Rosemount Model 8800C Vortex Flowmeter
E-4
Calculating Output
Variables with Known
Input Frequency
Use the following equations with a known input frequency for
verification of a flow rate or 4–20 mA output within a given
calibrated range. Select the proper equation depending on if
you are verifying a flow rate, mass flow rate, 4–20 mA output, or
special units. Example calculations starting on page E-6 may
clarify how these equations are used.
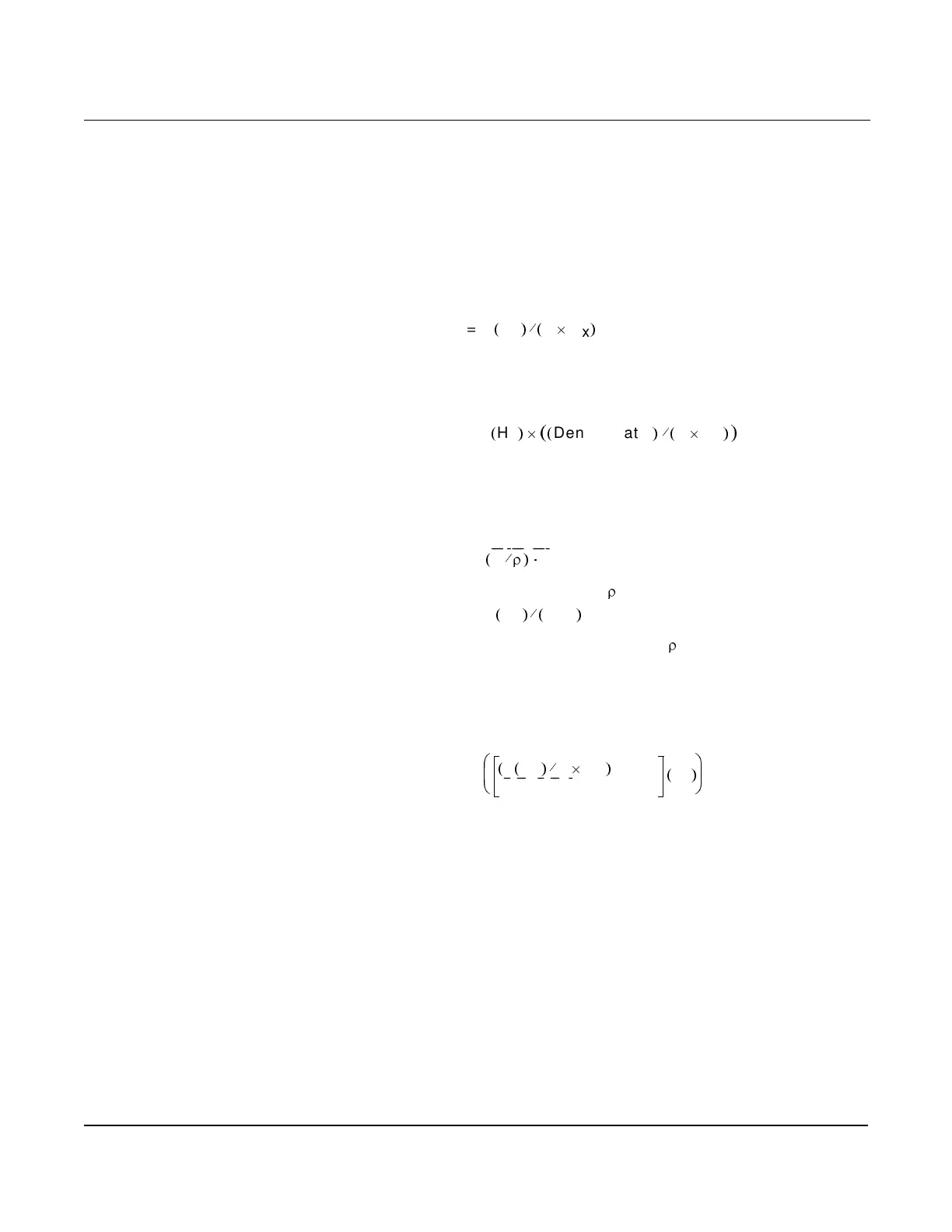
To Verify a Flow Rate
For a given frequency F (Hz), and K-factor (compensated), find the
flow rate Q:
where C
x
is the unit conversion (Table E-1).
To Verify a Standard or Normal Flow Rate
To Verify a Mass Flow Rate
For a given mass frequency F (Hz), and K-factor (compensated), find
the mass flow rate M:
where C is the unit conversion and
r
is density at operating conditions:
where C
x
is the unit conversion using density (
r
) (Table E-1).
To Verify a 4–20 mA Output
For a given input frequency F (Hz), and K-factor (compensated), find
output current I:
where C
x
is the unit conversion (Table E-1), URV is the upper range
value (user units), and LRV is the lower range value (user units).
To Verify a Special Units Output
For special units, first divide the special unit-conversion factor into the
base unit factor C
x
.
C
20
= C
x
/sp. units conv. factor (Table E-1).
QFHz
()
KC
x
()
=
QFHz
()
DensityRatio
()
(
KC
x
()
)
=
M
F
K
r)(
C
¼
-------------------------=
MFHz
()
KC
x
()
=
I
FHz
()
KC
x
)
LRV–
(
URV LRV–
--------------------------------------------------------------
16
()
ÍÝ
ÌÜ
ËÛ
4+=
 Loading...
Loading...