Operation and parameterization 52
Manual econ sens3 Version 3.0
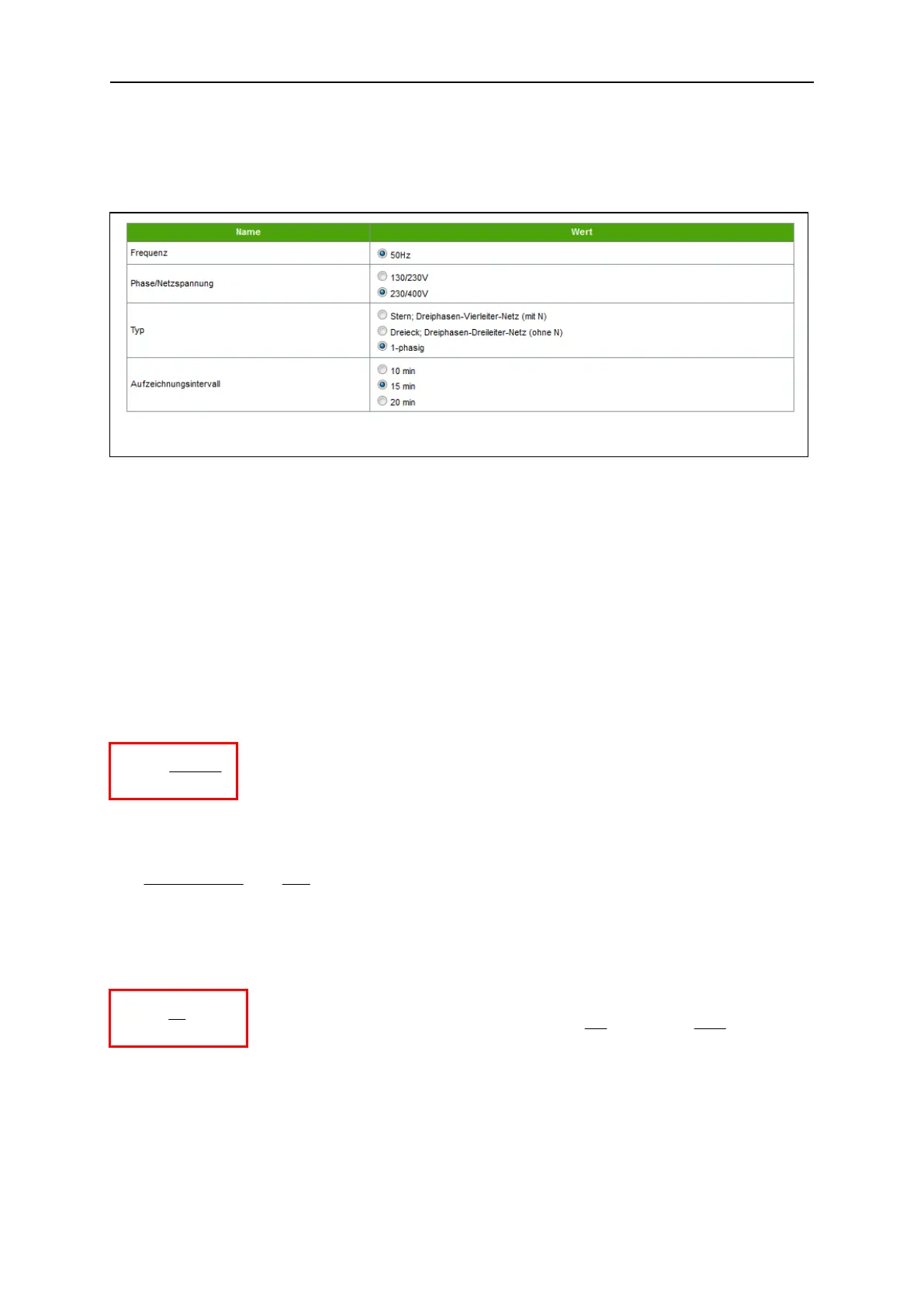
Therefore, you can still choose among the triangle option (three-phase, three-wire network without
neutral conductor) and the star option (three-phase, four-wire network with neutral conductor) or a
one-phase network.
The setting for recording interval defines whether you receive 15-minute or 20-minute mean values
when exporting the energy consumption data, as described in the Export menu in Chapter 6.
Calculation of pulse weights:
Every pulse output over the two pulse outputs corresponds to an energy amount in Wh.
This is required because the pulse output can deliver a maximum pulse frequency of 10 Hz; this
corresponds to 36,000 pulses/h.
The following equation can be used to calculate the maximum permissible pulse weighting factor.
P = connected maximum load in watts
X = pulse weighting factor in Wh/pulse
Example: The user to be measured is a machine with P
Total
= 100 KW
In practice, with electricity meters there is often a pulse constant (referred to here as K) in imp/kWh.
Conversion from X to this constant K is calculated by:
For our example, this means:
Practice has shwon that a pulse rate of 100 imp/kWh (= 10 Wh/imp) is completely adequate. This
calculation is the same as in setting the relationship with the input / output setting.
 Loading...
Loading...