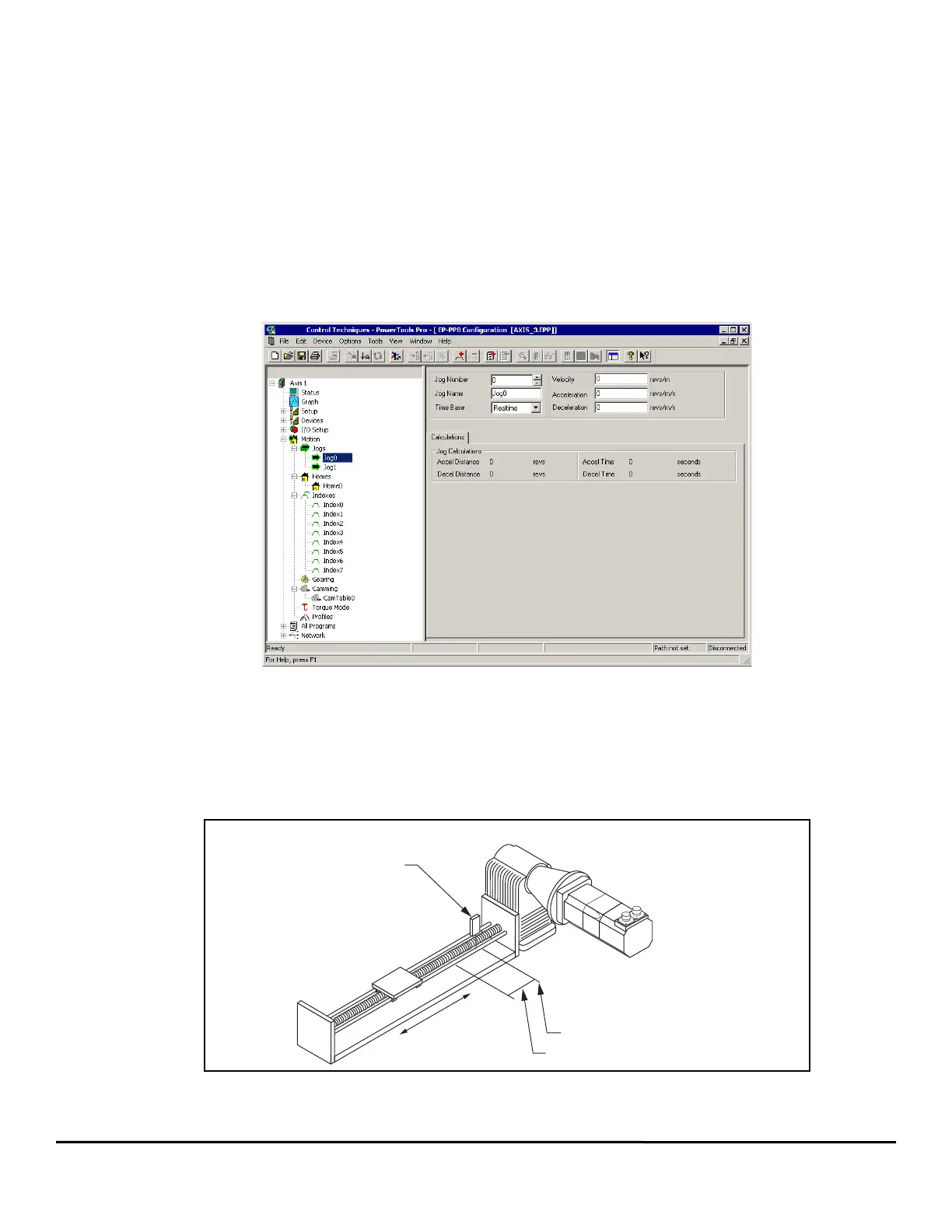
Figure 5: Jog View
2.5 How Home Works
The Home is used in applications in which the axis must be precisely aligned with some part of the machine. The Home is initiated in one of
three ways: with the Initiate Destination function found in the Assignments view, through a program, or with the Online tab. A Home or Define
Home is required to set the Absolute Position Valid so that any index to absolute position can work.
The Epsilon EP-P drive can home the motor to an external sensor, the motor’s encoder marker pulse, or to a sensor and then to the encoder
marker pulse.
Figure 6: Basic Home Function, Example
The figure above show a basic home function using a ball screw. This example uses most of the setup features in the PowerTools Pro Home
NT Motor
with Encoder
Gear Reducer
Carriage
External
Home Sensor
Home Offset
Distance
Sensor Point
+
-
Direction
 Loading...
Loading...