2 — INSTALLATION SPECIFICATIONS AND WIRING
Curtis Model 1351 – December 2018
Return to TOC
pg. 22
Pot Inputs
e 1351 System Controller provides Analog Inputs 9 and 10 to be congured for connection to a
potentiometer. Potentiometers can be connected as 2-wire using only the wiper (Analog 9/pin 20)
and ground (I/O Gnd, pin 8), or 3-wire, using the wiper, ground, and Analog 10 (pin 21) for pot
high. e potentiometer input can be congured for a throttle, brake, steer, or other uses. e wiring
diagram (Figure 4) illustrates this usage as a 3-wire li/lower conguration.
When the analog inputs are congured for use with a potentiometer, the signals are dynamically
tested, increasing the fault detection of the potentiometer and wiring beyond just basic out-of-range
detection. e total resistance and the wiper position are constantly measured and calculated.
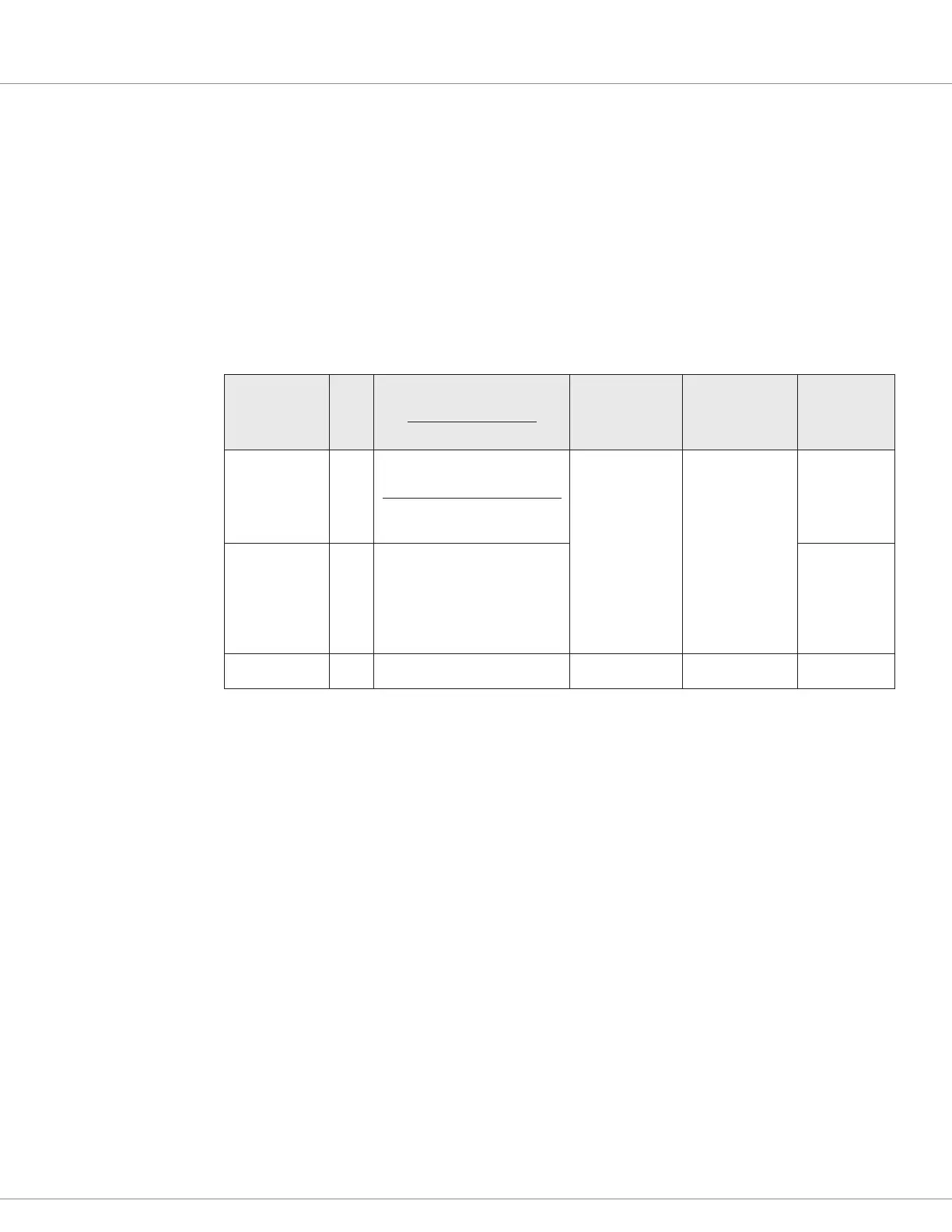
Table 10 Potentiometer Input Electrical Specifications
Signal Name Pin
Pot Resistance
Range / Tolerance
Available Current
Input
Impedance
Output
Voltage
Fault
Detection
Pot Hi 21
3-wire: 0 – 15 kΩ / 0 – 2k Ω
3 mA supplied, max.
> 178 kΩ
15 V
(nominal)
Shorted to:
B+
B–
I/O Gnd
Open
Wiper 20
2/3-wire: 0 – 15 kΩ / 0 – 2k Ω
3 mA supplied, max.
Shorted to:
B+
B–
I/O Gnd
Pot Hi
Open
I/O GND 8 — — — Open
RTD Inputs
e resistive temperature device (RTD) inputs, RTD Inputs 1 – 4, are connected to Analog Inputs
5 – 8 respectively. Specic or selectable RTD devices are not oered—rather each RTD input is
congured (mapped) according to its resistive characteristics. is means the 1351’s RTD Inputs can
accommodate resistive devices for temperature, position, pressure, etc., solely based upon the resistive
sensor and/or a given range determined by the user. For example, a 3-wire “steer angle” potentiometer
is illustrated in the example wiring diagram (Figure 4) for RTD 4 input, with RTDs utilized for the
oil temperature, oil pressure, and engine temperature connected to RTD inputs 1, 2, and 3.
e RTD parameter-mapping feature can be used for linearizing temperature diodes or NTC resistors
to provide values in Fahrenheit or Celsius. Another example is when a potentiometer is used to
measure drive wheel angle by a cam or level arm, which provide a non-linear movement based on
angle. is happens on 4-wheel trucks with Ackerman steering geometry and/or dual drive vehicles.
e steered angle can also be picked up o the actual hydraulic ram using the RTD mapping feature.
Alternatively, use the RTD to convert a tiller steering arm to have more sensitivity near center and
then greater angle gain when close to the limits.
 Loading...
Loading...