76
EXCEL HR OPERATOR MANUAL
D1796, REV. D, 12/16
• Always observe the epidermis during the treatment, watching for signs of damage (e.g.,
epidermal separation, frosting, or gray coloration).
- If damage is observed, stop the treatment, cool the skin, and evaluate the area for
possible complications and wound care.
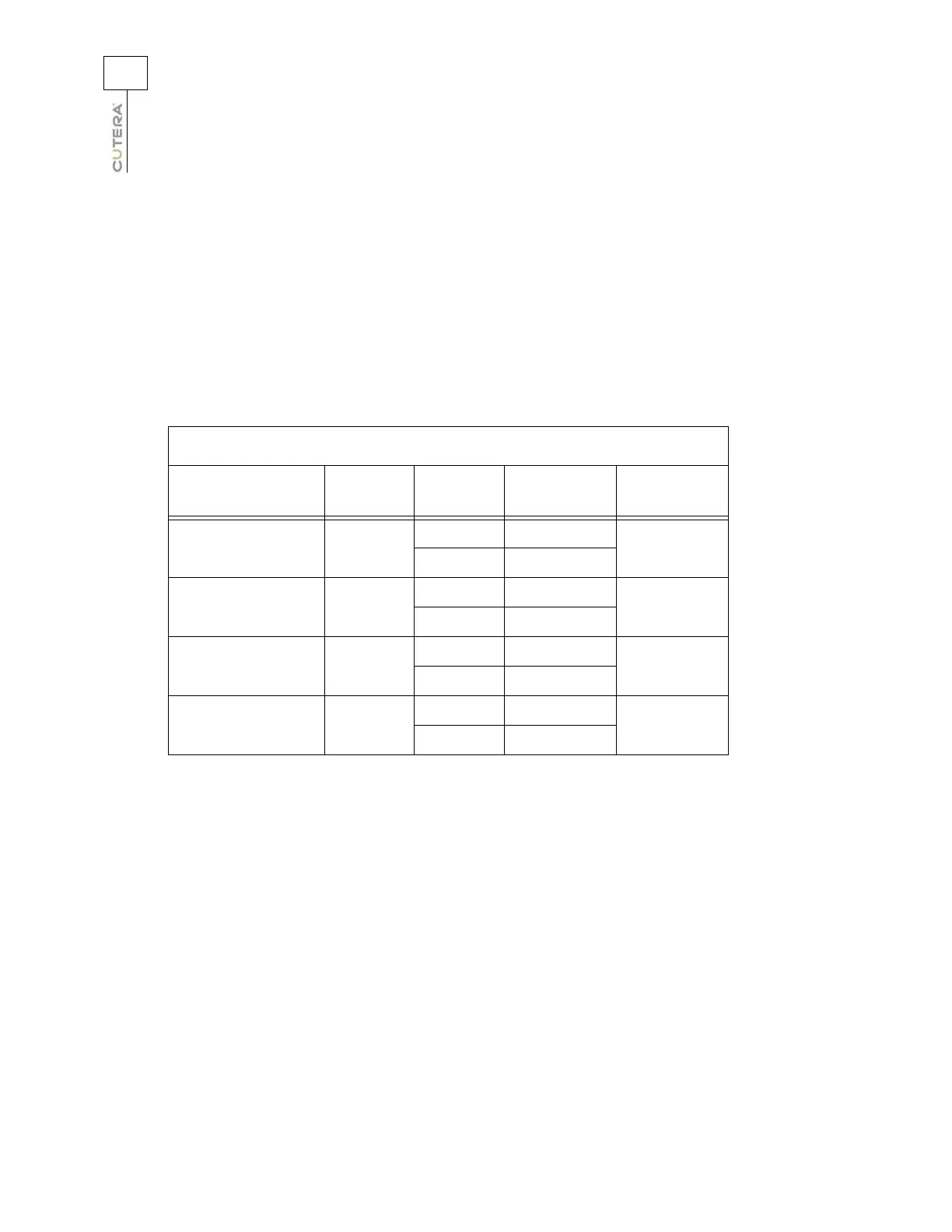
Benign Pigmented Lesion Treatment Guidelines - 755 nm Only
The following parameters are provided as a guide only and are based on practitioner feedback. Start at
the lowest fluence, and observe laser-tissue interaction and clinical endpoints to determine appropriate
settings.
Indication Skin Type Spot Size Fluence
Window
Temperature
Light Pigment I-III
5 mm 30-50 J/cm²
16-20°C
8 mm 25-50 J/cm²
Medium Pigment I-IV
5 mm 25-45 J/cm²
14-20°C
8 mm 15-35 J/cm²
Dark Pigment I-IV
5 mm 20-30 J/cm²
8-12°C
8 mm 15-25 J/cm²
Seborrheic Keratosis I-III
5 mm 20-50 J/cm²
16-20°C
8 mm 15-40 J/cm²
Benign Pigmented Lesion Technique and Endpoints
• Ensure that the handpiece is in full contact with the skin during treatment.
- Pay particular attention when treating rounded/bony areas.
• Treat the pigmented lesion only and not the surrounding area.
• The clinical endpoint is a slight darkening of the lesion.
- A subtle color change is sufficient.
-
It is important to achieve a color change over the full diameter of the lesion.
- Localized erythema and/or edema may develop up to 15 minutes after treatment.
• If the desired clinical endpoint is not achieved, adjust the settings accordingly
.
- Darker lesions are more responsive and typically respond to lower settings.
-
Lighter lesions may require higher settings.
Benign Pigmented Lesion Parameter Guidelines
 Loading...
Loading...