Epsilon EP-P Drive Reference Manual 11
Revision A4 www.controltechniques.com
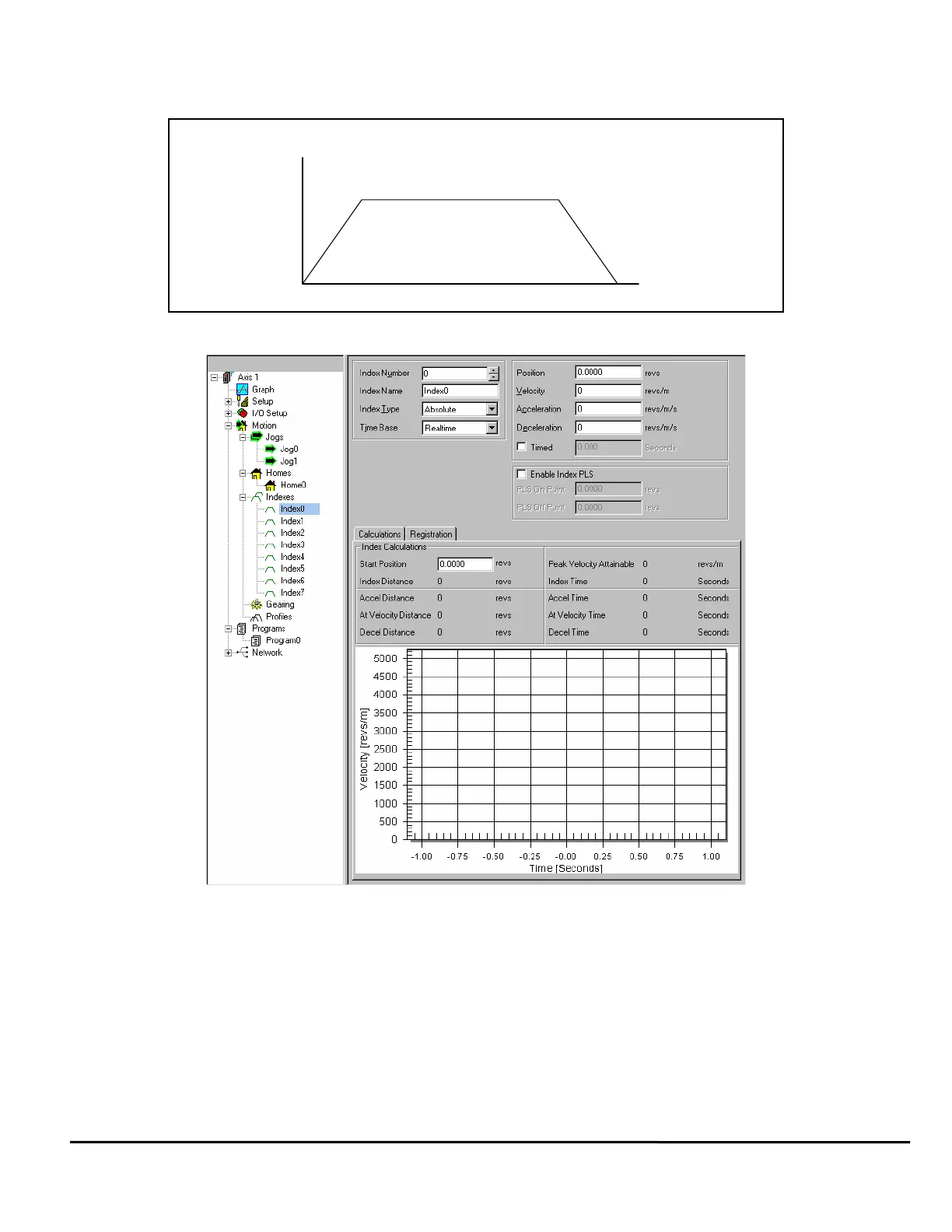
2.6 How Indexes Work
An index is a complete motion sequence that moves the motor a specific incremental distance or to an absolute position. This
motion sequence includes an acceleration ramp to a programmed velocity, a run at velocity, and a deceleration ramp to a stop.
Figure 21: Index Motion Sequence
Figure 22: Indexes View
Indexes use acceleration and deceleration ramps which may or may not reach the specified velocity depending on the total
distance and the ramp values. For example, a short move with long acceleration and deceleration ramps may not reach the
target velocity entered.
Indexes cannot be initiated when any other motion (jogging, homing, or program) is in progress. Indexes can be aborted with
the Stop destination found in the Ramps group on the Assignments View.
The Epsilon EP-P supports eight types of indexes: absolute, correction, incremental, posn track cont., posn track once,
registration, rotary plus and rotary minus.
2.6.1 Absolute vs. Incremental
The difference between absolute and incremental indexes is that absolute indexes move to a specific absolute position and
incremental indexes move the motor a specific distance. The following figures and explanations demonstrate this concept.
Velocity
Time
Acceleration
Deceleration
Run at Velocity

 Loading...
Loading...