`
show ip
GFK-2572 Chapter 2 Monitor Level Commands 2-33
IP Counters
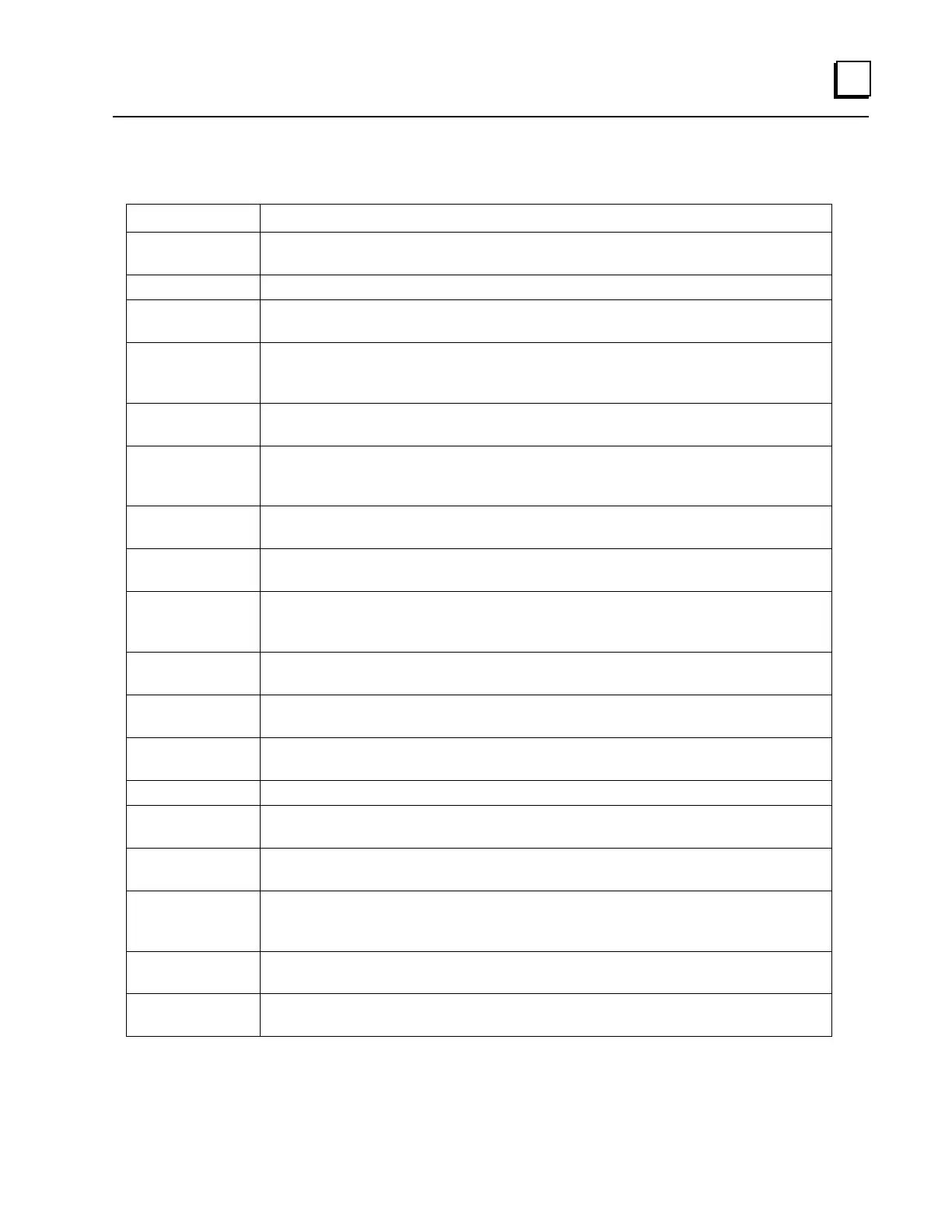
The following table defines each of the IP Counters.
The total number of input datagrams received from interfaces, including those
received in error.
The number of input datagrams discarded due to errors in their IP headers.
The number of input datagrams discarded because the IP address in their IP
header’s destination field was not a valid address to be received at this entity.
The number of input datagrams for which this entity was not their final IP
destination, as a result of which an attempt was made to find a route to forward
them to that final destination. (Not used in this release.)
The number of locally–addressed datagrams received successfully but
discarded because of an unknown or unsupported protocol.
The number of input IP datagrams for which no problems were encountered to
prevent their continued processing, but which were discarded (for example, for
lack of buffer space).
The total number of input datagrams successfully delivered to IP user–protocols
(including ICMP).
The total number of IP datagrams which local IP user–protocols (including
ICMP) supplied to IP in requests for transmission.
The number of output IP datagrams for which no problem was encountered to
prevent their transmission to their destination, but which were discarded (for
example, for lack of buffer space).
The number of IP datagrams discarded because no route could be found to
transmit them to their destination.
The maximum number of seconds during which received fragments are held
while they are awaiting reassembly at this entity. (Not used in this release.)
The number of IP fragments received which needed to be reassembled at this
entity.
The number of IP datagrams successfully re–assembled.
The number of failures detected by the IP re–assembly algorithm (for example,
timed out, errors, message size too big….)
The number of IP datagrams that have been successfully fragmented at this
entity.
The number of IP datagrams that have been discarded because they needed to
be fragmented at this entity but could not be, e.g., because their Don’t Fragment
flag was set.
The number of IP datagrams that have been generated as a result of
fragmentation at this entity.
IP packets ignored because not addressed to this node and destination is
unreachable.

 Loading...
Loading...




