- 93 -
Particle Properties
The list of Particle Properties contains 22 different properties including two submenus (see Appendix II
for a list of particle property definitions). There are six parameters associated with the Color submenu:
Average Blue, Average Green, Average Red, Ratio Blue/Green, Ratio Red/Blue, and Ratio Red/Green.
There are ten parameters associated with the PMT/Scatter submenu: Ch1 Area, Ch1 Peak, Ch1 Width,
Ch2 Area, Ch2 Peak, Ch2 Width, Ch2/Ch1 Ratio, Scatter Area, Scatter Peak, and Scatter Width.
Select from the available list the particle property desired and the particle images will be sorted
according to the blue Ascending and Descending order arrow found on the tool bar. As an example,
with the sort order set to Ascending (arrow in up position), select ESD Diameter for the particle
parameter and observe how the View Window changes. When VisualSpreadsheet has finished sorting,
the first image collage will show the smallest particles based upon ESD Diameter, and the last collage
will contain the largest particles. If the user sets the arrow in the down (descending position), this will
have the opposite effect-the largest particles are displayed in the first collage and the smallest are
displayed in the last collage.
Filter Score
The Filter Score is a dynamic derived particle value calculated whenever a statistical filter is applied to
the data set. The value has no units and is only useful as a relative value tool. A lower filter score
represents a better match to the statistical filter target goal. See the Filter section below for more
information.
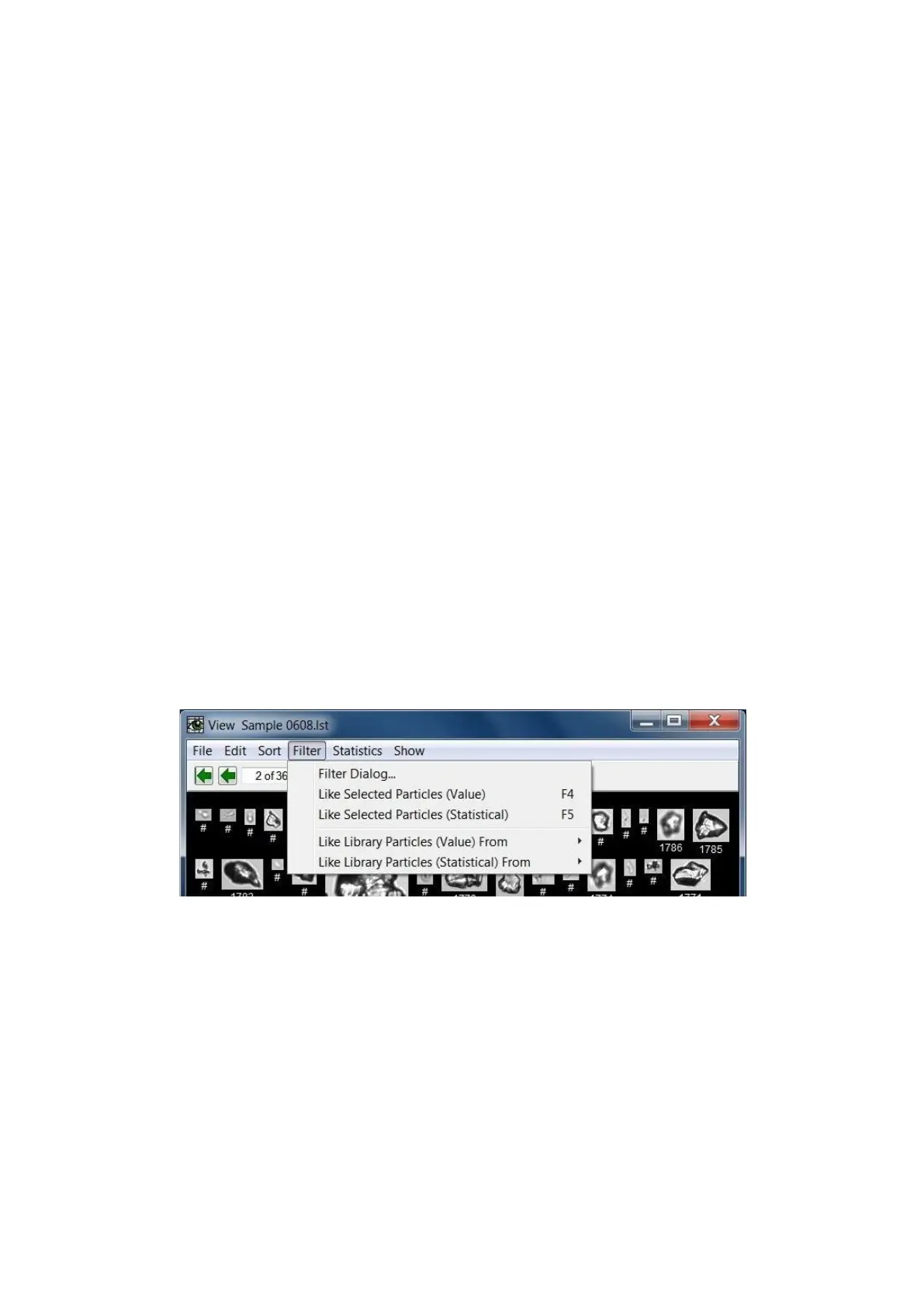
View Window… Filter Menu
VisualSpreadsheet provides two general methods for extracting subsets of a complete data set into a
filtered data set. These methods are referred to as Value filtering and Statistical filtering.
Value (absolute) filtering uses strict comparisons of existing field values to reduce the data set. An
example of a Value filter would be to extract the subset of data that has Diameter (ESD) between 10-20
µm. Multiple fields can be compared in a single Value filter. Multiple-field value filters are performed
as a series of logical AND operations meaning that the condition for every test must be met for the
particle to remain in the subset of filtered data. The Filter > Like Selected Particles (Value)... operation
creates a multiple-field value filter that employs all the fields.
 Loading...
Loading...